In our ESG and Climate report tomorrow we are focusing on the very wide range of carbon prices and the structures of the various emission reduction incentive schemes, with a focus on what it does to the competitive landscape within the impacted markets. For example, with the government subsidy being offered to BASF and Air Liquide for the CCS project in Antwerp, some level of competitive edge will be granted to the companies, because similar subsidies might not be available to others. Last week we discussed the very wide range of potential carbon abatement costs for companies in the same business, driven by technology and geography. If we add to that the potential for some projects to attract subsidies, while others do not, we change the landscape of the competitive playing field. Could we, for example, see BASF shutter production in Germany, where abatement costs are high, and move more manufacturing to Antwerp – something likely to be very unpopular with the German government and trade unions. This is more problematic in Europe because of the open trade policy. For Germany to give the same benefit that BASF has at Antwerp to chemical manufacturers in Germany could be prohibitively expensive given the much higher inland costs of CCS in Europe, assuming any permits would be issued. Alternatives to CCS, such as the electrification of industrial heating processes or the use of hydrogen as fuel might be equally expensive. We see some of the select European subsidies possibly causing discord between the member states.
As The Focus On Carbon Increases, Fairness Will Become An Issue
Nov 23, 2021 12:31:25 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Sustainability, LNG, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Carbon Price, Air Products, decarbonization, BASF, carbon abatement, climate, Venture Global, Freeport LNG, Golden Pass, Cameron, NextDecade, decarbonize LNG, Cheniere
Green Hydrogen Plans Look Expensive, Blue Looks Easier
Nov 5, 2021 3:15:29 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Energy, Air Products, Ammonia, carbon footprint, natural gas, solar, carbon pricing
Net-Zero Goals Need Stronger Action Plans
Oct 29, 2021 1:56:53 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Energy, Air Products, Industrial Gas, LyondellBasell, Net-Zero, Dow, carbon footprint, carbon emissions, climate, COP26, materials, low carbon polyethylene, Linde
It is interesting to contrast Linde and LyondellBasell with Air Products and Dow. Air Products and Dow have transitioned away from the more generic messaging around broad objectives, and while they still have them, have started talking about concrete plans and spending aimed at lowering carbon emissions. Dow has a project on the books that will lower the emissions of existing capacity while Air Products is talking about greenfield low carbon investments at this point. Many of the commentators and climate activists are calling for concrete plans as opposed to broad objectives and we suspect that most of the narrative will move that way across energy and materials.
Dow And Air Products Have Got The Ball Rolling, But How Fast?
Oct 21, 2021 1:54:22 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Sustainability, Polyethylene, Blue Hydrogen, Air Products, decarbonization, Dow, climate, low carbon polyethylene
The Dow chart below was included in the presentation around the Canada project and repeated today in the earnings call. We have talked about the Canada project at length as well as the more recently announced Air Products blue hydrogen project in the US. The more interesting debate from here is what will happen next. Are Dow’s and Air Product’s phones ringing off the hooks with potential customers saying “we want some of that”, or is it quieter? We suspect that the phones are ringing and ringing a lot. Perhaps because people genuinely want the low carbon polyethylene or hydrogen, but also perhaps because users of polyethylene and hydrogen are likely obligated to find out more so that they can explore both the opportunities of buying from Dow or Air Products, or evaluating what their alternatives might be. We suspect that a surge in genuine customer interest is likely, good for both Dow and Air Products, but also good for others either considering decarbonizing projects or offering a carbon-free alternative already. See our ESG and Climate piece from yesterday for more on this.
Air Products Is Right On Carbon Capture, Washington Needs To Get On Board
Oct 15, 2021 2:42:27 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Energy, Air Products, Net-Zero, carbon credit, natural gas, EIA, COP26, energy sources
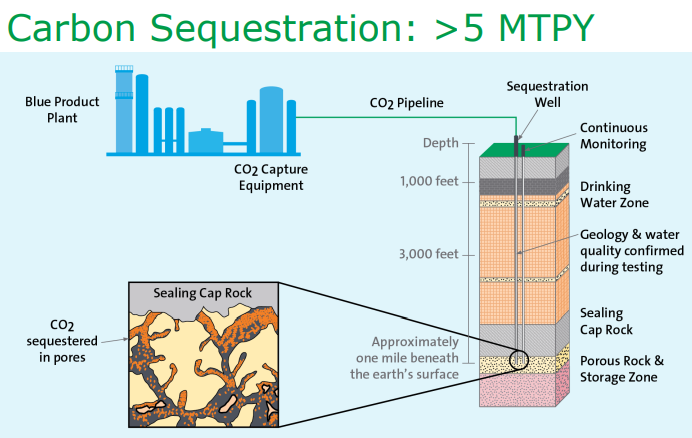
If you look back at our ESG and Climate piece this week (EIA View Suggests Natural Gas & CCS Critical To Net-Zero Goals), you will note that we focused on the recent EIA global energy outlook, and another chart from this outlook is shown below. In the ESG report, we talked about the global need to support increased “clean” natural gas use to offset as much of the coal predictions in the chart as possible and to drive additional hydrogen production to offset some of the petroleum product demand that the EIA still expects to be sued as a transport fuel in 2050. We also called for the broad and warm embrace of CCS so that some of the fossil fuel that the EIA is predicting – especially all of the fuel used for power in the exhibit below. Yesterday Air Products announced not only a large blue hydrogen complex for Louisiana but also the CCS to support it and made a very compelling argument in its presentation for the need for substantial volumes of blue hydrogen – something we fully agree with. We covered the subject in detail in yesterday’s daily. “Blue Is The Color, Hydrogen Is The Game…”
Air Products Claiming The Hydrogen Highground
Oct 14, 2021 3:04:12 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Air Products, Ammonia, natural gas, carbon values, blue ammonia, Carbon Sequestration
In our ESG piece yesterday we talked about the competitive edge that Canada now has with respect to both natural gas (because of lower prices versus the US) and CCS, both because of relatively low costs but also because of the clear value on carbon. Yet today we see an announcement in the US!
More Green Credentials On Show; More To Come
Oct 8, 2021 12:25:55 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Chemicals, Climate Change, Sustainability, Air Products, Dow, COP26, chemical companies
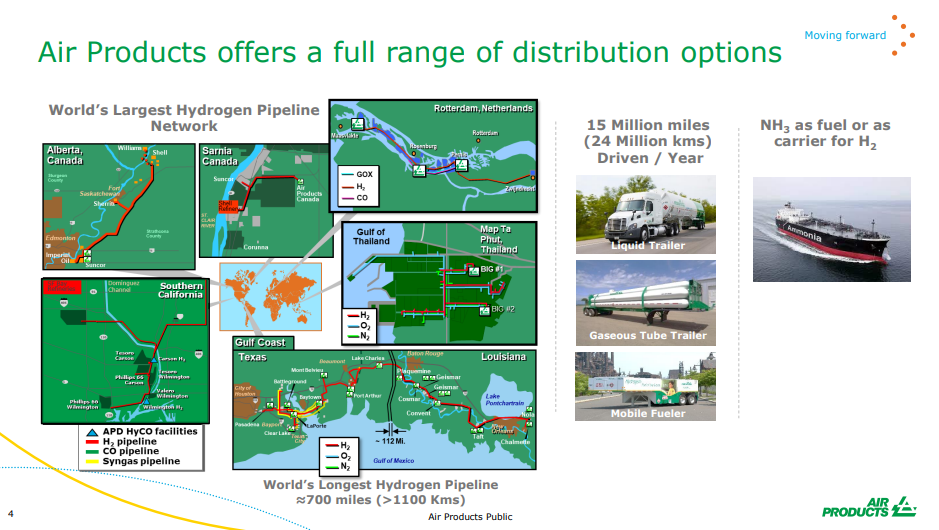
We expect to see a step up in chemical companies parading their green credentials – or plans for more green credentials, not just because COP26 is ahead but because it has now become a competitive issue. Dow’s view that it may be able to sell low carbon polyethylene in the US at a premium to regular polyethylene reflects a fairly rapidly changing narrative with customers, many of whom are also trying to accelerate their green credentials. For a couple of years, we saw packaging companies, for example, talk in broad terms about ambitions around recycled/renewable content, carbon footprints, etc. Now we are seeing the results of them trying to put their ambitions into practice and they are looking for tangible solutions from their suppliers to help them meet the pledges that they have made to consumers. For many of the packagers, the cost of the packaging is a very small component of the product cost and we would expect the packagers to look at more expensive packaging solutions if it gives them a better label. In the Air Products chart below, the company is using the La Porte start-up to remind us that it is already a huge player in hydrogen and hydrogen infrastructure. See our recent ESG and Climate Report.
Shipping Hydrogen: Expensive Anyway You Do It
Aug 31, 2021 2:09:19 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Wind Power, Climate Change, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, Renewable Power, Air Products, Ammonia, renewable energy, solar energy, shipping, transportation, nitrogen, hydrogen electrolyser, toluene, methylcyclohexane
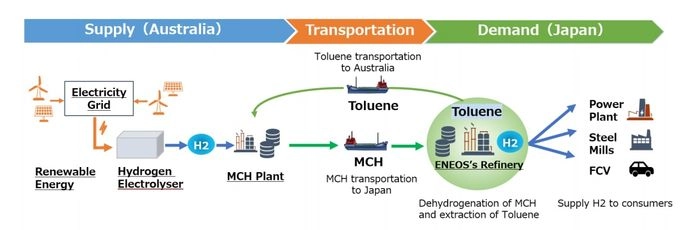
The exhibit below highlights one of the more significant constraints for green hydrogen, which is that the abundant low-cost power opportunities (strong wind and lots of sunshine) are often not where demand for hydrogen exists and the challenge is how to transport it. The problem with reacting it to make something else and then recovering it at the point of use or a distribution hub is that hydrogen is very light and you end up moving a lot of something else to get a little hydrogen. Air Products is looking at making ammonia in Saudi Arabia and shipping the liquid ammonia and the project below is looking at using toluene as a carrier in what appears to be a closed-loop with toluene moving one way and methylcyclohexane moving the other way. The liquid shipping would be cheap, but with the MCH route, only 5% of what you would be moving to Japan would be the green hydrogen. Using ammonia the green hydrogen content is slightly less than 18%, but you have to make the nitrogen on-site. The cost of making the nitrogen would be a function of the local cost of power and these remote locations should have very low-cost renewable power. In the example below, the opportunity is likely unique to the refinery structure and shipping opportunity and we doubt that it is easily replicated in a way that would be more economic than shipping ammonia or shipping compressed hydrogen itself.
Source: H2 Bulletin, August 2021
If Carbon Prices Don't Rise, The Tax Payer Will Foot The Bill Anyway
May 12, 2021 1:28:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Chemicals, CO2, Carbon Price, ESG Investing, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Emission Goals
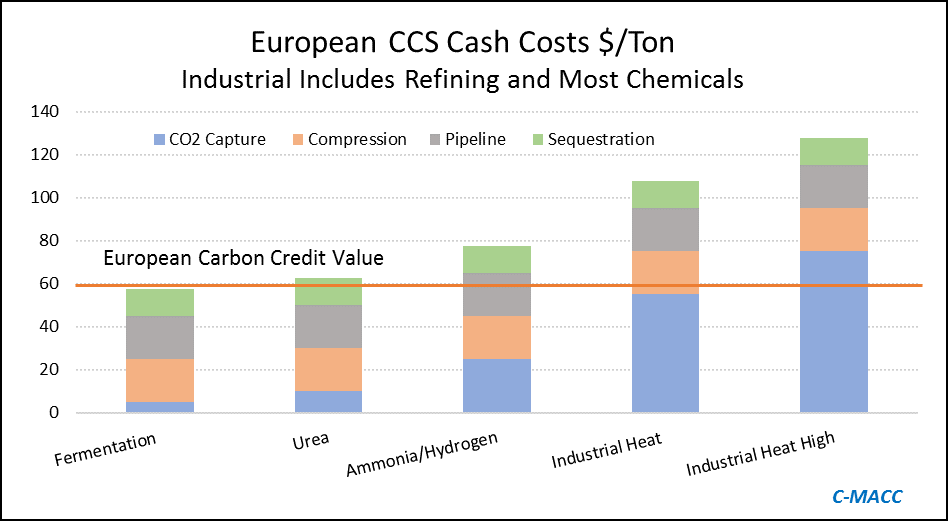
The big news of the week is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be localized within the Port of Rotterdam, where both oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the $2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $65 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs – see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir). For more see today's ESG report.
Source: Global CCS Institute and C-MACC Analysis and Estimates
Another Expensive CCS Project With Limited Capacity
May 11, 2021 11:39:27 AM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, Emissions, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Gulf Coast Sequestration, Emission Goals
The big news of the day is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved yesterday for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be focused within the Port of Rotterdam, where both of the oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the 2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $60 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs –see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir).
Source: Global CCS Institute, C-MACC Analysis, 2021
This is another example of a grossly inflated project, in terms of costs and while it may be the best option for the Port of Rotterdam we would make the following observations.
- It will consume a fraction of the CO2 in the local area
- It might give the Dutch operators a competitive edge over other European companies – either because they can produce low carbon fuel or hydrogen or other chemicals (which may get a premium price), or because they avoid paying the carbon prices. This may cause issues within the EU
- It might artificially lower the European carbon price by creating (subsidized) credits – if this project and other government-backed projects (the UK and Scandinavia so far) overwhelm the credit market, they may depress carbon values and discourage other moves to lower CO2 footprints
- Note that we expect a potential fly up in European carbon prices near-to-medium-term, and these mega-projects will not come into operation for a couple of years
- Like the ExxonMobil proposal for Houston, the implied cost per sequestered ton of CO2 is extremely high and while it might reflect problems with land rights, pipeline “right of ways” and other constraints specific to The Netherlands, it is multiples of the cost that we would expect US for on-shore sequestration and we would encourage all to check out the plans (currently with the EPA) that Gulf Coast Sequestration has in Louisiana.