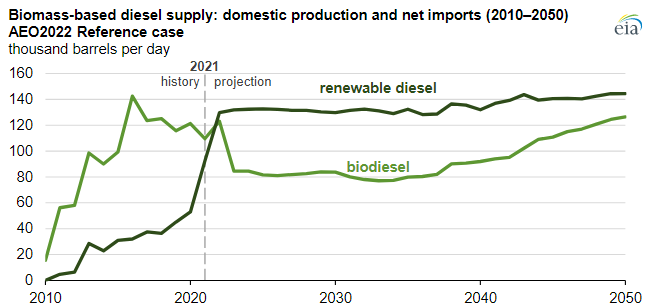
The EIA renewable diesel projections are based on a couple of things – who plans to make it and who will pay for it. All eyes are focused on the California market today as that is where the incentive lies – through the LCFS credit – and production plans plateau associated with that opportunity. As other states in the US adopt similar programs – which seems likely – we would expect to see production plans increase and the EIA will likely adapt its market view model and the chart will change. Note the dominance of renewable diesel over time, and this is where we would expect all future growth to occur. The plug-and-play nature of renewable diesel makes it a far more attractive option for refiners assuming the cost works. See more in today's daily report.
Renewable Diesel Will Grow If Other States Adopt LCFS
Mar 25, 2022 2:32:12 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Energy, power, renewable energy, LCFS credit, EIA, renewable diesel, renewable fuels, power capacity, renewable capacity, CO2 pricing, diesel
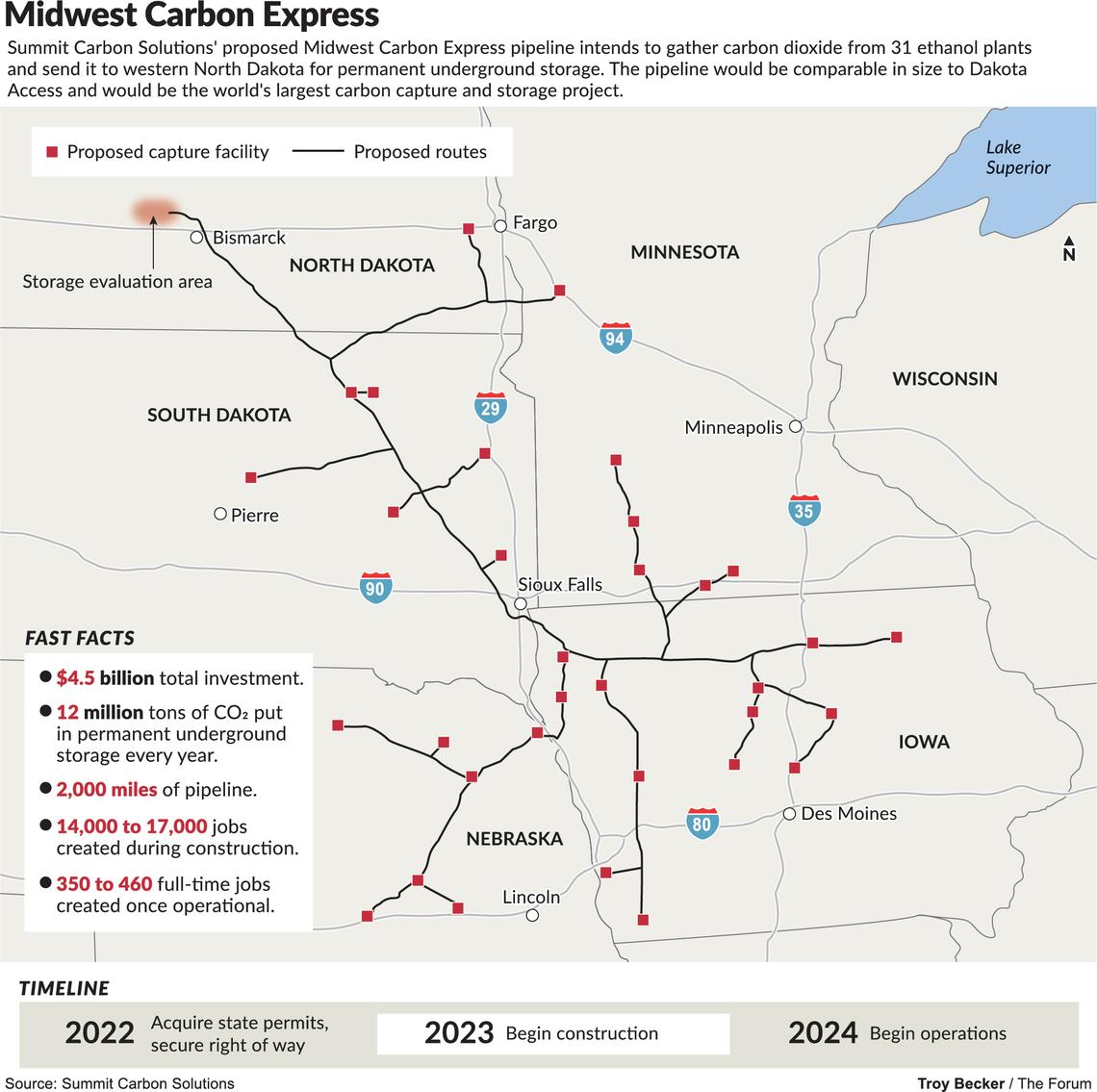
CCS Is A Cost And Some Projects Look Too Expensive
Dec 15, 2021 1:53:44 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, carbon dioxide, carbon abatement, LCFS credit, climate, pipelines, 45Q, Carbon Sequestration, abatement costs, CAPEX, CO2 pipelines, OPEX, Summit Carbon Solutions
As we have mentioned before, we see a couple of major challenges with the CO2 pipelines proposed for the mid-West, one of which is summarized in the Exhibit below. The first issue is pipeline right-of-ways, as there are already activists determined to oppose the pipelines, and opposition to pipelines has been a core them of the last 10 years. The second issue is cost. Carbon abatement is a cost for all looking for solutions and even where incentives exist, such as the 45Q program or the LCFS fuels program, the challenge will still be creating a path with the lowest. Compression and pumping costs are high for CO2, especially if the pipeline wants a pressure that will allow for direct injection into a series of wells. Lower pressure transportation by pipe is inefficient and raises the capital cost of the pipeline – so it becomes a trade-off – CAPEX vs OPEX. $4.5 billion of investment – as suggested by Summit – is $375 per annual ton of carbon dioxide sequestered - $37per ton assuming 10-year straight-line payback – twice that if you want a 10% return. This is before a dollar of OPEX and pipeline costs could easily exceed another $30+ per ton, with separation and purification of the CO2 stream also not free. Unless the ethanol producers are paying Summit and Navigator to take the CO2, the math becomes very challenging. See today's daily report and our weekly ESG and Climate report for more.
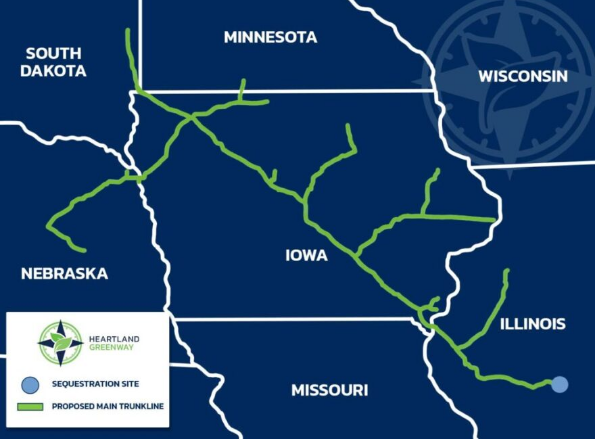
CCS Can't Afford Long Pipelines
Dec 2, 2021 2:20:56 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, Emissions, Carbon Price, Net-Zero, LCFS credit, climate, pipelines, carbon storage, carbon prices
In our ESG and Climate piece yesterday we briefly discussed the mid-west carbon capture projects, questioning their economic viability. Two of the most expensive components of any CCS project are pipelines and compression costs and we cannot see how a long network of pipe in the mid-west to pick up what are essentially small volumes can work economically. These projects are reliant on very high LCFS-like credits, and as we showed in last week’s report, LCFS credits have fallen this year and could fall further. The pipeline right of way issue is another major hurdle and we have seen growing resistance to pipelines of any sort over the last few years. Those who oppose CCS in principle could cripple these mid-west plans simply by co-opting enough land-owners on the path of the proposed pipelines and refusing access. We are supporters of CCS, but have done substantial work on economics and show that the process only begins to make economic sense if the sequestration is close to the emissions. Relying on possible artificially high carbon prices to justify the projects will only lead to pain, assuming the pipeline right of ways can be obtained.
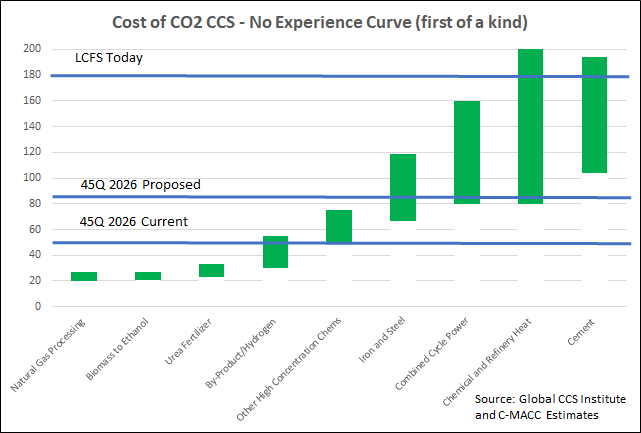
The US Remains Divided On How To Price Carbon
Nov 3, 2021 1:34:59 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, LNG, CCS, CO2, Energy, Emissions, Carbon Price, carbon credit, renewables, LCFS credit, COP26
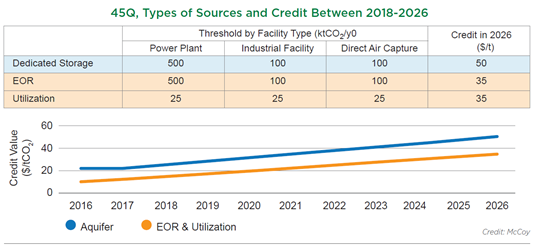
We want to focus today on the headlines around the possible increase in the 45Q CCS credit in the US and discuss the false logic of those that are objecting to it. There is no scenario where the US can move to a lower emissions power and transport profile while avoiding runaway inflation and social disorder without the continued use of fossil fuel-based power and transportation fuels for decades. The reliance on these fuels should and will decline over the years, but it is unreasonable to expect a transition that causes it to stop overnight. In the meantime, CCS is a mechanism that would allow fossil fuels to play a part with a much lower emissions footprint, and given that the CO2 impact on global warming is cumulative, if we can capture and store several billion tons of CO2 underground over that transition period it should be a good thing. Members of the Sierra Club and others would do well to look at the energy inflation problems in Europe and the move this week to put natural gas and nuclear back in the energy transition mix (too late in our view) because the move to renewables cannot keep pace with demand, which will grow faster as more EVs hit the road. The proposed 45Q credit is shown in the chart below vs. the current credit, the LCFS credit, and estimates of CCS costs.
Fairness & A Step Change In Investment Could Come From Revised CCS Bill
Jun 25, 2021 1:01:59 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, LNG, Carbon Tax, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Sequestration, carbon abatement, US Government, 45Q carbon credits, LCFS credit, tax credit, blue ammonia
Senator Cramer’s proposed Bill to increase the value of the 45Q carbon credits for sequestration and use as well as remove the annual cap could be a game-changer in many ways. The threshold removal is necessary regardless of the credit value. In our view, the cap creates a potential competitive disadvantage for smaller companies competing with larger ones, especially in the chemical space. Should the Bill increase the tax credit enough to drive real investment in abatement but not remove the threshold we would expect to see litigation from smaller disadvantaged companies. The chart below shows the current expectations for 45Q. To date, the only real investment activity we are seeing is around sequestering CO2 from ethanol production in the US. This is because the CO2 stream is easy to separate in a fermentation process and because some of the ethanol can benefit from the much higher LCFS credit if the fuel is sold into California.