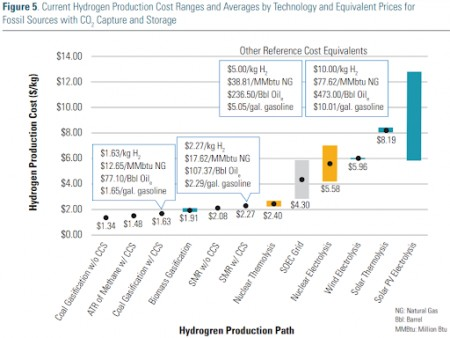
Despite all of the rhetoric about the need for green hydrogen, we see most of the large ammonia producers pursuing large blue projects – with Nutrien’s announcement yesterday coming on the heels of a CF new facility announcement and the CO2 capture project announced by LSB a couple of weeks ago. While there are some small (proof of concept) green projects in the works, they are very small, tiny when compared with the ammonia need, whether to replace lost material from Russia and Ukraine or whether to supply what could be substantial needs in Asia to co-fire coal plants, or as a shipping fuel, or as a carrier for hydrogen (see third chart below). The ammonia majors are not waiting around for “green” economics to improve as they see meaningful near-term demand that cannot wait for scale efficiencies of available power on the green side. Large-scale sources of cheap renewable power are hard to find, and where they may exist, there is competition from uses that may be able to pay more.
So Fresh So Clean, Nutrien Looks To Be Going Green
May 19, 2022 2:45:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, Coal, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Renewable Power, Ammonia, blue ammonia, electrolysis, CF Industries, fuel, green ammonia, Denbury, Nutrien, LSB Industries
Green Hydrogen: Not So Good If Power Prices Do Not Come Down
Sep 3, 2021 1:14:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Methanol, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Ammonia, bp, feedstock, carbon dioxide, solar, wind, electrolysis
Last week, and in our dedicated ESG and climate report this week, we talked about the challenges of shipping hydrogen, and the linked bp project for Western Australia will have the same problem to solve – choosing ammonia according to the announcement over the very inefficient toluene/cyclohexane option we discussed last week. The appeal of Western Australia is the unpopulated available land that has little alternative use and sees abundant sunshine. The bp project assumes that the facility can buy attractively priced renewable power from third parties, but the company must have a specific power project in mind for the bulk of the electricity needed. The stumbling block here will likely be when the power project(s) bid out the solar module contract, find out that the suppliers are sold out and are asking higher prices to cover reinvestment and higher material prices, and then have to go back to bp with a much higher than expected cost of power. The advantage of solar and wind projects is that inflation only impacts upfront capital costs, which can be amortized over the life of the project – feedstocks are free! That said, most of the announced projects have declining capital costs per megawatt in their planning assumptions today.