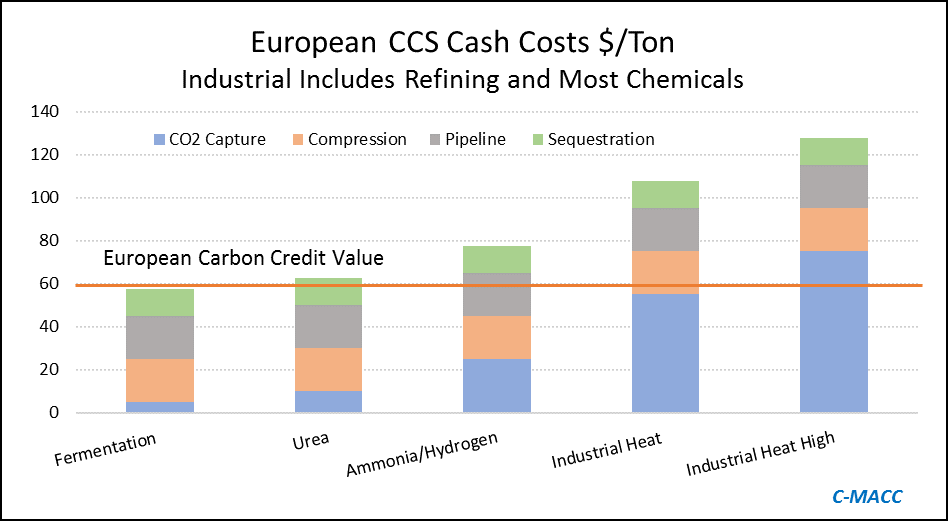
The big news of the week is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be localized within the Port of Rotterdam, where both oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the $2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $65 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs – see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir). For more see today's ESG report.
Source: Global CCS Institute and C-MACC Analysis and Estimates