There has been a lot of press over the last couple of months around carbon offsets – not least because of Mark Carney’s efforts to legitimize the idea. Mr. Carney’s focus is to create a robust trading platform for the buying and selling of legitimate offsets so that a carbon market can operate efficiently. He believes that without accurate and realistic carbon values, and the ability to buy and sell them, the capital markets around emission reduction will be inefficient and that less money will be attracted into the area. On this, he is probably correct, but in our view, the carbon offset markets have a long way to go.
Carbon Offsets: Direct Air Capture Is Not The Only Option
Jul 28, 2021 12:55:50 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, carbon abatement, carbon values, carbon offsets, direct air capture, methane emission, DAC
Economics Have Driven US Emission Reductions More Than Policy
Jul 27, 2021 2:01:49 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, Sustainability, Coal, CO2, Renewable Power, Energy, Emissions, natural gas, EV, clean power investments, power sector
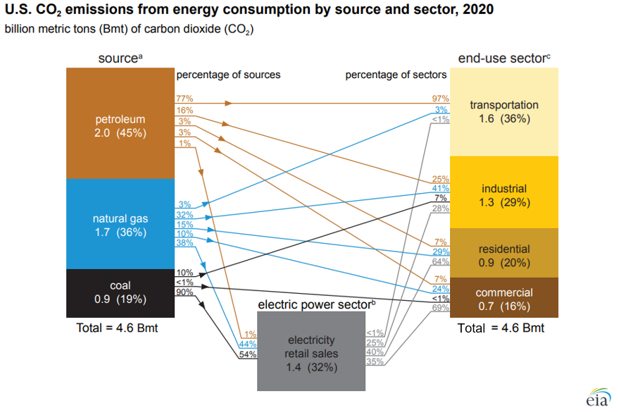
We are increasingly concerned that the US will remain a laggard concerning climate change initiatives given the major challenges of moving to the next steps and the bifurcated congressional views. The emissions reductions that the US has seen over the last 10 years have been more happenstance than planning, with the abundance of natural gas following the shale boom of the last decade creating economic reasons to replace coal-fired power with natural gas rather than environmental reasons. Lower costs for wind and solar power and focused industrial demand for that clean power have been the bigger driver of clean power investments. In the chart below, the decline in emission from the power sector is evident and it should continue. The diagram below shows sources and uses for US emissions in 2020, but the accompanying write-up talks about the step down in emissions overall in 2020. Except for the continuing electric power transition, most of the other 2020 declines are COVID-related and are expected to rebound in the near term, especially transport. The market share gains of EVs are not significant enough yet to make a difference. See more in today's daily report.
Pressuring The Banks To Pressure Their Corporate Customers
Jul 13, 2021 12:50:28 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, Emissions, Net-Zero, carbon abatement, Investors, banks, Green bond markets, Repsol
We have talked at length in our dedicated ESG pieces about the inevitable role that investors and financial regulators will play in addressing climate change, and we see more evidence that some of this pressure to conform is going to be pushed down to banks and lenders as standards are set for disclosing financial exposure to high emission industries. The banks will have little choice but to add their weight to the calls for better disclosure and eventually mitigation plans, as it will impact their ability to lend and their ability to defend lending portfolios to their stakeholders. Green bond markets are developing around the world, but still need some definitional oversight and it will be interesting to watch corporate behavior if a significant borrowing cost delta emerges between “green lending” and other lending – it might be a lot cheaper to get debt focused on net-zero related projects than expansion projects and it was interesting to note that Repsol’s announcement (linked here) talks about carbon abatement (in general terms) as part of the investment in Portugal.
Natural Gas Based Power Not Going Away Anytime Soon
Jul 8, 2021 2:03:50 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Coal, CO2, Renewable Power, Emissions, carbon abatement, natural gas, power demand, carbon emissions, EIA, US carbon emissions
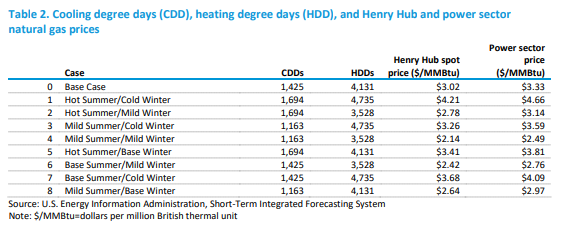
The table below is from an interesting analysis published by the EIA this week that focuses on possible power demand scenarios for the US – all weather-related – and then backs into the power sources that would be needed to meet the demand, concluding with the US carbon emissions that would correspond to each scenario. The conclusions should not be surprising, which are that carbon emissions rise disproportionately faster as power demand rises – as more coal is required to balance generation needs, and fall disproportionately more quickly as power demand falls (as less coal is needed). The analysis is effectively a study of how much less CO2 emissions are using natural gas to generate power versus coal. As renewable generation increases as a share of the total, however, the math will change, and the EIA study does not take into account the weather factor on renewable power, it looks at cooling degree days and heating degree days at a national level only. This is reasonable as there is likely not enough data to be able to put good reliability estimates yet around renewable power annual volatility and more importantly, the impact of weather on renewable power is likely to be short-term in nature. Perhaps this analysis could be improved by adding a “daily risk band” around each scenario, showing how much renewable power volatility could cause peaks in the high scenario and lows in the low, etc.
More Climate Discord Unlikely To Help Necessary Progress
Jun 18, 2021 1:51:45 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, CO2, Carbon, Emissions, ESG Investing, carbon credit, investment managers, US Government, carbon values, carbon offsets, carbon trading
There have been some disappointing headlines out of the UN climate meeting this week, which is intended to pave the way for some of the COP26 discussions and come up with proposals that are likely to be agreed upon at the meeting. Most of the issues are around who is paying for what and whether developed nations are investing enough to help developing nations, using the guidelines put forward when the Paris Agreement was signed. In the US, the climate agenda and the Biden plan are bogged down in Congress and the plan is unlikely to pass in its current form.
We Need To Be More Inventive On Carbon Values In The US
Jun 16, 2021 2:00:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, Emissions, carbon credit, carbon abatement
In our ESG and Climate report published today we focus on hydrogen and what we believe are some unrealistic cost/timing estimates for green hydrogen. One of our concerns is that the hope of cheap green hydrogen, and absent any other strong incentives, will put the brakes on other carbon abatement initiatives and if the cost of hydrogen does not fall we could reach 2030 having made little progress on any front.
Navigator: A Pipe Dream or Pipe Nightmare?
Jun 3, 2021 9:56:39 AM / by Graham Copley posted in Carbon Capture, CO2, Sequestration, Emissions, Pipeline, carbon dioxide, ethanol, corn based ethanol
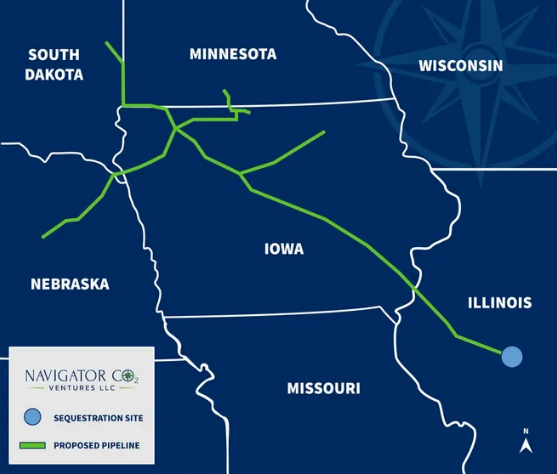
The Navigator CCS announcement is extraordinary in its boldness and potential lack of any real chance of economic success. The idea of building 1200 miles of high-pressure CO2 pipe (See exhibit below) to collect small volumes from corn-based ethanol producers and potentially have multiple sequestration sites is extremely expensive and would not begin to be covered by the 45Q tax credit, which would easily be consumed by the compression and pipeline costs alone. If some of the ethanol is making it into the LCFS markets, each ethanol producer that has some material heading that way will want a piece of the pie and if each had to jointly file with CARB, with Navigator, for what would be small portions of the overall ethanol output, the administration might be overwhelming, as would be a chain of custody process which satisfies CARB. Navigator is not an altruist fund and consequently, must see a way to make a return on the idea. This may be based on the hope that LCFS or something like it will spread to other states.
Friday Question: What Is Next For Oil? Help Us Write Our Next Report!
May 28, 2021 1:50:42 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Oil Industry, Energy, Emissions, Shell, Oil
We talked about the Dutch ruling against Shell in yesterday's report and the latest refinery sale in the US is another indication of one of the risks of unilateral court-based decisions. Shell could easily get to lower emissions by divesting assets, as can anyone else with a medium-term emission target on the books. We have written previously about the possibility of an energy equivalent of the “bad bank” structure that was set up during the financial crisis, where emissions challenged assets are divested into either private entities or public holding companies that have mandates to improve excessive emission pools but also have significant cash flows and pay investors to wait.
ESG Friday Question: Can Technology Keep Pace?
May 21, 2021 1:12:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Ethylene, Emissions, Net-Zero, IEA, Dow, propane, Technologies, ethane dehydrogenation, carbon footprint, BASF
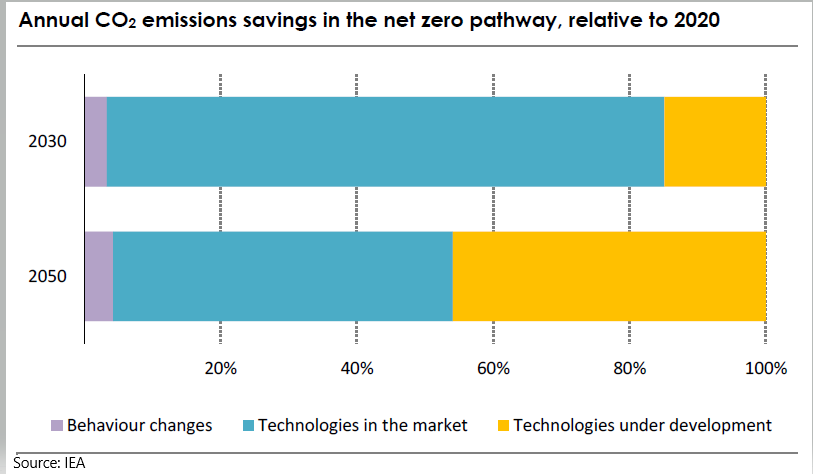
There is a broad technology theme to the articles that we have chosen today, which is in keeping with one of the core conclusions of the IEA report earlier this week. The IEA is estimating that roughly half of the path to net-zero will require technologies still in the test phase, or in some cases still conceptual. The Dow headline around ethane dehydrogenation and electric furnaces is a good example. Both technologies could lower the carbon footprint of making ethylene, but the dehydrogenation route will require some catalyst or other breakthrough as current propane dehydrogenation technologies require a lot of heat. The electric furnace idea is complex and would require extremely high levels of power, all of which would have to be renewable for the carbon footprint to fall – this type of technology is likely implied in the BASF announcement today. The IEA talked about some of the transition moves required to allow the technology advances time to become either commercial or cost effective, or both. Carbon capture features meaningfully in the IEA plans, but the study has carbon capture volume rising through 2050, which we find odd. The idea of carbon capture is to act as a bridge between where we are today and where we could be once new technology is developed – therefore, while companies like Dow should be aiming for technologies that lower the carbon production of its processes, carbon capture should be an almost immediate bridge to lower emissions while both the technology is developed, and its costs are reduced. Carbon capture needs should then decline. View today's Daily Report for more.
Another Expensive CCS Project With Limited Capacity
May 11, 2021 11:39:27 AM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, Emissions, Shell, Air Products, Air Liquide, ExxonMobil, Industrial Gas, Gulf Coast Sequestration, Emission Goals
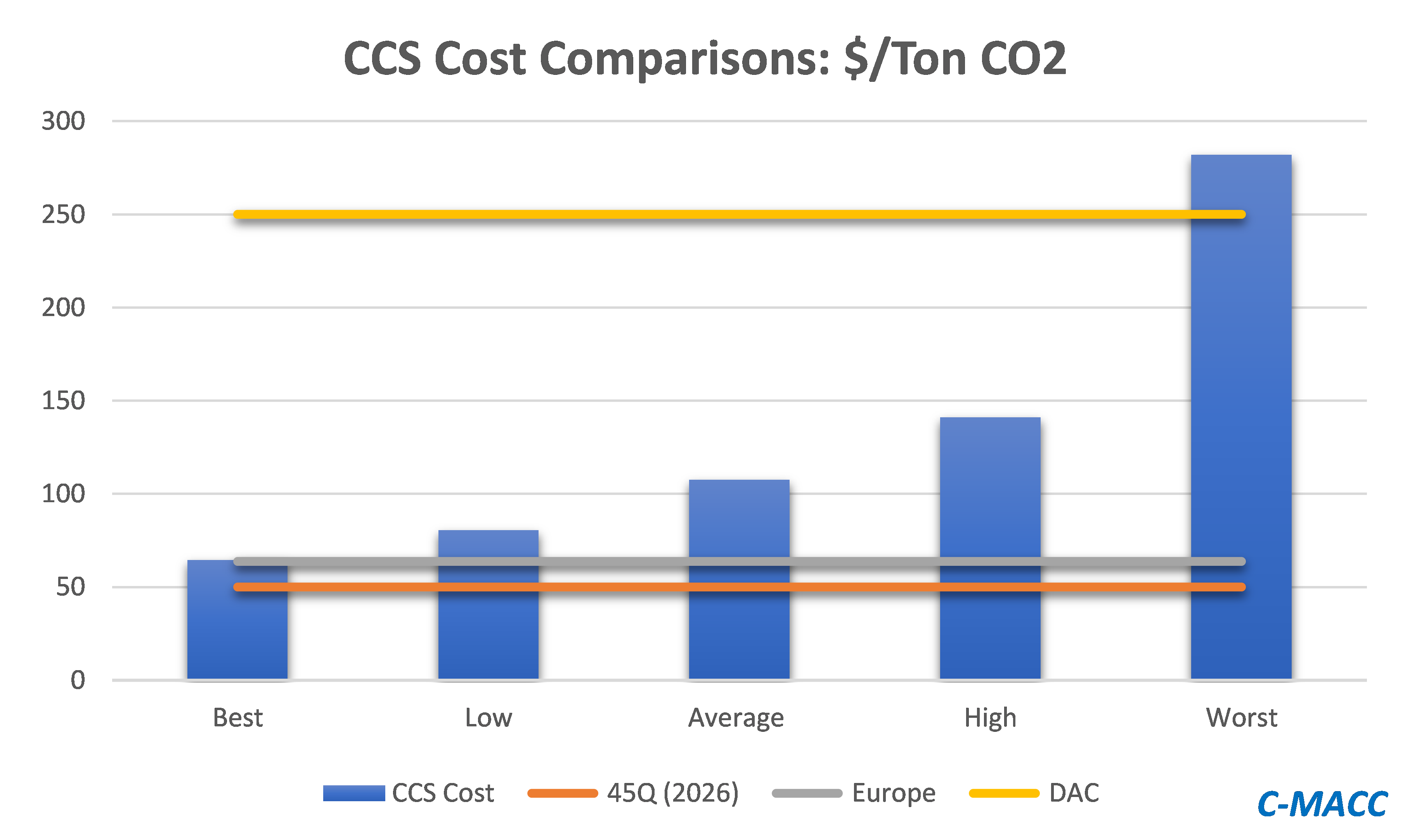
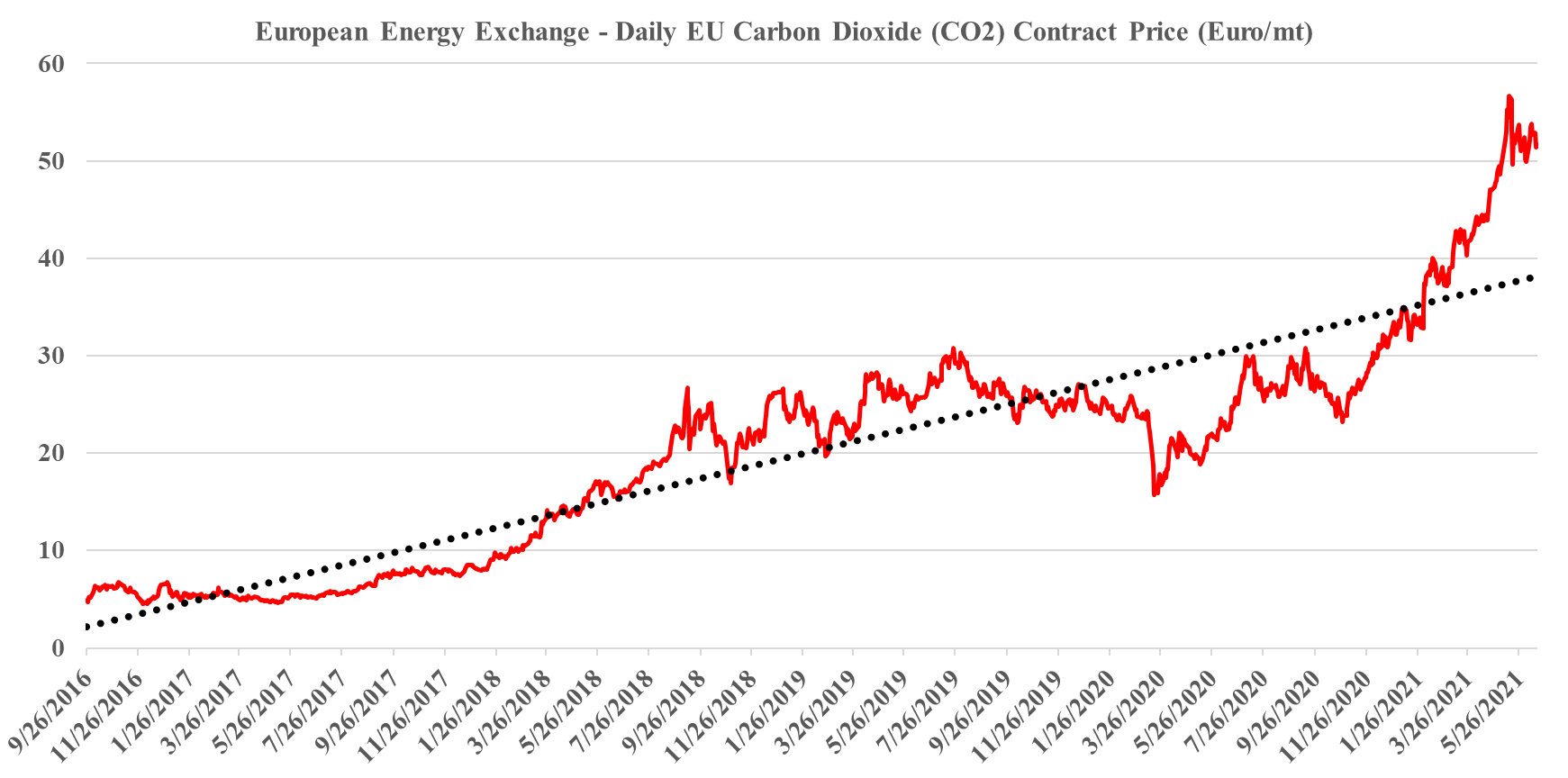
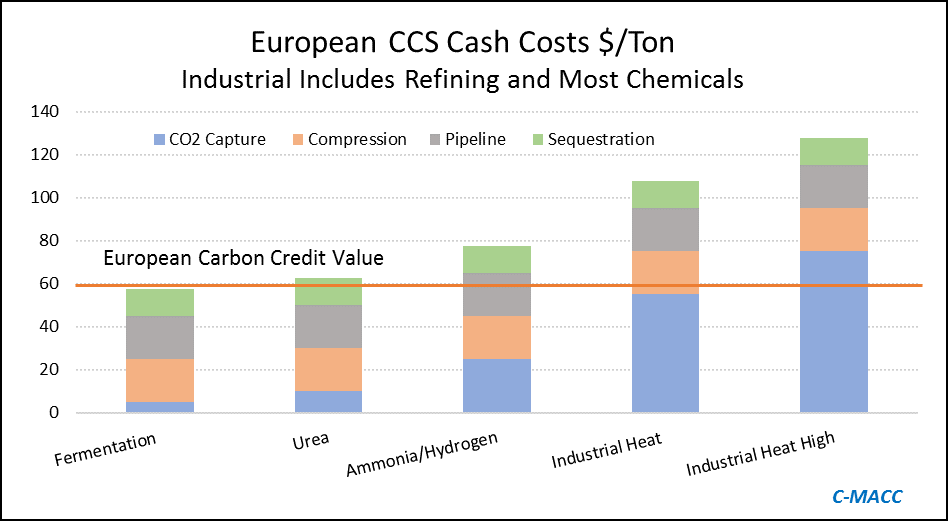
The big news of the day is the massive grant that the Dutch government approved yesterday for an offshore carbon capture project that will be focused on the operations of Shell, ExxonMobil, Air Products, and Air Liquide. This looks to be focused within the Port of Rotterdam, where both of the oil majors operate large refineries, Shell also operates a large chemical site and the industrial gas companies have significant hydrogen capacity. The Dutch government believes that the country cannot achieve its emission goals without carbon capture as it has one of the largest refining and chemical footprints in Europe and the 2.4 billion grant (likely achieved through a series of subsidies) is an indication that the country is willing to invest to make its emission goals a reality. The grant is likely aimed to help close the gap between the current European carbon price – which is just over $60 per ton today and what is estimated to be the full cost of capture and storage under the North Sea, which the linked article suggests is closer to $100 per ton, but this likely underestimates the capture costs –see chart below - even if the CO2 streams are pooled and treated as one stream. Interestingly, despite the high level of subsidy, this project is estimated to store only 2.5 million tons a year and will only last 15 years (likely because of the capacity of the offshore reservoir).
Source: Global CCS Institute, C-MACC Analysis, 2021
This is another example of a grossly inflated project, in terms of costs and while it may be the best option for the Port of Rotterdam we would make the following observations.
- It will consume a fraction of the CO2 in the local area
- It might give the Dutch operators a competitive edge over other European companies – either because they can produce low carbon fuel or hydrogen or other chemicals (which may get a premium price), or because they avoid paying the carbon prices. This may cause issues within the EU
- It might artificially lower the European carbon price by creating (subsidized) credits – if this project and other government-backed projects (the UK and Scandinavia so far) overwhelm the credit market, they may depress carbon values and discourage other moves to lower CO2 footprints
- Note that we expect a potential fly up in European carbon prices near-to-medium-term, and these mega-projects will not come into operation for a couple of years
- Like the ExxonMobil proposal for Houston, the implied cost per sequestered ton of CO2 is extremely high and while it might reflect problems with land rights, pipeline “right of ways” and other constraints specific to The Netherlands, it is multiples of the cost that we would expect US for on-shore sequestration and we would encourage all to check out the plans (currently with the EPA) that Gulf Coast Sequestration has in Louisiana.