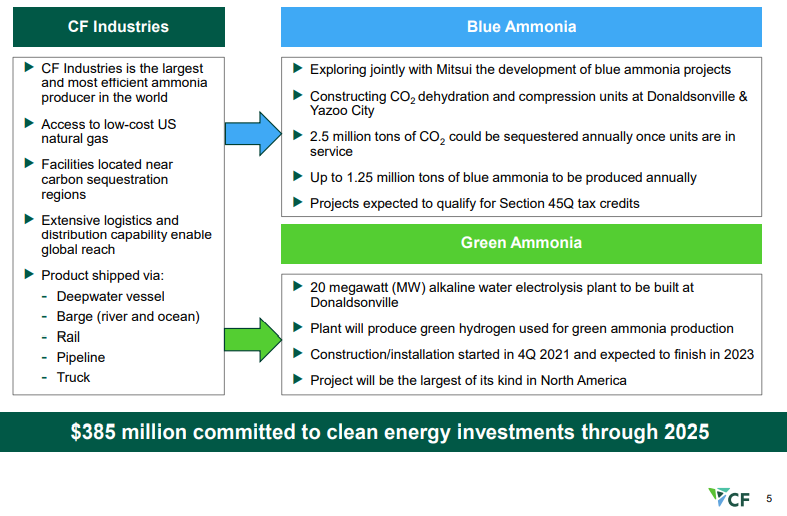
We continue to believe that the US has a cost advantage in CCS versus many of the other regions of the world and that when coupled with low natural gas prices the US should be able to take a lead in developing low carbon chemicals. CF is pushing the idea of both blue ammonia in the US as well as green ammonia, and while the company has yet to announce sequestration plans for the CO2 it is working to purify – see Exhibit - once dehydrated and compressed the incremental cost of storage should be low.
Low Cost CCS Could Be A Game Changer For The US
Feb 16, 2022 1:41:38 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, CCS, CO2, Sequestration, Ammonia, blue ammonia, CF Industries, crude oil, low carbon, green ammonia, carbon intensity, carbon market
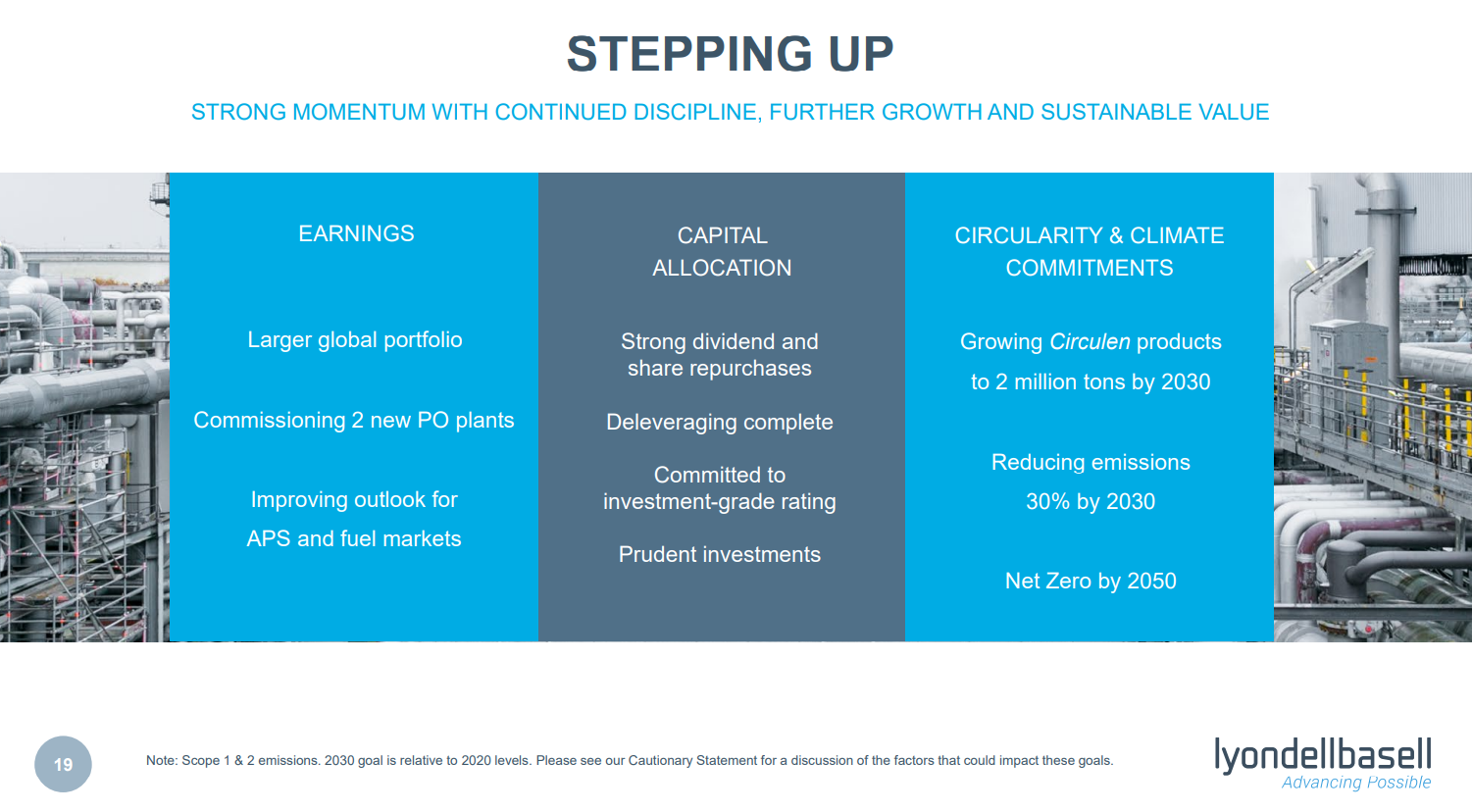
Emission Pledges Will Need To Become Emission Investments Soon
Jan 28, 2022 3:35:32 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Emission Goals, LyondellBasell, Chemical Industry, Dow, climate, materials, Investments, 2022
2022 is the year in which the rubber will need to meet the road for many of the chemical and other material and industrial companies who have made 2030 emission pledges. In the Dow release yesterday, the company used the call as an opportunity to remind investors about the Canada investment and tie that into the 2030 emission goals. We note LyondellBasell’s 30% emission reduction goal by 2030 and like others, LyondellBasell will not be able to get there without substantial investment. LyondellBasell and others do not necessarily have to spend in 2022 (neither does Dow), but unless there are some concrete plans by the end of the year stakeholders will likely start to question whether the emission goals are real. We suspect that most companies are trying to work out whether investments in hydrogen (likely blue hydrogen because of the volumes needed) are a better solution than trying to capture CO2 from a natural gas furnace. Any large hydrogen investment with associated CCS will take 5-6 years from concept to production. Like Dow, we would expect others to focus emission-reduction investments in countries/states that have a clear value on CO2. See today's daily report for more.
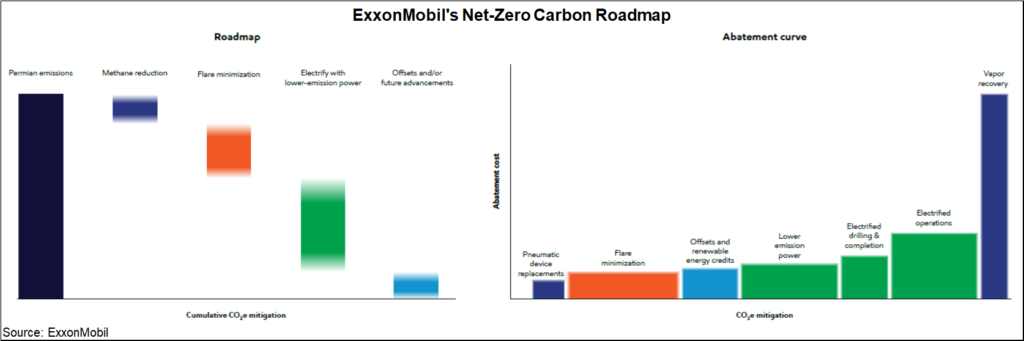
Could Cutting Emissions Give ExxonMobil A Competitive Edge?
Jan 19, 2022 2:11:51 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, LNG, Plastics, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Emissions, ExxonMobil, Net-Zero, carbon abatement, climate, carbon neutral hydrocarbons, Climate Goals
One piece of big news early this week was ExxonMobil’s announcement that it is developing plans that will drive net-zero emissions by 2050 and the company shared a detailed overview. We have picked some charts from the report, some of which can help us draw conclusions for ExxonMobil, but others are more general. The company is banking on a lot of emission reduction and CCS to get to the 2030 target and a large part of the goal is likely to come from the plans for the Permian and the previously stated net-zero target that the company has for 2030 – detail on how this will be achieved is shown in the Exhibit below, see more in today's ESG report.
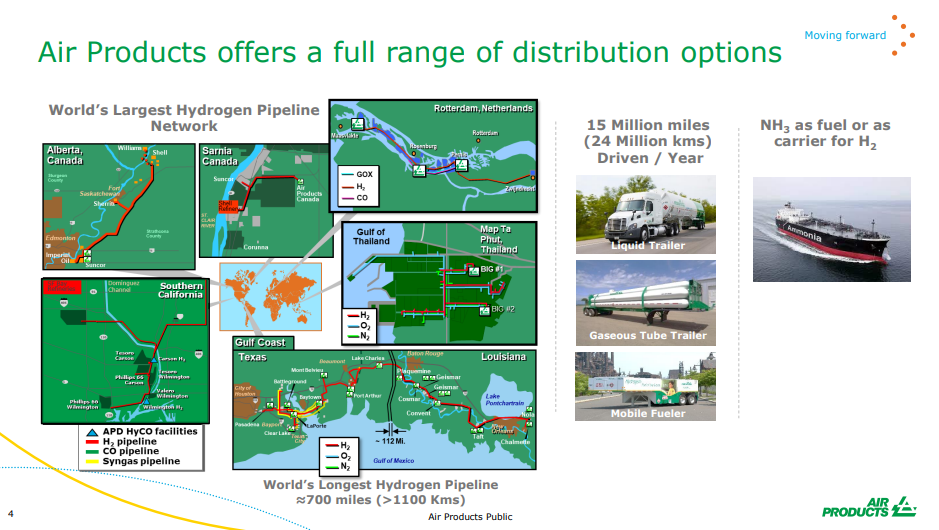
More Green Credentials On Show; More To Come
Oct 8, 2021 12:25:55 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Climate Change, Sustainability, Air Products, Dow, COP26, chemical companies
We expect to see a step up in chemical companies parading their green credentials – or plans for more green credentials, not just because COP26 is ahead but because it has now become a competitive issue. Dow’s view that it may be able to sell low carbon polyethylene in the US at a premium to regular polyethylene reflects a fairly rapidly changing narrative with customers, many of whom are also trying to accelerate their green credentials. For a couple of years, we saw packaging companies, for example, talk in broad terms about ambitions around recycled/renewable content, carbon footprints, etc. Now we are seeing the results of them trying to put their ambitions into practice and they are looking for tangible solutions from their suppliers to help them meet the pledges that they have made to consumers. For many of the packagers, the cost of the packaging is a very small component of the product cost and we would expect the packagers to look at more expensive packaging solutions if it gives them a better label. In the Air Products chart below, the company is using the La Porte start-up to remind us that it is already a huge player in hydrogen and hydrogen infrastructure. See our recent ESG and Climate Report.
Carbon Capture: Front and Center & Enabling Hydrogen Growth
Aug 5, 2021 1:17:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Polymers, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Emissions, Emission Goals, natural gas, carbon emissions, CBAM, NGLs, gray hydrogen
The primary reason for the flurry of carbon capture related headlines in the US over the last few weeks – and our analysis shows a significant step up – is because it looks like this will be the one technology/route to lower carbon emissions that will get a real boost from the infrastructure bill. There is bipartisan support for CCS because the fossil fuel industry sees it as a way to stay in the game and the unions believe that it will create jobs. This combination should garner enough votes to push it into the bill and get it passed, although the details around how CCS would be supported remain unclear. The infrastructure bill has very few real sources of income in it to offset the very high costs – something we will discuss on Sunday – and consequently giving a bigger tax break, through the 45Q program would create an even larger funding gap than we have today. The value/cost dynamic has to rise to get the activity that everyone is looking for and maybe that could be achieved by overlaying a carbon credit onto the program. Anyone exporting to Europe and concerned about the CBAM extending to natural gas, NGLs, chemicals, and polymers would likely consider CCS if they were eligible for 45Q and could also claim an offset on their exported products to neutralize the CBAM tax/fee.
If Carbon Prices Don't Rise, The Tax Payer Will Foot The Bill Anyway
May 12, 2021 1:28:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Chemicals, CO2, Carbon Price, ESG Investing, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Emission Goals
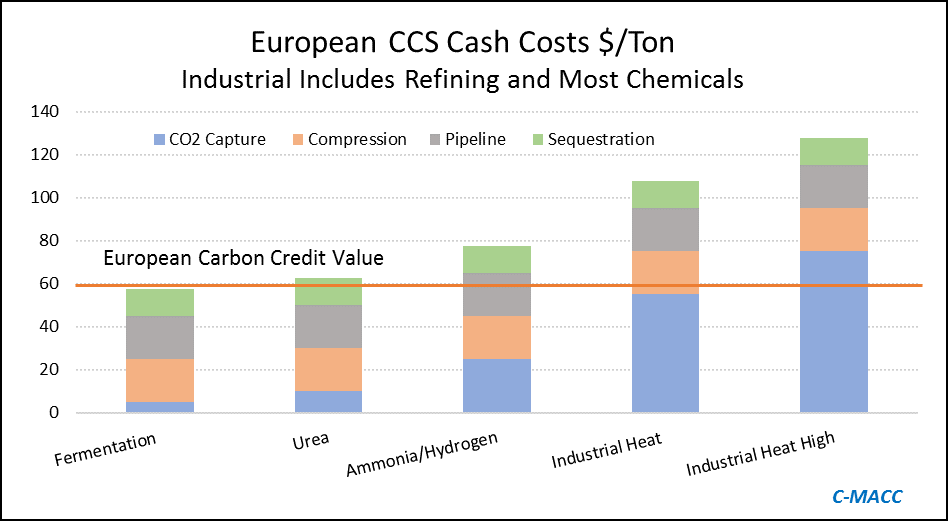
The big news of the week is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be localized within the Port of Rotterdam, where both oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the $2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $65 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs – see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir). For more see today's ESG report.
Source: Global CCS Institute and C-MACC Analysis and Estimates
Another Expensive CCS Project With Limited Capacity
May 11, 2021 11:39:27 AM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, Emissions, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Gulf Coast Sequestration, Emission Goals
The big news of the day is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved yesterday for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be focused within the Port of Rotterdam, where both of the oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the 2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $60 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs –see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir).
Source: Global CCS Institute, C-MACC Analysis, 2021
This is another example of a grossly inflated project, in terms of costs and while it may be the best option for the Port of Rotterdam we would make the following observations.
- It will consume a fraction of the CO2 in the local area
- It might give the Dutch operators a competitive edge over other European companies – either because they can produce low carbon fuel or hydrogen or other chemicals (which may get a premium price), or because they avoid paying the carbon prices. This may cause issues within the EU
- It might artificially lower the European carbon price by creating (subsidized) credits – if this project and other government-backed projects (the UK and Scandinavia so far) overwhelm the credit market, they may depress carbon values and discourage other moves to lower CO2 footprints
- Note that we expect a potential fly up in European carbon prices near-to-medium-term, and these mega-projects will not come into operation for a couple of years
- Like the ExxonMobil proposal for Houston, the implied cost per sequestered ton of CO2 is extremely high and while it might reflect problems with land rights, pipeline “right of ways” and other constraints specific to The Netherlands, it is multiples of the cost that we would expect US for on-shore sequestration and we would encourage all to check out the plans (currently with the EPA) that Gulf Coast Sequestration has in Louisiana.
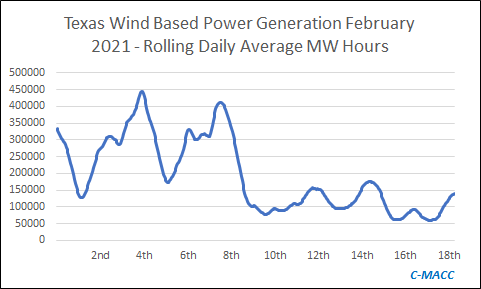
Wind Power - Volatility and Possible Solutions
Feb 22, 2021 9:18:07 AM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Wind Power
Texas wind-based power in February 2021:
The Need for Everything
Feb 19, 2021 12:22:53 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Chemicals, Recycling
We highlight a couple of themes today – one of which is the need for everything. One of the striking conclusions from Shell’s presentation last week was that the company is not putting its eggs in just one or two baskets, it is investing in almost everything – solar, hydrogen, biofuels, natural gas, physical carbon capture, and natural carbon capture through tree planting programs.
Global Coordination - Carbon
Feb 19, 2021 12:22:44 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Recycling
One of the subjects we covered in yesterday’s ESG and Climate piece was the need for global coordination around the price of Carbon. We used Canada as an example of how lack of coordination can potentially drive unintended consequences. Canada’s high carbon tax does not apply to products that are exported – which may drive an increase in exports and an increase in imports to exploit the loophole. One of the headlines in today's report talks about the need for Europe to impose a carbon-related tax on imports, to level the playing field for those paying the carbon tax in Europe versus importers (maybe from Canada) that are not paying the tax. We either need a system of global cooperation where everyone pays the carbon penalty equally, domestic users and exporters, or we need carbon-based import taxes that are equivalent, again on a globally consistent basis. The odds of this level of coordination happening are quite low, in our view and almost any legislation will have exceptions and loopholes that will allow traders to exploit unintended arbitrages. This is probably one of the hardest problems to solve as global Governments attempt to form a coordinated approach to climate-related initiatives.