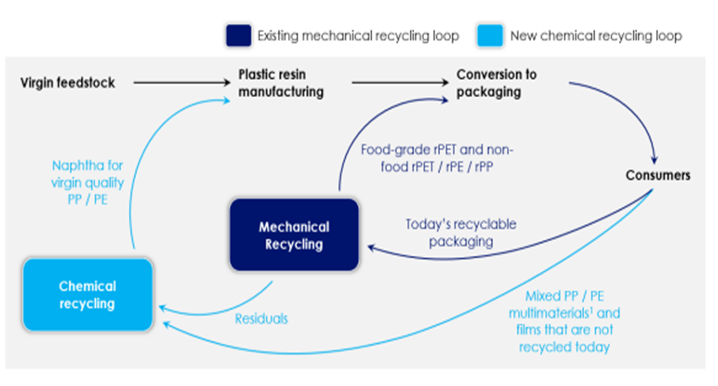
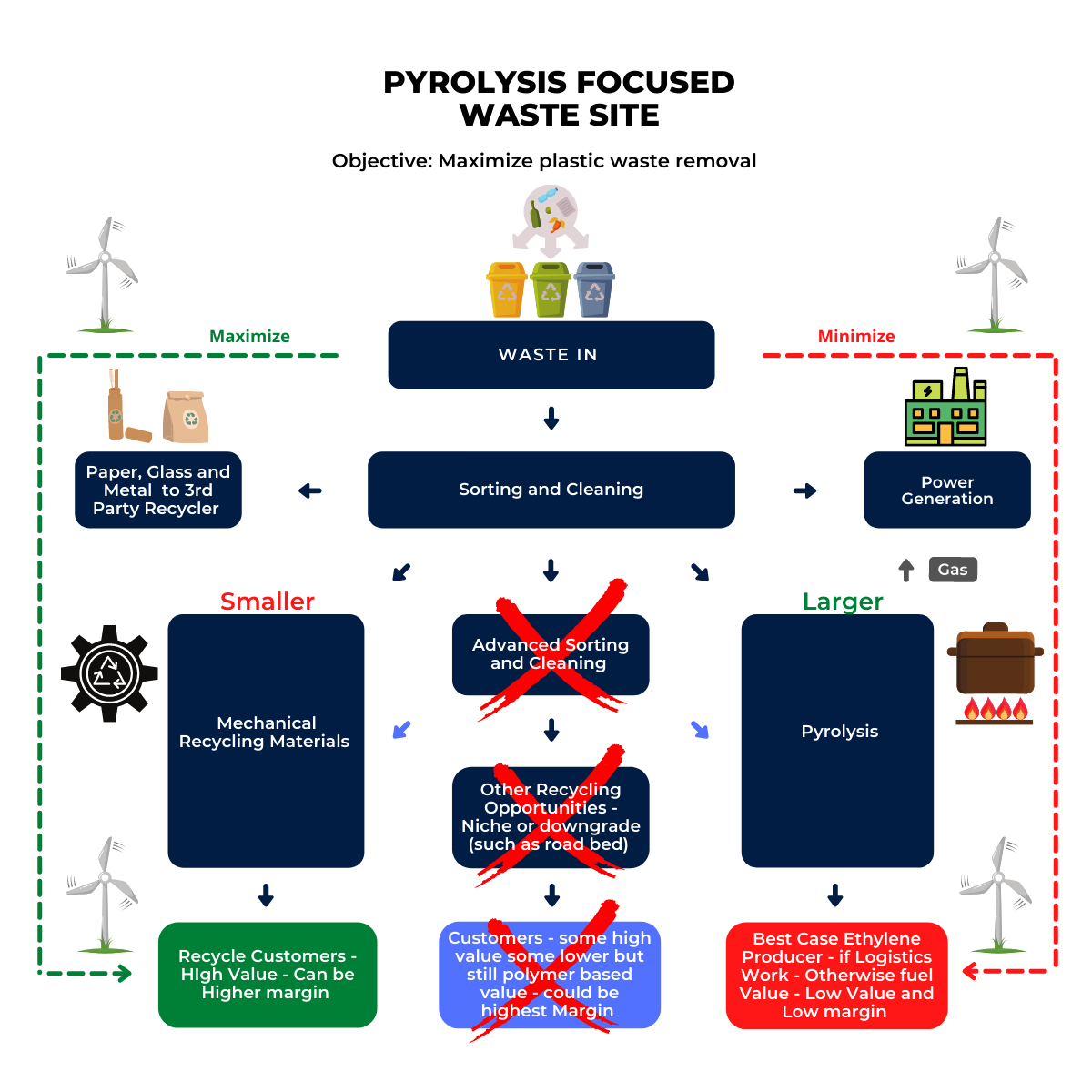
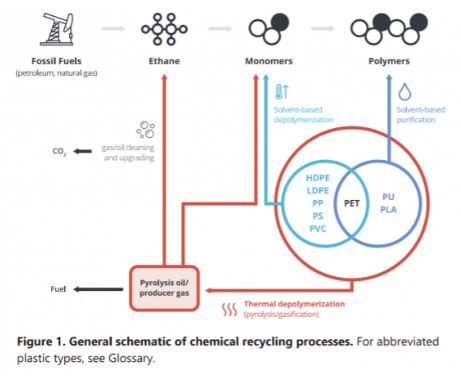
In the first picture below we see another schematic that shows how different options for polymer recycling could work together. We have suggested a more complex site than the one in the chart as there will be opportunities to recycle some polymers into non-like-for-like applications such as roadbed modification and other durable applications. In addition, there may be a better return in waste to energy versus chemical recycling and that may be an alternative or an add-on. This sort of complex site is what we believe LyondellBasell could be looking at for the Houston refinery site. An integrated waste treatment facility that optimizes that use for each tranche of the waste stream could improve the overall investment returns. In the second picture below we show our version of what a comprehensive waste recycling operation should look like. See more on recycling!
Managing Waste To Maximize Value Requires Multiple Processes
May 4, 2022 2:15:03 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Climate Change, Sustainability, LyondellBasell, chemical recycling, waste, polymer recycling, waste recycling
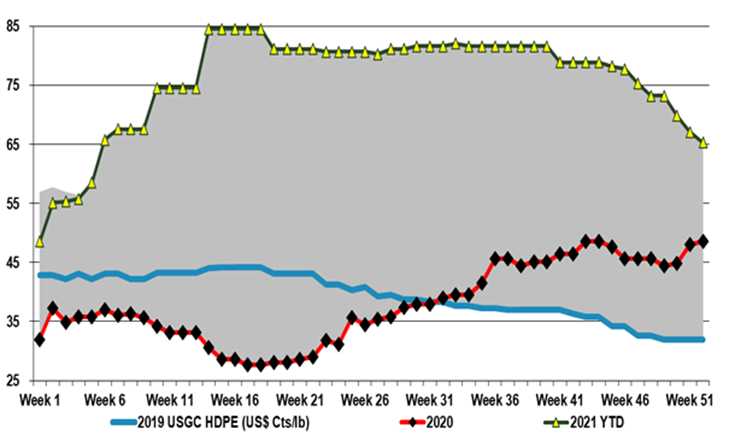
Will Falling Polymer Prices Put The Brakes On Recycling Investment In 2022?
Jan 4, 2022 12:19:17 PM / by Graham Copley posted in recycled polymer, chemical recycling, biodegradable plastics, recycled waste
In our ESG and Climate Piece tomorrow we will look at the impact on plastic waste initiatives of falling virgin polymer prices. If recycling initiatives stall – especially the more expensive mechanical piece – it will likely add to concerns that packagers already have around whether they can get enough material to meet their public goals on recycled content. If it then also looks likely that new materials – renewable based on biodegradable - may be either late to market or more expensive than anticipated the door opens wider for the chemical recycling advocates and also for alternative materials. The chemical recyclers also need collection and sorting to improve, but the more complex/forgiving the facility, the less rigorous the sorting needs to be. Also, this route is somewhat agnostic to the price of virgin polymers as the output is competing with fuels and chemical feedstock values. For chemical recycling to be economic, the price of crude oil must remain high. For chemical recycling to get the lion’s share of recovered plastic waste the price of oil needs to be high and the price of virgin polymers low – discouraging mechanical recycling. While this may spur more chemical recycling, the net effect of low virgin polymer prices would overwhelm the benefit of better recycling economics for the majors – many of whom make up the bulk of the existing and planned chemical recycling capacity today. That said, the more plastic waste that ends up in chemical recycling, the less of an impact there will be on virgin plastic demand
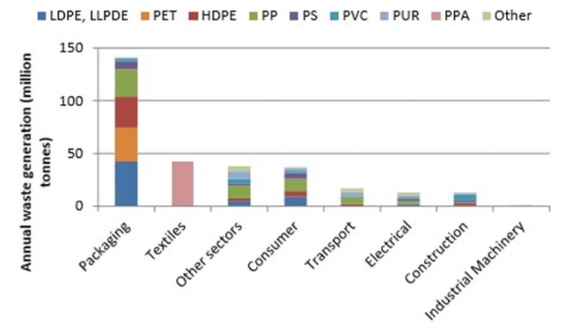
Packaging Waste Disposal May Not Mean Packaging Waste Recycled
Dec 17, 2021 1:59:37 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Sustainability, Pyrolysis, packaging, chemical recycling, renewables, climate, waste, carbon footprints, polymer recycling, waste disposal, recycled waste
We have spent a lot of time over the last few weeks talking about polymer recycling and renewables and the chart below is another look at where plastic waste is coming from. Packaging is the big piece and it is also the area where customers, i.e. the packagers, are looking for the largest increase in the use of recycled materials quickly. As we noted in our ESG and Climate piece this week, increasing volumes of this packaging waste is moving into different use applications, such as building products and durables, and even more could potentially flow into chemical recycling – note that there are 7 headlines on chemical/advanced recycling in today's daily report. The packagers have little chance of meeting their near-term recycling content goals in our opinion, but they have zero chance if they do not accept chemical recycling as part of the mix. It will be important to accurately audit the chain of custody of chemical recycling to avoid double counting. The separate challenge with chemical recycling is the now increased focus on carbon footprints, as the pyrolysis process is energy-intensive, whether direct heat from burning fossil fuel or electric power-based heat.
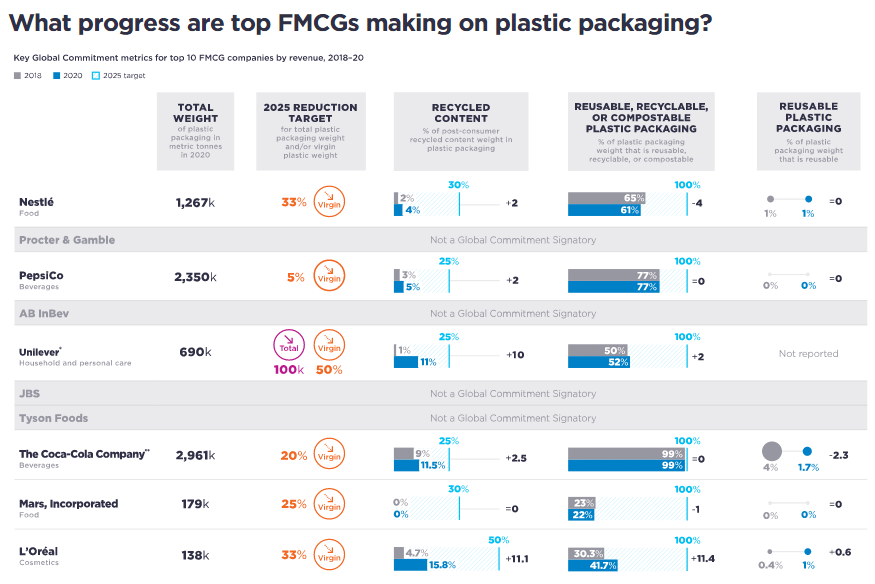
Recycle Availability Still Expected To Be A Headache For Packagers
Nov 16, 2021 1:02:05 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Polymers, Sustainability, PET, Coca-Cola, polymer producers, renewable polymers, chemical recycling, low carbon, PepsiCo, Unilever, zero carbon, recycled polymers, FMCG, recycling goals
The chart below on recycling progress by the major FMCG companies is timely as it bumps into plenty of “national recycling day” headlines which include as many stories around recycling polymers into new applications as stories about like for like recycling. The more polymer that moves through collection and sorting and into roadbeds or composite particleboard replacement, etc., the less there is available for the FMCG companies to meet recycling goals. We see this as a major opportunity for the renewable polymer makers, but it is unlikely that there will be enough renewable-based polymers available to close the 2025 gap for most of the companies listed below. What is likely, in our view, is that the packagers will embrace chemical recycling as a way to increase their recycled content and will strike very specific deals with those able to show a chain of custody from collection through new polymer production.
Pretty Charts Hide Very Complex ESG Problems
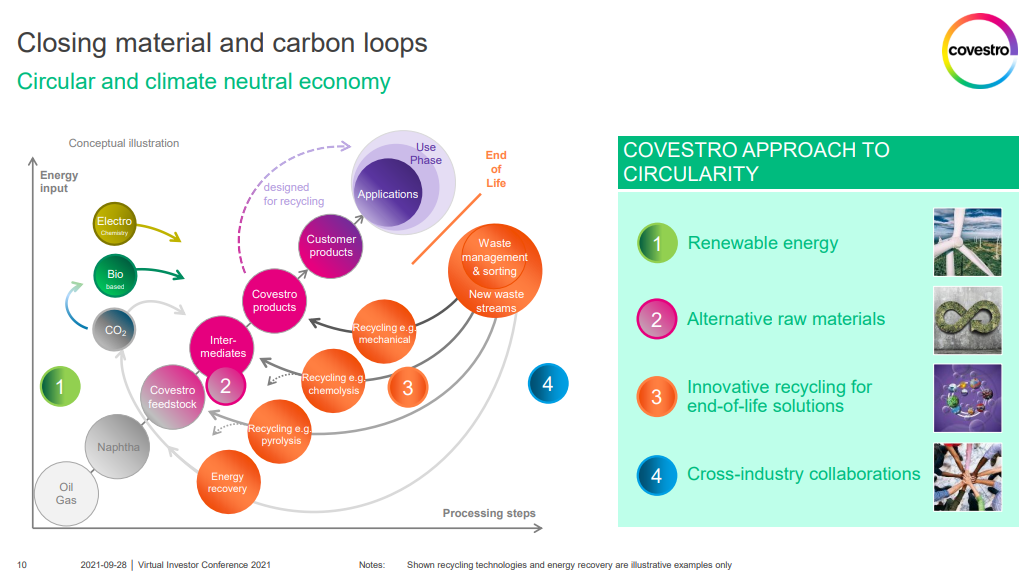
Sep 28, 2021 12:43:15 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Climate Change, Sustainability, Carbon, Emissions, Mechanical Recycling, recycled polymer, Gevo, feedstock, chemical recycling, polymer, biodegradable plastics, Origin, polymer demand, Covestro
Companies are being encouraged/forced to produce climate plans by ever more focused shareholders many of whom only have a passing understanding of how some of the companies operate and how they might best set a course to lower emissions and otherwise be better stewards of the environment. The pretty graphic by Covestro below likely looks much better than the data and ambition behind it really are. This is not necessarily meant as a criticism of Covestro, but the company like many others is being challenged to explain a very complex, process, and engineering-heavy set of options to an audience not really qualified to understand them – pictures with circles are easier.
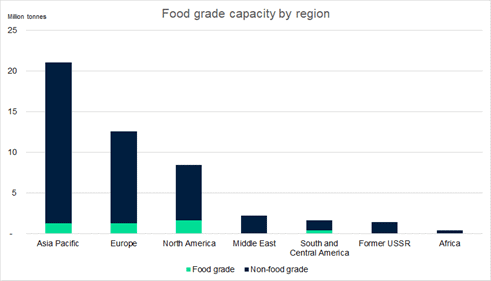
Food Grade Plastic Proving Difficult To Recycle - Pyrolysis Is The Answer
Aug 26, 2021 12:40:00 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Polymers, Climate Change, Plastic Waste, Plastics, Pyrolysis, chemical recycling, reuse, food packagers, food-grade polymer
The exhibit below will come to many as a surprise, and it underlines one of the most significant challenges facing the recycling world. It is the food packagers who want the recycled content, but most food-grade polymer is not easily recycled (mechanically) once it has been in contact with food. Shrink-wrap for example is hard to collect and even harder to clean to a standard that is deemed safe and then hard to regrind because it is thin-film. This is where the polymer industry can really push the benefits of “advanced” chemical recycling as the process can take a mixed and not thoroughly cleaned stream of waste polymers with the recycling process itself (pyrolysis) destroying the contaminants and for the output that gets redirected back to ethylene units an additional shot at 1600-1700 Fahrenheit should remove any fears of contamination. You will not get the pound for pound recycle, but 35% is much better than the numbers suggested in the chart. Plus, in the process, you can destroy and reuse a great deal of plastic waste. See our ACC initiative write-up in yesterday’s ESG and Climate report.
100% Recycling: A Bold But Necessary Ambition For The ACC
Aug 25, 2021 1:33:16 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Polymers, PVC, Plastic Waste, Plastics, chemical recycling, packaging polymers, ACC, plastics packaging, reuse, recycle, recover
The ACC goal of recovering 100% of packaging polymers is bold but likely necessary to show that its members are focused on a full solution, rather than some sort of halfway step. The goal is broken down as follows:
Chemical Recycling Is Good, But So Is Blue Hydrogen
Aug 12, 2021 2:02:17 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Climate Change, Plastics, Methane, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, carbon abatement, natural gas, chemical recycling, NGL, plastics industry, methane emissions, CO2 footprint
We believe that the plastics industry is right to get as much state backing for chemical recycling as it can – see Louisiana headline and diagram below. While chemical recycling is not as neat as mechanical recycling, it has far more chance of dealing with the core issue, which is the disposal of plastic waste – see report linked here. Our support for chemical recycling stems from the view that it will be very hard to get the behavioral change needed to ramp up mechanical recycling quickly and to a level that will impact waste.
Some Recycling Ambitions Expect Too Much Of The Consumer
Jul 23, 2021 12:43:02 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Sustainability, Plastic Waste, Mechanical Recycling, chemical recycling, reusable plastics
The analysis behind the projections in Exhibit 6 in today's daily report, likely makes more assumptions than just the level of reusable plastics. To get the waste reduction projected, there will still need to be a step up in collection, sorting and recycling and it will all need to work to get the results desired. We are still concerned that these “high recycle” plans ask too much of an unwilling public, a slow to move average packager, and underfunded municipalities.
Chemical Recycling: An Easier Plastic Waste Than Recycling Story
Jul 20, 2021 2:23:38 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Polymers, Plastic Waste, Pyrolysis, Mechanical Recycling, feedstock, chemical recycling, Agilyx, advanced recycling
The clear advantage of chemical recycling – as seen in the linked Agilyx headline – is that there are no issues with product cleanliness, etc., to get the material back into the cycle. As the polymers are essentially destroyed in the pyrolysis process and then reused as a feedstock in the traditional polymer production process, the rigors of sorting and cleaning for a mechanical recycling alternative are not needed. From a food contact perspective, chemical recycling is the easiest way to close the loop. What we are seeing in the headlines, however, is still “proof of concept” stuff and there remain plenty of challenges with logistics and/or proof of custody with the feedstocks that are flowing back to the ethylene unit, as well as how much recycling credit is appropriate, given that roughly half of the recycled feedstock does not end up as a polymer.