Despite all of the rhetoric about the need for green hydrogen, we see most of the large ammonia producers pursuing large blue projects – with Nutrien’s announcement yesterday coming on the heels of a CF new facility announcement and the CO2 capture project announced by LSB a couple of weeks ago. While there are some small (proof of concept) green projects in the works, they are very small, tiny when compared with the ammonia need, whether to replace lost material from Russia and Ukraine or whether to supply what could be substantial needs in Asia to co-fire coal plants, or as a shipping fuel, or as a carrier for hydrogen (see third chart below). The ammonia majors are not waiting around for “green” economics to improve as they see meaningful near-term demand that cannot wait for scale efficiencies of available power on the green side. Large-scale sources of cheap renewable power are hard to find, and where they may exist, there is competition from uses that may be able to pay more.
So Fresh So Clean, Nutrien Looks To Be Going Green
May 19, 2022 2:45:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, Coal, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Renewable Power, Ammonia, blue ammonia, electrolysis, CF Industries, fuel, green ammonia, Denbury, Nutrien, LSB Industries
CCS And Plastic Recycling Ambitions Running High
May 5, 2022 12:31:00 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Carbon Capture, Recycling, LNG, CCS, CO2, natural gas, fermentation, Talos, urea, low carbon, CCUS, Denbury, Plastics recycling, LSB Industries, Berry Global
We are seeing a flood of CCUS announcements in the US in 2022, but they look like “gathering” exercises at this stage rather than projects that are ready for FID. Companies are chasing potential pore space and, like Talos, leasing onshore and offshore (mainly offshore) acreage, where they believe opportunities exist to sequester CO2. These announcements sometimes include firm commitments from companies that have CO2 surpluses and sometimes are more speculative. At this stage, it seems like a “land grab” and “customer grab”. There is wide agreement that the incentive structure in the US – centered around the 45Q tax credit scheme – is not enough to drive much real investment, unless it can be stacked with other credits like the LCFS structure, which only applies to fuels in California today. We see the land grab as relatively low-cost and low-risk positioning in the hope that incentives or economics change. There are some instances where investments will go ahead, and these will focus on processes that have a reasonably low cost of carbon capture – fermentation, urea, natural gas clean-up for LNG, and a handful of other processes. The LSB Industries announcement for Arkansas, highlighted this week, is likely an example of where the economics work even if LSB cannot get much of a premium for the low-carbon urea.
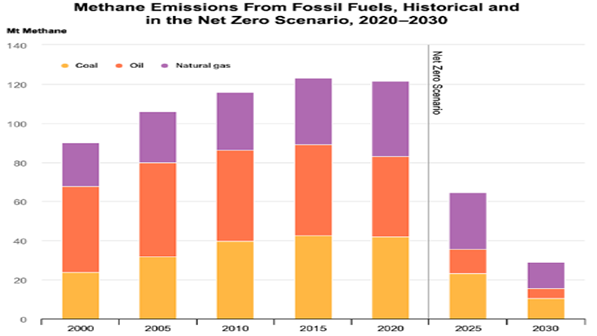
A Carbon Tax Could Cut Methane And Carbon Emissions, But Not Quickly
Apr 29, 2022 3:31:19 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Carbon Tax, Methane, CCS, CO2, methane emissions, 45Q
Methane emissions are one of the more challenging carbon equivalent problems in part because it is lots of small emitters, associated with many thousands of wells and many thousands of miles of pipelines, rather than a large source of CO2 that can be eliminated with a specific investment. The API carbon tax, proposed last week, has a condition in the proposal that would prevent any other emission-based legislation for many years to evaluate the effect of the tax. This will not drive lower methane emissions unless it is a broad carbon “equivalent tax”, which could potentially drive a very punitive tax on methane and would get an almost instant response from those that own the wells and the pipes. Some of the abatement solutions are easier than they first appear and all pipeline operators should look at the technology offered by Pipeotech, for example. Wellhead emissions are more problematic but not beyond the engineering skills that exist within the major E&P companies. The harder problem is what to do with emissions from abandoned wells – here the tax idea would not work as there is no one to pay the tax and a fairly complex financial structure would be needed to encourage someone to take on the role of cleaning up these properties. That said, all these pathways will need to be explored to get to the targets outlined below.
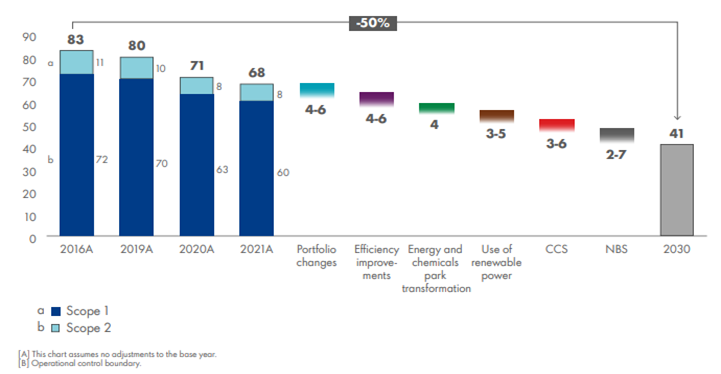
Shell Saying All The Right Things, But Likely Not Enough
Apr 20, 2022 2:24:59 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, LNG, CCS, CO2, Energy, Shell, fossil fuel, carbon values, energy transition, carbon intensity
Shell issued its 2021 energy transition progress this morning and the report contains a lot of detail about what Shell has done so far and what the company intends to do. The report is a record of progress and intent and is targeting both general stakeholders as well as the Shell board and annual meeting, where approval of the plan will be sought. When compared with other reports we have seen from other companies, this summary is comprehensive. It provides some concrete steps to achieving emission goals in 2030 – exhibit below - while remaining appropriately vague about getting to 2040 and 2050 targets. However, we would note how much portfolio changes likely added to the 2016 to 2021 progress – likely proportionately much more than they are expected to contribute from 2022 to 2030. Both renewable power and CCS figure in the 2030 projections below and Shell will need to get moving on the CCS front of it is to sequester 3-6 million tons of CO2 per annum by 2030. The expectations are likely based on the European offshore projects, as it may take longer than 8 years to get permits and investments in place in the US. The US could move faster but the EPA would likely need to grant primacy to at least Louisiana and Texas for things to speed up and we are not convinced that this will happen soon. Like many of the other company 2030 plans that we have seen, it is likely that much of Shell’s progress will come in the last couple of years of the decade – especially on CCS.
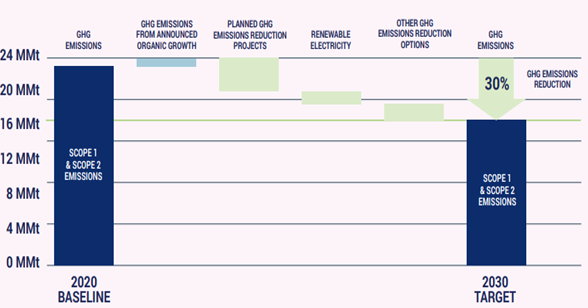
Many Of The 2030 Climate Targets Will Not Come Much Before 2030
Apr 13, 2022 3:14:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Emissions, ExxonMobil, LyondellBasell, Dow, carbon abatement, renewable fuels
Given the lead time to get some of the emission abatement projects in place – whether it be renewable power or hydrogen with carbon capture – many of the 2030 goals that we see, like the LyondellBasell chart below – are likely to be just that – plans for 2030, with not much in the years in between. We see very little CCS coming online in the US over the next 5 years because of permitting and because of the lead time for any large hydrogen or power project that might be associated with the CCS. Not too many companies seem interested in cleaning up existing CO2 streams and are more interested in building alternative capacity that generates easier to capture CO2 – such as hydrogen from an ATR. These are expensive and long lead-time projects. LyondellBasell, ExxonMobil, Dow, and others might meet their 2030 targets but it might all happen in 2029/30.
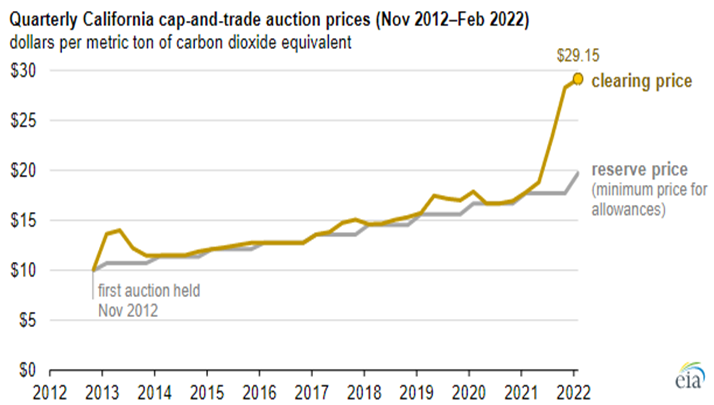
Carbon Prices Rising, Wind & Solar Costs Also
Apr 5, 2022 12:32:08 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, CO2, Energy, Net-Zero, carbon abatement, solar, renewable energy, wind, carbon prices
We have written extensively about carbon prices over the last two years and followers of our dedicated ESG and Climate service will know that our expectation is for all CO2 markets to see prices rise to levels that justify large investments to avoid CO2 production or sequester it. We see that price closer to $100 per ton than the $50 per ton that 45Q will rise to by 2026. The California price shown below has much more upside as credits demand rises. Many of the net-zero pledges made by manufacturers and energy producers today cannot be achieved without buying some sort of credit and we expect demand to rise relative to supply through the balance of the decade and possibly quite quickly.
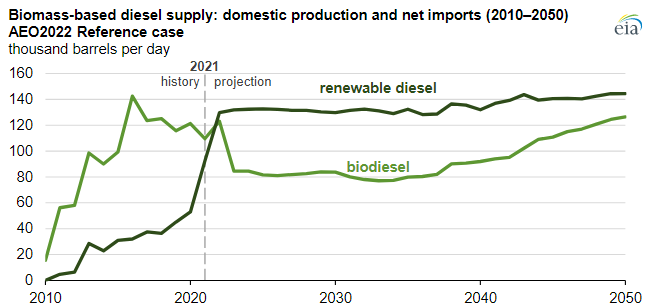
Renewable Diesel Will Grow If Other States Adopt LCFS
Mar 25, 2022 2:32:12 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Energy, power, renewable energy, LCFS credit, EIA, renewable diesel, renewable fuels, power capacity, renewable capacity, CO2 pricing, diesel
The EIA renewable diesel projections are based on a couple of things – who plans to make it and who will pay for it. All eyes are focused on the California market today as that is where the incentive lies – through the LCFS credit – and production plans plateau associated with that opportunity. As other states in the US adopt similar programs – which seems likely – we would expect to see production plans increase and the EIA will likely adapt its market view model and the chart will change. Note the dominance of renewable diesel over time, and this is where we would expect all future growth to occur. The plug-and-play nature of renewable diesel makes it a far more attractive option for refiners assuming the cost works. See more in today's daily report.
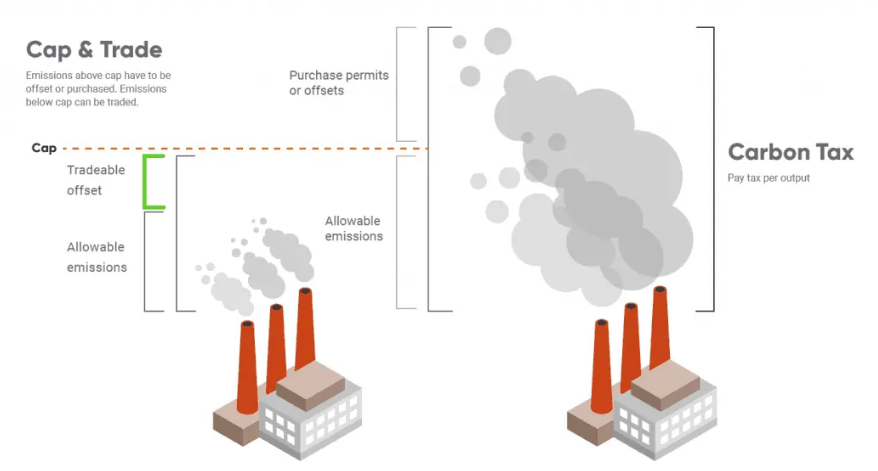
Everyone Is Pushing For A US Carbon Policy, Except Congress
Mar 24, 2022 2:54:22 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, Sustainability, Carbon Tax, CO2, Carbon Price, Emission Goals, Inflation, Chemical Industry, Net-Zero, decarbonization, Dow, carbon abatement, carbon emissions, carbon pricing, nuclear power, WPC
There was a very strong focus at the WPC on the need for carbon pricing in the US to facilitate investment decisions around many initiatives focused on carbon abatement. The consensus was very much that a carbon price – so a cap and trade system like they have in Europe – was the best mechanism, and far more likely to drive action and limit inflation than a carbon tax. This is something that we broadly agree with but the US is a bit late to the game and the right caps need to be set so that CO2 prices don’t languish at very low levels for years, as they did in Europe. Jim Fitterling of Dow was somewhat provocative in his comments around nuclear power, but we see this as part of a broader initiative aimed at getting a serious dialogue moving around how we make the practical steps needed to drive carbon lower. Nuclear power provides stable baseload and is carbon-free – a small modular nuclear reactor could generate enough steam and enough power to drive the decarbonization of major chemical complexes – one investment for example could transform one of the larger Dow sites. If we are going to get to net-zero targets without nuclear, we need much more progressive policies – especially around carbon pricing – which is likely the direction that Dow would like to take the discussion.
CCS Wont Work Without Policy And Neither Will Energy Conservation
Mar 22, 2022 12:48:43 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Energy, Emissions, IEA, Oil, natural gas, clean energy, renewable, fossil fuels, renewable capacity, EPA
One of the subjects that we will cover at length in the ESG and Climate report tomorrow (to be found here) is the significant need for CCS globally, but especially in the US, as we see more balanced forecasts of energy supply emerging which show more use of fossil fuels for longer – especially, but not limited to natural gas. These forecasts recognize the current energy momentum as well as some of the more practical realities around the rate of construction of renewable capacity relative to energy demand growth. The CCS plans that are appearing all over the place are nothing more than plans right now and if the EPA permit activity is a true barometer – not much has moved beyond planning. This needs to change and we likely need both an increase in CCS incentives – which could take many forms – as well as some streamlining around the permitting process. Simply waiting and hoping for a renewable miracle is not going to work – nor is some sort of CCS cost breakthrough.
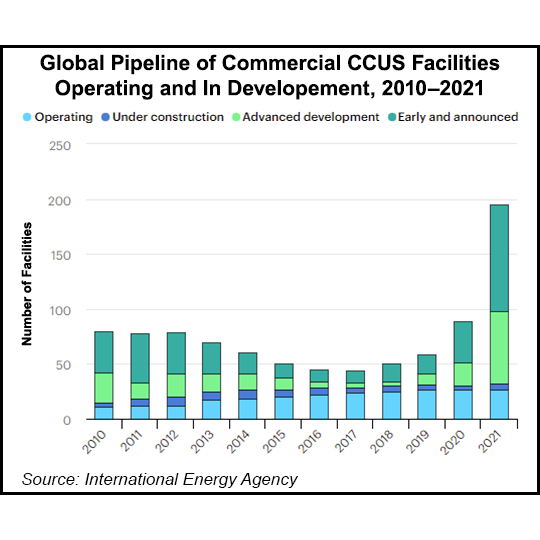
Lots Of Needed CCS Waiting For The Right Incentives
Mar 17, 2022 12:23:31 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, IEA, 45Q, CCUS, Denbury
The CCS chart below is one that we have shown before and we make the same observations again as little has changed on the “action” side. The number of facilities under discussion, advanced or otherwise, continues to rise – see the Denbury announcement below, for instance - but very little is moving to the construction phase. While in the US this is in part a permitting issue, with the permit process taking several years, once you have a site plan, we get the sense that everyone is waiting for a more supportive incentive program – either a large CO2 penalty (tax) or an increased incentive – such as increasing the 45Q value. MOUs are being signed with landowners – as is the case with Denbury – and potential offtake partners, but very little cash is going out of the door for any of the US projects yet. Given the EIA analysis above, it would seem critical that something is done to move these projects from planning to action fairly quickly – if the US is going to need CCS at scale in 15-20 years, we need to start down that learning curve now. For more see the energy section of today's daily report.