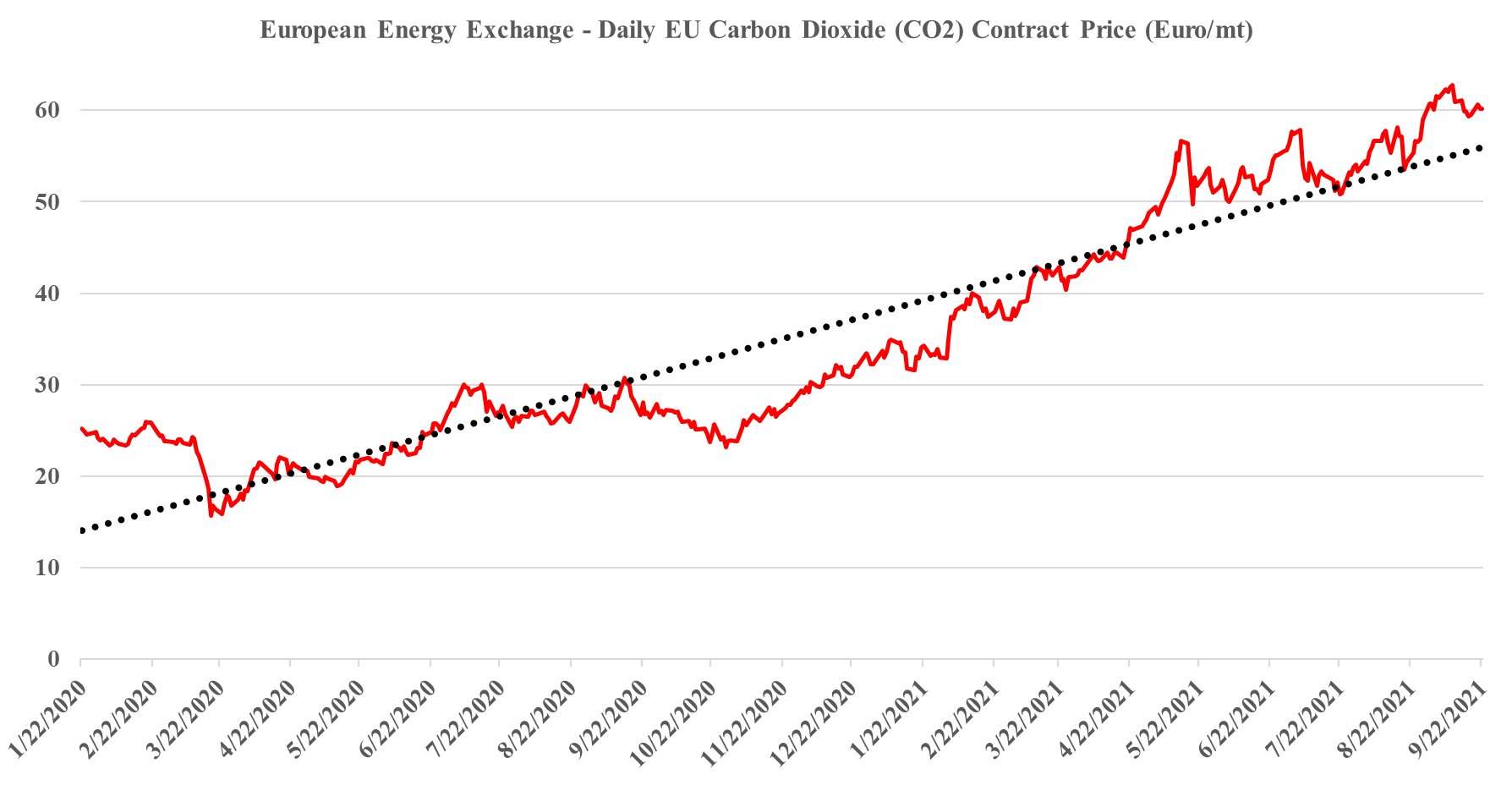
It is worth a short explanation of what is going on with European CO2, given the mixed signals of shortages in headlines today and then the slight weakness in pricing shown in the image below. These are two very different markets, with the food, beverage, medical and nuclear industries looking for pure streams of CO2 rather than the contaminated streams that make up the bulk of emissions. Historically, the food and beverage industry looked to fermentation – so alcohol production – as its source of a pure CO2 stream, but as demand grew, the next best place became ammonia production, which also has a pure CO2 stream as a by-product. Most ammonia is further converted into urea, which is a consumer of CO2 and there is not enough CO2 produced in a natural gas-based ammonia plant to convert all of the ammonia to urea. You sometimes see urea facilities also selling ammonia, but more frequently they take the carbon monoxide by-product of the syngas reaction and convert that to CO2. The result is enough CO2 to convert all of the ammonia to Urea and surplus CO2 to sell. Because of this more dominant supply of food and beverage grade CO2, and shutdowns caused in this case by runaway natural gas prices, have an immediate impact on the industries that rely on the CO2.
How Can We Have Too Much & Too Little CO2 At The Same Time?
Sep 22, 2021 2:04:48 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Carbon Price, Inflation, Ammonia, natural gas, European Carbon price, urea, CF Industries
Carbon Capture (If Supported) Will Create Competitive Dislocations
Jul 21, 2021 1:08:19 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, CO2, fossil fuel, carbon footprint, carbon abatement, renewables, European Carbon price, climate
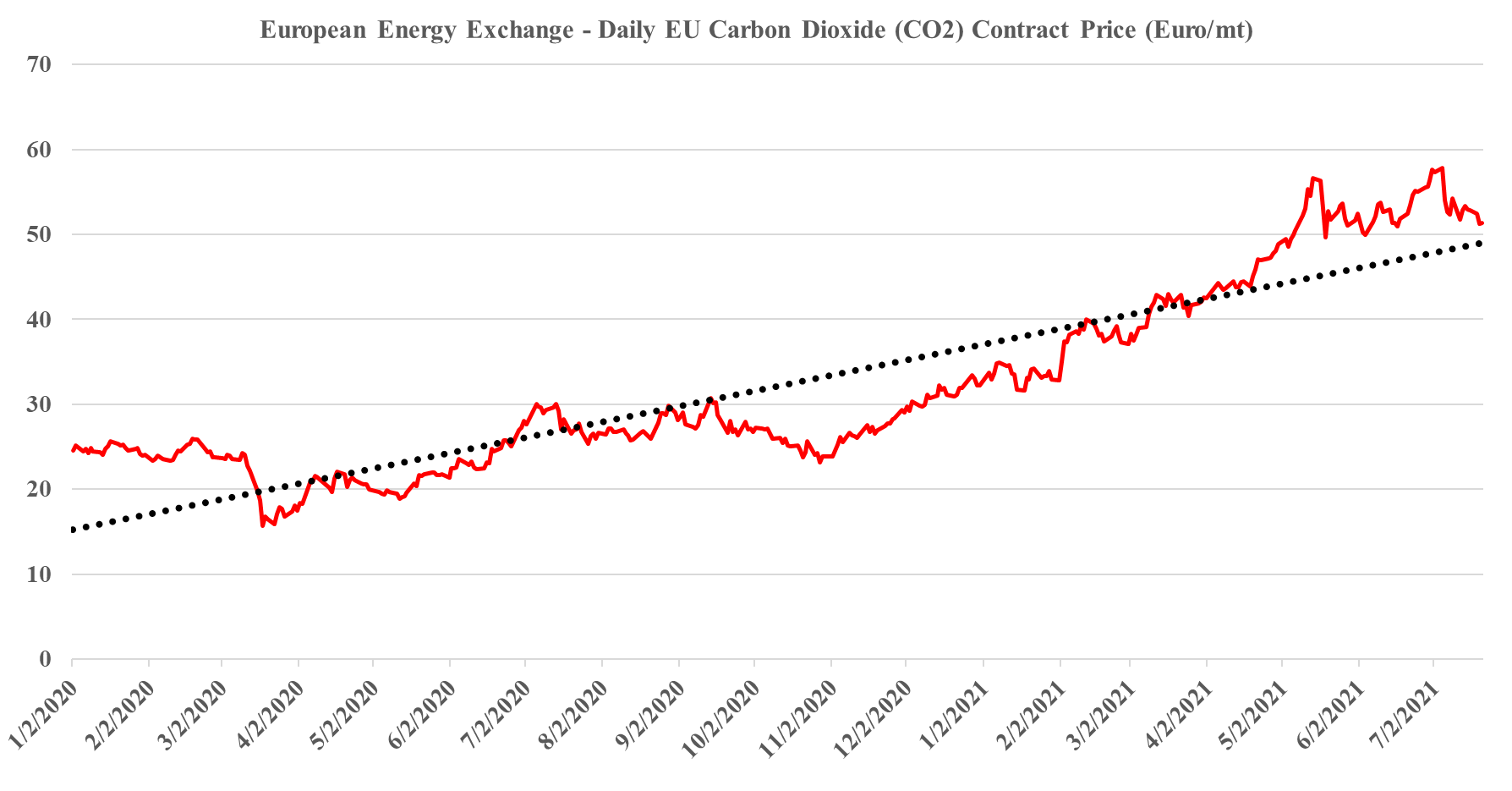
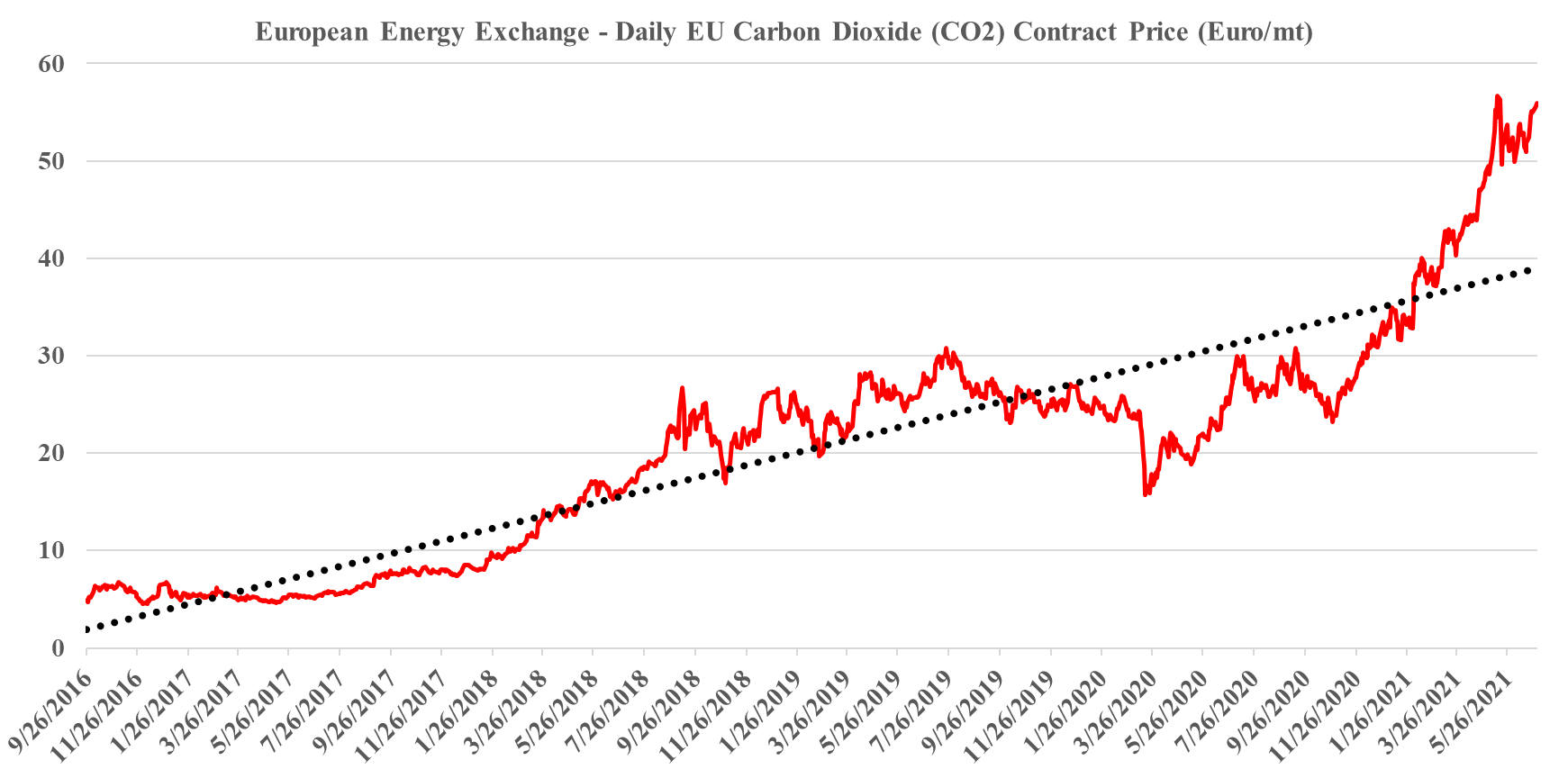
In our ESG and climate piece today we focus on Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) and the likely very steep cost curve between the mega projects and those less fortunate. But as we discuss CCS, we should not forget that the World is still not convinced about CCS as part of the solution set for carbon abatement, as the headline linked discusses. The naysayers are focused on the lifeline that CCS offers to the fossil fuel industry, but always fail to offer an economic rationale for the quick elimination of fossil fuels and their replacement by renewables. Few of the proponents of CCS see it as an alternative to a long term path to alternative means of abatement, but all recognize that relying on renewable power investments will likely leave the World with a much larger CO2 footprint from 2030 to 2050 than what could be achievable with CCS – note that the 45Q incentive in the US has a finite lifespan as there is an expectation that eventually CCS will be unnecessary because of fossil fuel replacement. Chevron has not helped the CCS proponents with its missed targets in Australia as it adds fuel to the argument that CCS has not lived up to its potential. While the European carbon price trend has stalled in recent weeks – chart below – the trend remains distinct and it would be foolhardy to ignore the likelihood of prices rising to a level that makes CCS attractive – especially for the mega-projects.
Expected ESG Regulation Likely Good For Pure-Play Energy Transition Stocks
Jun 30, 2021 4:05:20 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Biofuels, Plastic Waste, CCS, Carbon, Dow, ESG Fund, solar, ESG investment, wind, European Carbon price, carbon emissions
The ESG investment shakeup could be one of the major events of this year, and as many of the headlines in our daily report suggest, there is a lot of work to be done, whether it is agreeing on a common set of measurement metrics – note the US and European differences discussed in one story – or the introduction of more empirical methods to judge whether what is labeled as an ESG investment fund is labeled correctly. There is also the issue of comparable disclosures, especially for companies in complex industries. It is interesting to note that in many analyses we see around carbon footprint or greenhouse gas emissions, and the potential routes to and cost of abatement, the chemical industry is omitted, except for ethanol and hydrogen. This is despite the industry accounting for 15% of the non-power emissions in the US industrial sector (similar in size to refineries). We believe that this is because the complexity of the industry makes it hard to model, and analysts choose to exclude it because they are not sure what they are doing.