As we discussed in yesterday’s ESG and Climate report, the SEC has some challenges ahead, not just because there are high hopes that it will start mandating a change in terms of disclosure accuracy and consistency, as well as fund definition, but also because, as yet, it does not have the mandate to do so. All eyes are on the regional regulators, in the US, Europe, and other countries to police what is the wild west of reporting. The E piece of ESG is the major challenge and it is where corporates and fund managers alike are dealing with issues and measures that are likely very different company by company within a sector, let alone between the sectors themselves – it is far more complex and harder to analyze than, for example, board diversity.
The Pressure Is On The SEC For Better ESG Metrics & Disclosures
Jul 29, 2021 1:32:27 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, CO2, Emissions, Emission Goals, LyondellBasell, ESG investment, Environment, Borealis, SEC, Chemical Sector, OMV, ESG Metrics
Carbon Abatement – A Multi-client Analysis
Jul 7, 2021 1:01:06 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Carbon Tax, Carbon Fuels, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Carbon, Carbon Neutral, Emission Goals, Net-Zero, decarbonization, carbon footprint, ESG Fund, carbon dioxide, carbon credit, carbon value, carbon abatement, power, carbon cost, carbon offset, offsets, ESG investment, carbon emissions, clean energy, climate
A major initiative by C-MACC in collaboration with the Power Research Group
Could DoE Ambitious Hydrogen Plans Have Unintended Consequences?
Jun 11, 2021 1:17:40 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Renewable Power, Electric Vehicles, Materials Inflation, Emission Goals, Net-Zero, Ammonia, carbon footprint, natural gas, R&D, capital cost, Praxair, DoE, production cost
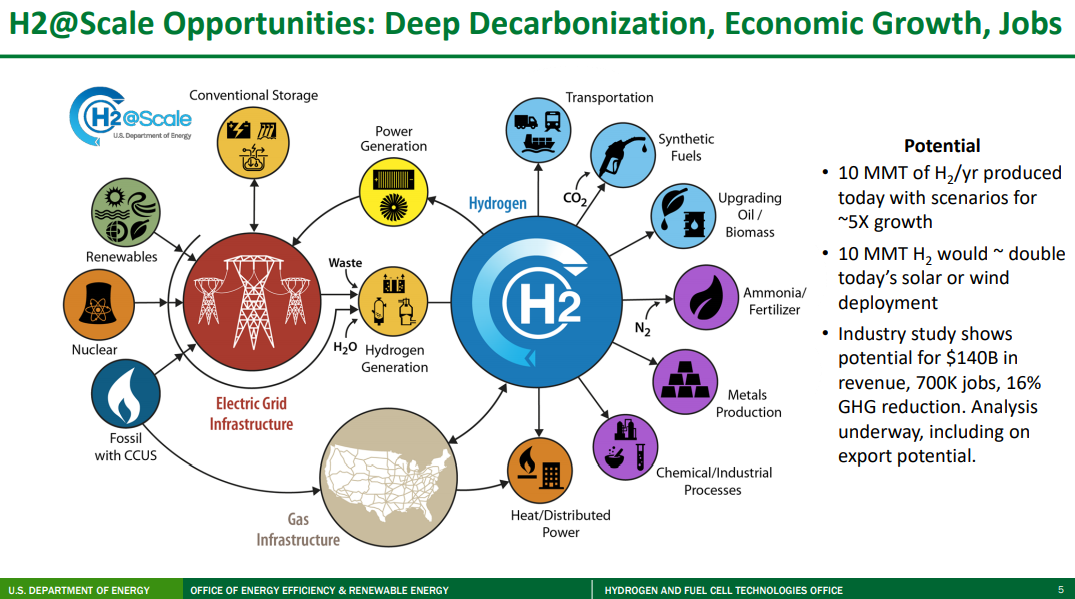
We will cover the very comprehensive DoE hydrogen work in more detail in the ESG report next week, but a couple of the charts from that work are worth mentioning today. The first picture below accurately depicts all of the potential uses of hydrogen and shows that over time it could solve a lot of “hard to solve” CO2 emission problems, especially where electricity cannot do the job efficiently. The reason why so many countries and companies are so interested in hydrogen is because of its potential versatility and because of its minimal carbon footprint (there is some carbon leakage in the full lifecycle of the production coming from construction around the plants themselves and infrastructure to use the hydrogen).
If Carbon Prices Don't Rise, The Tax Payer Will Foot The Bill Anyway
May 12, 2021 1:28:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Chemicals, CO2, Carbon Price, ESG Investing, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Emission Goals
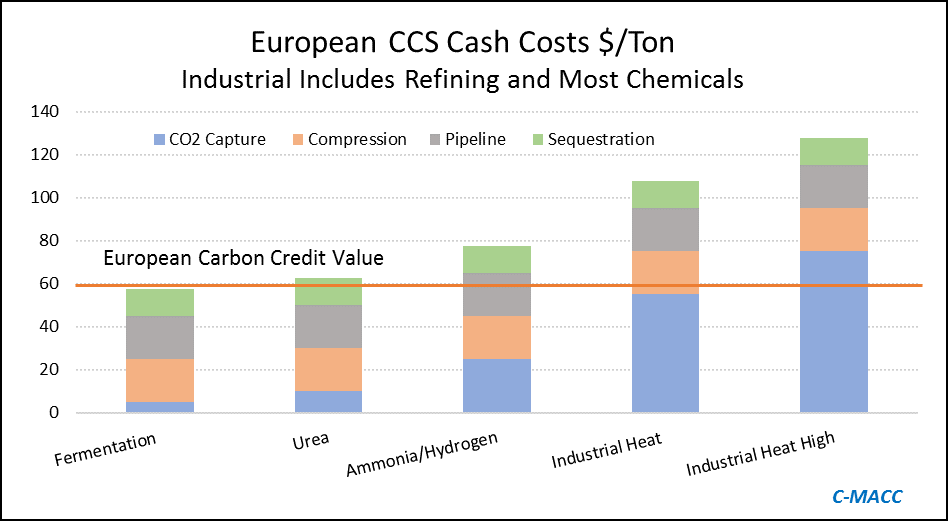
The big news of the week is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be localized within the Port of Rotterdam, where both oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the $2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $65 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs – see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir). For more see today's ESG report.
Source: Global CCS Institute and C-MACC Analysis and Estimates
Another Expensive CCS Project With Limited Capacity
May 11, 2021 11:39:27 AM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, Emissions, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Gulf Coast Sequestration, Emission Goals
The big news of the day is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved yesterday for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be focused within the Port of Rotterdam, where both of the oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the 2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $60 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs –see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir).
Source: Global CCS Institute, C-MACC Analysis, 2021
This is another example of a grossly inflated project, in terms of costs and while it may be the best option for the Port of Rotterdam we would make the following observations.
- It will consume a fraction of the CO2 in the local area
- It might give the Dutch operators a competitive edge over other European companies – either because they can produce low carbon fuel or hydrogen or other chemicals (which may get a premium price), or because they avoid paying the carbon prices. This may cause issues within the EU
- It might artificially lower the European carbon price by creating (subsidized) credits – if this project and other government-backed projects (the UK and Scandinavia so far) overwhelm the credit market, they may depress carbon values and discourage other moves to lower CO2 footprints
- Note that we expect a potential fly up in European carbon prices near-to-medium-term, and these mega-projects will not come into operation for a couple of years
- Like the ExxonMobil proposal for Houston, the implied cost per sequestered ton of CO2 is extremely high and while it might reflect problems with land rights, pipeline “right of ways” and other constraints specific to The Netherlands, it is multiples of the cost that we would expect US for on-shore sequestration and we would encourage all to check out the plans (currently with the EPA) that Gulf Coast Sequestration has in Louisiana.