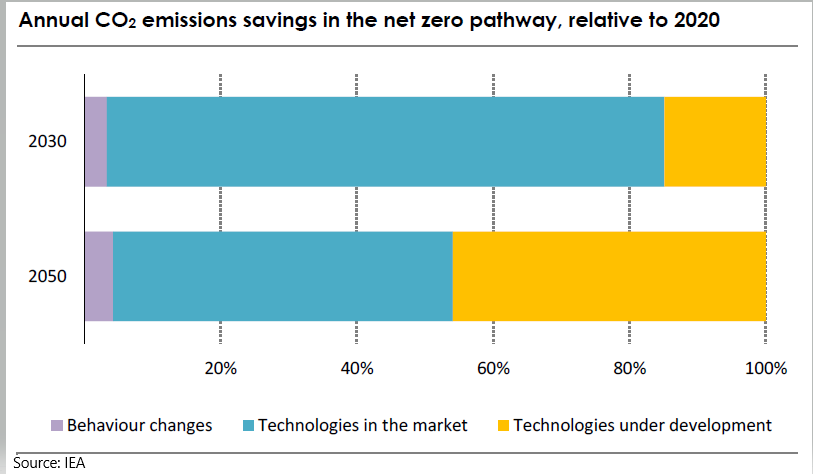
There is a broad technology theme to the articles that we have chosen today, which is in keeping with one of the core conclusions of the IEA report earlier this week. The IEA is estimating that roughly half of the path to net-zero will require technologies still in the test phase, or in some cases still conceptual. The Dow headline around ethane dehydrogenation and electric furnaces is a good example. Both technologies could lower the carbon footprint of making ethylene, but the dehydrogenation route will require some catalyst or other breakthrough as current propane dehydrogenation technologies require a lot of heat. The electric furnace idea is complex and would require extremely high levels of power, all of which would have to be renewable for the carbon footprint to fall – this type of technology is likely implied in the BASF announcement today. The IEA talked about some of the transition moves required to allow the technology advances time to become either commercial or cost effective, or both. Carbon capture features meaningfully in the IEA plans, but the study has carbon capture volume rising through 2050, which we find odd. The idea of carbon capture is to act as a bridge between where we are today and where we could be once new technology is developed – therefore, while companies like Dow should be aiming for technologies that lower the carbon production of its processes, carbon capture should be an almost immediate bridge to lower emissions while both the technology is developed, and its costs are reduced. Carbon capture needs should then decline. View today's Daily Report for more.
ESG Friday Question: Can Technology Keep Pace?
May 21, 2021 1:12:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Ethylene, Emissions, Net-Zero, IEA, Dow, propane, Technologies, ethane dehydrogenation, carbon footprint, BASF