Despite all of the rhetoric about the need for green hydrogen, we see most of the large ammonia producers pursuing large blue projects – with Nutrien’s announcement yesterday coming on the heels of a CF new facility announcement and the CO2 capture project announced by LSB a couple of weeks ago. While there are some small (proof of concept) green projects in the works, they are very small, tiny when compared with the ammonia need, whether to replace lost material from Russia and Ukraine or whether to supply what could be substantial needs in Asia to co-fire coal plants, or as a shipping fuel, or as a carrier for hydrogen (see third chart below). The ammonia majors are not waiting around for “green” economics to improve as they see meaningful near-term demand that cannot wait for scale efficiencies of available power on the green side. Large-scale sources of cheap renewable power are hard to find, and where they may exist, there is competition from uses that may be able to pay more.
So Fresh So Clean, Nutrien Looks To Be Going Green
May 19, 2022 2:45:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, Coal, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Renewable Power, Ammonia, blue ammonia, electrolysis, CF Industries, fuel, green ammonia, Denbury, Nutrien, LSB Industries
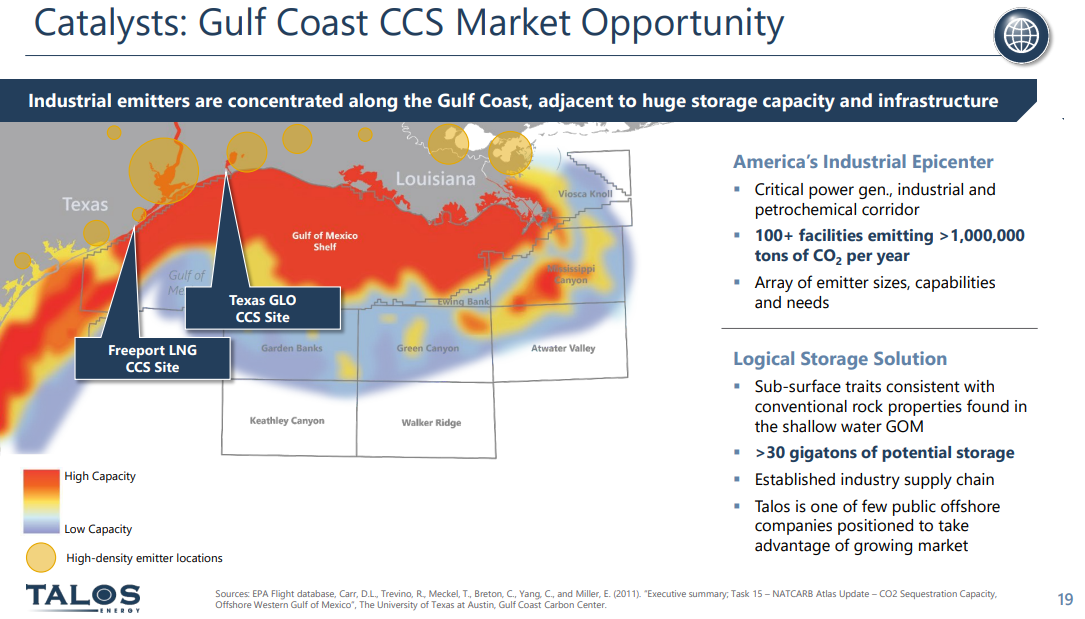
CCS In The US: The Potential Is Significant
Feb 17, 2022 12:55:54 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, decarbonization, carbon value, urea, CF Industries, Climate Goals, oxygen
There should be little doubt that the US has a significant opportunity to decarbonize through CCS and if the US has a carbon value close to the level in Europe today we would be seeing investments announced almost weekly. While permitting would cause some significant lead time between announcement and construction/operation, the other uncertainty might be how best to capture the CO2. In its earnings release yesterday, CF talked about purifying CO2 streams at its two large Urea plants on the Gulf Coast, such that the CO2 would be ready to sequester, but the Urea process creates a relatively concentrated stream of CO2 and that makes separation much easier. For others, the better route might be hydrogen investments – driven by the relative ease of capturing the CO2, especially if it is part of the process design. If this route is more economic, the net new investment would be substantial, not just for the SMR, ATR, or fuel cell hydrogen generators, but also for the infrastructure and oxygen capacity for any ATR investment. This seems like a no-brainer bi-partisan opportunity for the US as there is broad support for CCS but incentives need to be higher. For more on this topic see our ESG and Climate research.
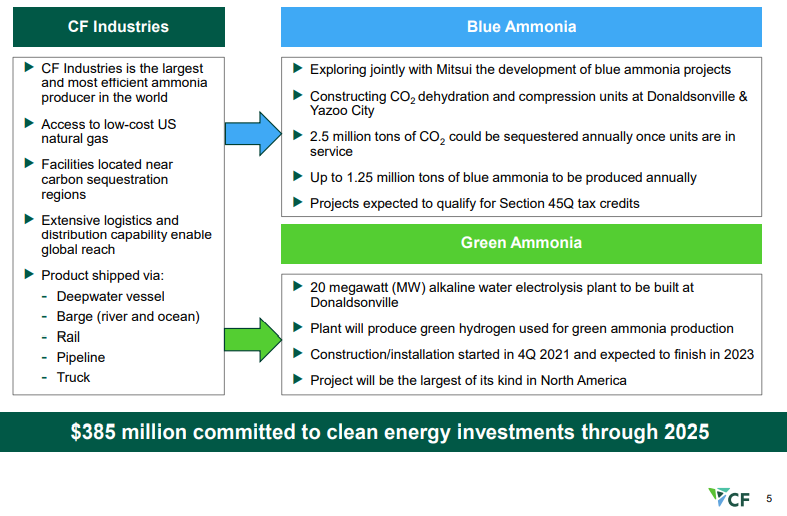
Low Cost CCS Could Be A Game Changer For The US
Feb 16, 2022 1:41:38 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, CCS, CO2, Sequestration, Ammonia, blue ammonia, CF Industries, crude oil, low carbon, green ammonia, carbon intensity, carbon market
We continue to believe that the US has a cost advantage in CCS versus many of the other regions of the world and that when coupled with low natural gas prices the US should be able to take a lead in developing low carbon chemicals. CF is pushing the idea of both blue ammonia in the US as well as green ammonia, and while the company has yet to announce sequestration plans for the CO2 it is working to purify – see Exhibit - once dehydrated and compressed the incremental cost of storage should be low.
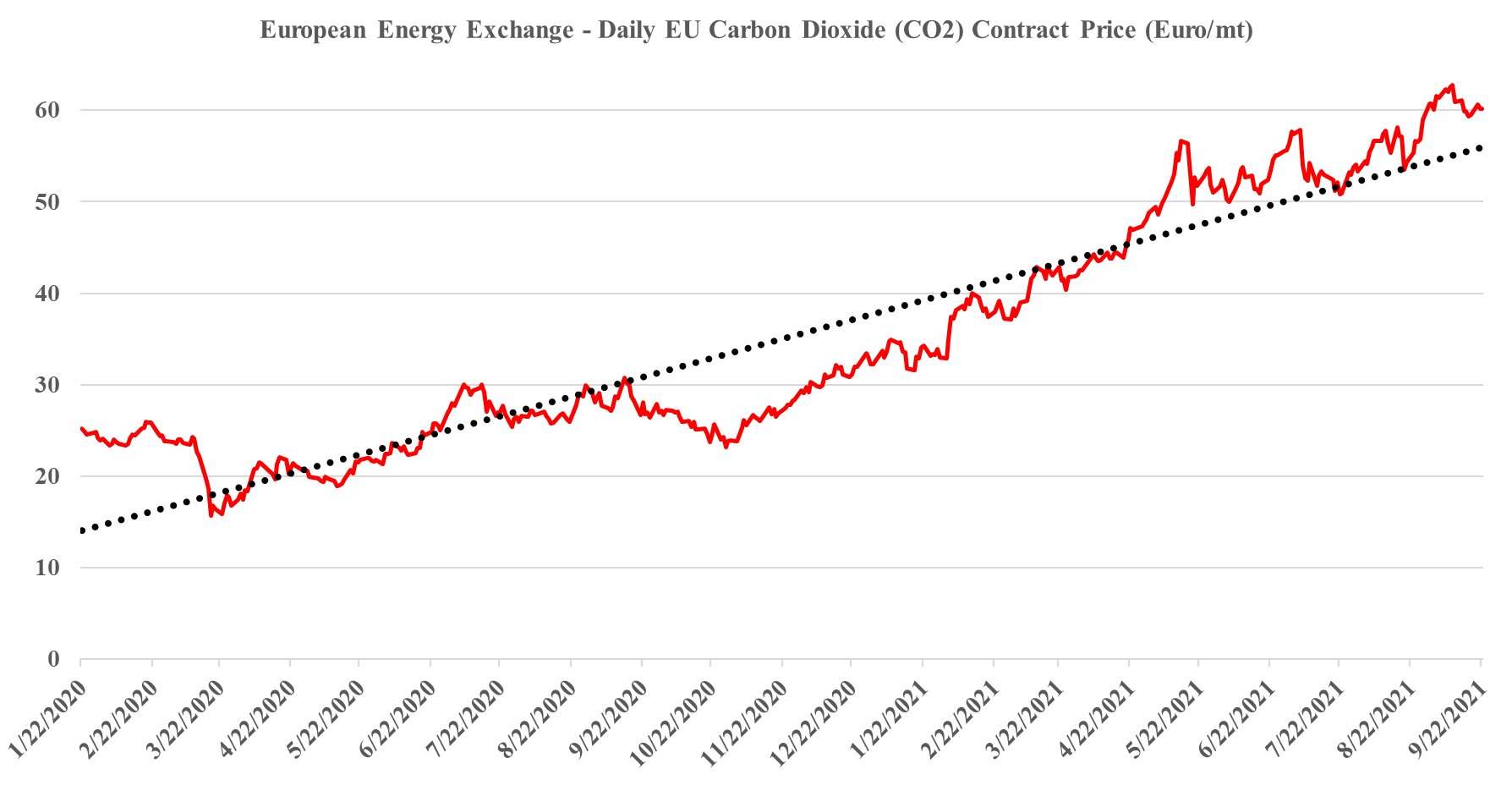
How Can We Have Too Much & Too Little CO2 At The Same Time?
Sep 22, 2021 2:04:48 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Carbon Price, Inflation, Ammonia, natural gas, European Carbon price, urea, CF Industries
It is worth a short explanation of what is going on with European CO2, given the mixed signals of shortages in headlines today and then the slight weakness in pricing shown in the image below. These are two very different markets, with the food, beverage, medical and nuclear industries looking for pure streams of CO2 rather than the contaminated streams that make up the bulk of emissions. Historically, the food and beverage industry looked to fermentation – so alcohol production – as its source of a pure CO2 stream, but as demand grew, the next best place became ammonia production, which also has a pure CO2 stream as a by-product. Most ammonia is further converted into urea, which is a consumer of CO2 and there is not enough CO2 produced in a natural gas-based ammonia plant to convert all of the ammonia to urea. You sometimes see urea facilities also selling ammonia, but more frequently they take the carbon monoxide by-product of the syngas reaction and convert that to CO2. The result is enough CO2 to convert all of the ammonia to Urea and surplus CO2 to sell. Because of this more dominant supply of food and beverage grade CO2, and shutdowns caused in this case by runaway natural gas prices, have an immediate impact on the industries that rely on the CO2.