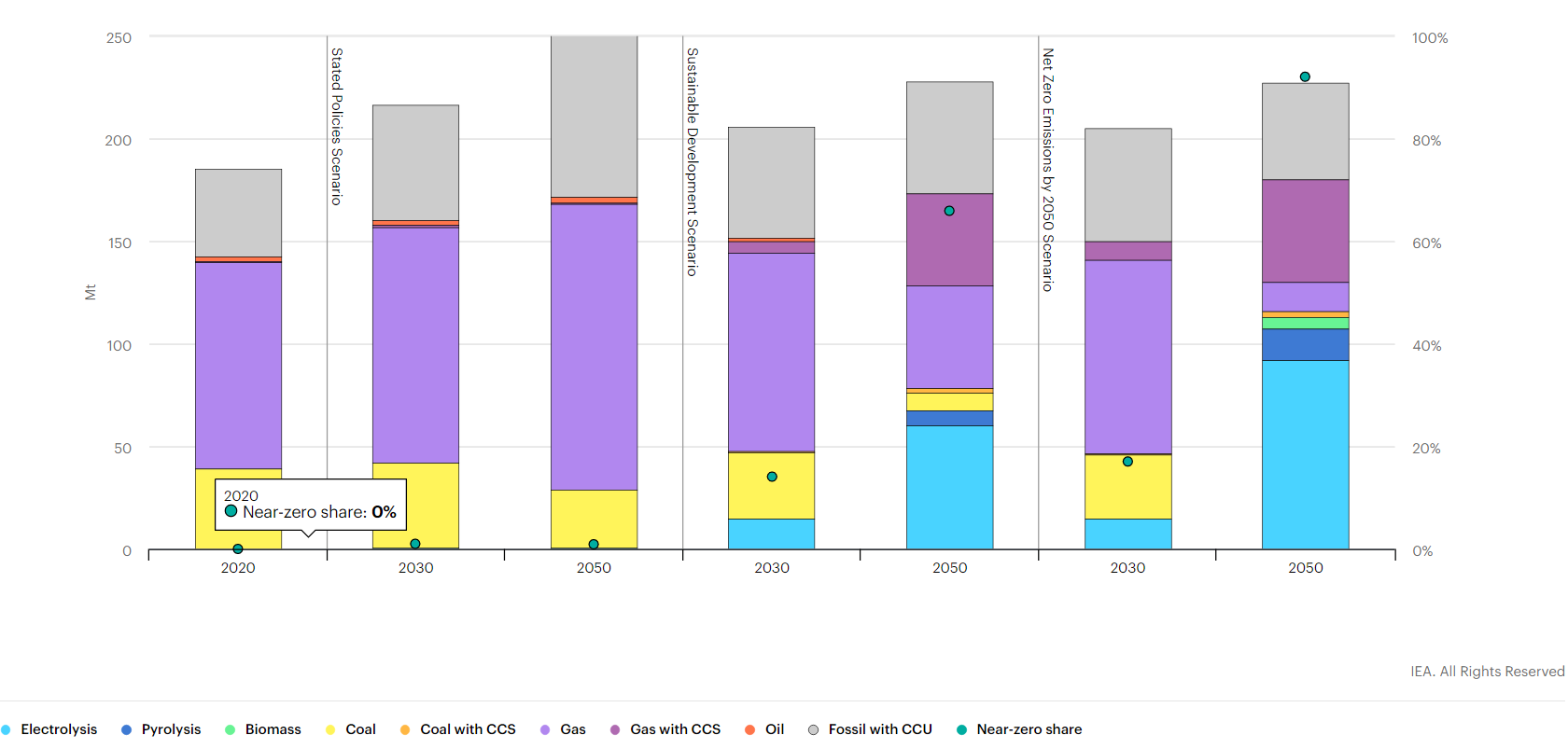
One question we would have concerning the IEA ammonia projections in the charts below is whether the absolute demand assumption for 2050 is too low. If Japan has success co-firing its coal-based facilities with ammonia over the next 6-7 years, we could see a step-change in ammonia demand. The chart likely reflects expectations in Japan, but we would expect other coal-heavy economies to follow Japan's lead. If this were the case, we would expect the share of hydrocarbon-based ammonia to rise with accompanying CCS.
If Ammonia Can Offset Coal In Power Plants, Demand Estimates May Be Too Low
Nov 9, 2021 1:45:47 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Sustainability, Coal, CCS, Ammonia, Power Plants, demand
Economics Have Driven US Emission Reductions More Than Policy
Jul 27, 2021 2:01:49 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, Sustainability, Coal, CO2, Renewable Power, Energy, Emissions, natural gas, EV, clean power investments, power sector
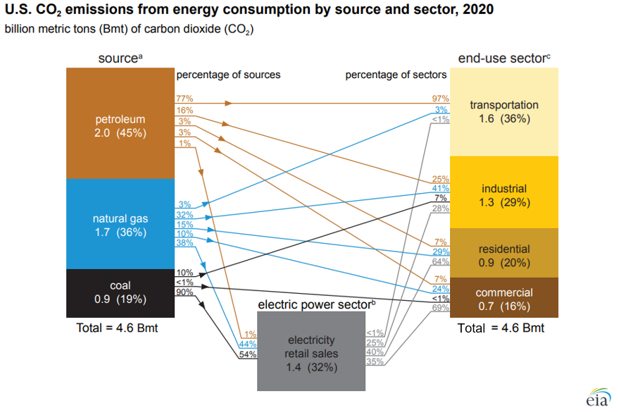
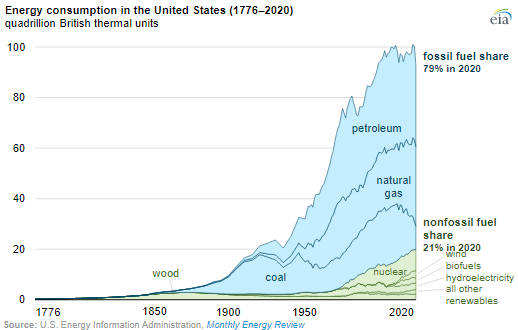
We are increasingly concerned that the US will remain a laggard concerning climate change initiatives given the major challenges of moving to the next steps and the bifurcated congressional views. The emissions reductions that the US has seen over the last 10 years have been more happenstance than planning, with the abundance of natural gas following the shale boom of the last decade creating economic reasons to replace coal-fired power with natural gas rather than environmental reasons. Lower costs for wind and solar power and focused industrial demand for that clean power have been the bigger driver of clean power investments. In the chart below, the decline in emission from the power sector is evident and it should continue. The diagram below shows sources and uses for US emissions in 2020, but the accompanying write-up talks about the step down in emissions overall in 2020. Except for the continuing electric power transition, most of the other 2020 declines are COVID-related and are expected to rebound in the near term, especially transport. The market share gains of EVs are not significant enough yet to make a difference. See more in today's daily report.
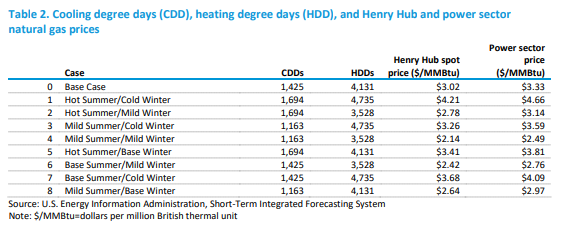
Natural Gas Based Power Not Going Away Anytime Soon
Jul 8, 2021 2:03:50 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Coal, CO2, Renewable Power, Emissions, carbon abatement, natural gas, power demand, carbon emissions, EIA, US carbon emissions
The table below is from an interesting analysis published by the EIA this week that focuses on possible power demand scenarios for the US – all weather-related – and then backs into the power sources that would be needed to meet the demand, concluding with the US carbon emissions that would correspond to each scenario. The conclusions should not be surprising, which are that carbon emissions rise disproportionately faster as power demand rises – as more coal is required to balance generation needs, and fall disproportionately more quickly as power demand falls (as less coal is needed). The analysis is effectively a study of how much less CO2 emissions are using natural gas to generate power versus coal. As renewable generation increases as a share of the total, however, the math will change, and the EIA study does not take into account the weather factor on renewable power, it looks at cooling degree days and heating degree days at a national level only. This is reasonable as there is likely not enough data to be able to put good reliability estimates yet around renewable power annual volatility and more importantly, the impact of weather on renewable power is likely to be short-term in nature. Perhaps this analysis could be improved by adding a “daily risk band” around each scenario, showing how much renewable power volatility could cause peaks in the high scenario and lows in the low, etc.
Unrealistic US Green Power Targets May Cause More Harm Than Good
Jul 1, 2021 2:16:28 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Climate Change, Coal, CCS, raw materials inflation, fossil fuel, natural gas, renewables, batteries, US Green Power, power storage, clean energy, petroleum
One of the themes that we have focused on in our ESG and Climate work is the lack of realism in the Biden climate plan as it relates to power generation and the same with the plan in California. The more limited reliability factor in renewable power (because of its dependence on cooperation from the weather), means that you have to build a lot more new power capacity than you are replacing and you need to build a storage system for the power – batteries, hydrogen or hydraulic. This gets very expensive and will be more so if the push drives inflation in raw materials – which is already a factor YTD in 2021. Natural gas turbines are a cleaner and reliable source of power and cleaner still if combined with CCS. Politicians in the US are taking a considerable risk by promoting plans that could leave the power grid more vulnerable to some of the issues that we have already seen over the last 12 months (California and Texas). Of course, as the plans call for natural gas phase-outs in 10-12 years, none of those making the decisions today will be in the office to face the consequences!
Larry Fink Finally Gets It! And The Carbon Value Of LNG
Jun 4, 2021 12:00:51 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, LNG, Coal, fossil fuel, carbon footprint, ESG Rhetoric, Power Plants, Larry Fink, carbon credit, carbon value
Finally, Larry Fink has recognized the flaw in his aggressive ESG rhetoric. Maybe he knew this all along, but it is good to see him step into the debate in favor of not crippling the fossil fuel industry by denying it access to capital and investors too quickly. However, that boat may have sailed, with investors like Engine No. 1 feeling empowered by their win over ExxonMobil and raising more money as a consequence. We have covered this subject at length in our ESG and climate weekly this week: Big Oil’s Big Problem – Hard To Find A Favorable Scenario – maybe Larry read it!
Green Hydrogen - Still Far Too Expensive
Mar 16, 2021 1:15:39 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Coal
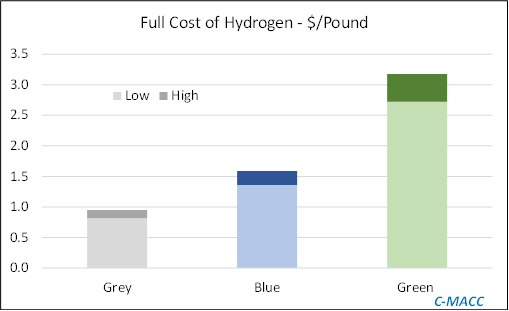
The cost of the green hydrogen project in Australia listed below is extremely high. Ethylene (a complex petrochemical) is now down to a cost of around $1.00 per pound if built efficiently – which is $2,200 per metric ton of capacity. The hydrogen project linked - if the $0.5bn and the 33,000 metric ton hydrogen capacity are correct, works out at around $15,000 per metric ton of capital costs. To get a 15% return on the project they will need $2,300 per ton of margin, above all operating costs. In the chart below, this would represent a capital charge of more than one dollar per pound, much more than is implied in the green bar. This does not look economic to us and will require either significant government subsidies – or severe penalties on hydrocarbons to make the hydrogen economic on a relative basis. The project does involve selling some power to the grid, but we still struggle to see how this hydrogen can be an economic fuel alternative.