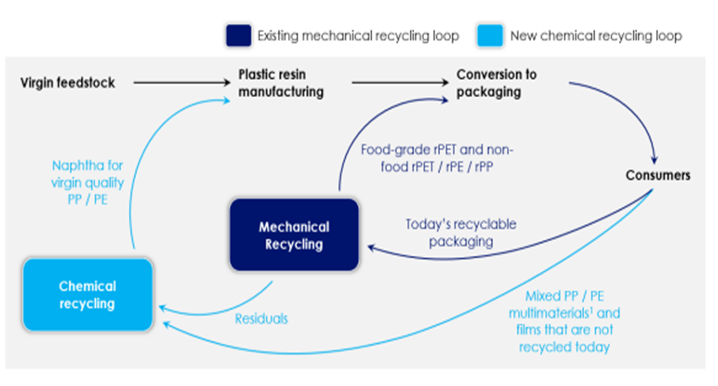
In the first picture below we see another schematic that shows how different options for polymer recycling could work together. We have suggested a more complex site than the one in the chart as there will be opportunities to recycle some polymers into non-like-for-like applications such as roadbed modification and other durable applications. In addition, there may be a better return in waste to energy versus chemical recycling and that may be an alternative or an add-on. This sort of complex site is what we believe LyondellBasell could be looking at for the Houston refinery site. An integrated waste treatment facility that optimizes that use for each tranche of the waste stream could improve the overall investment returns. In the second picture below we show our version of what a comprehensive waste recycling operation should look like. See more on recycling!
Managing Waste To Maximize Value Requires Multiple Processes
May 4, 2022 2:15:03 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Climate Change, Sustainability, LyondellBasell, chemical recycling, waste, polymer recycling, waste recycling
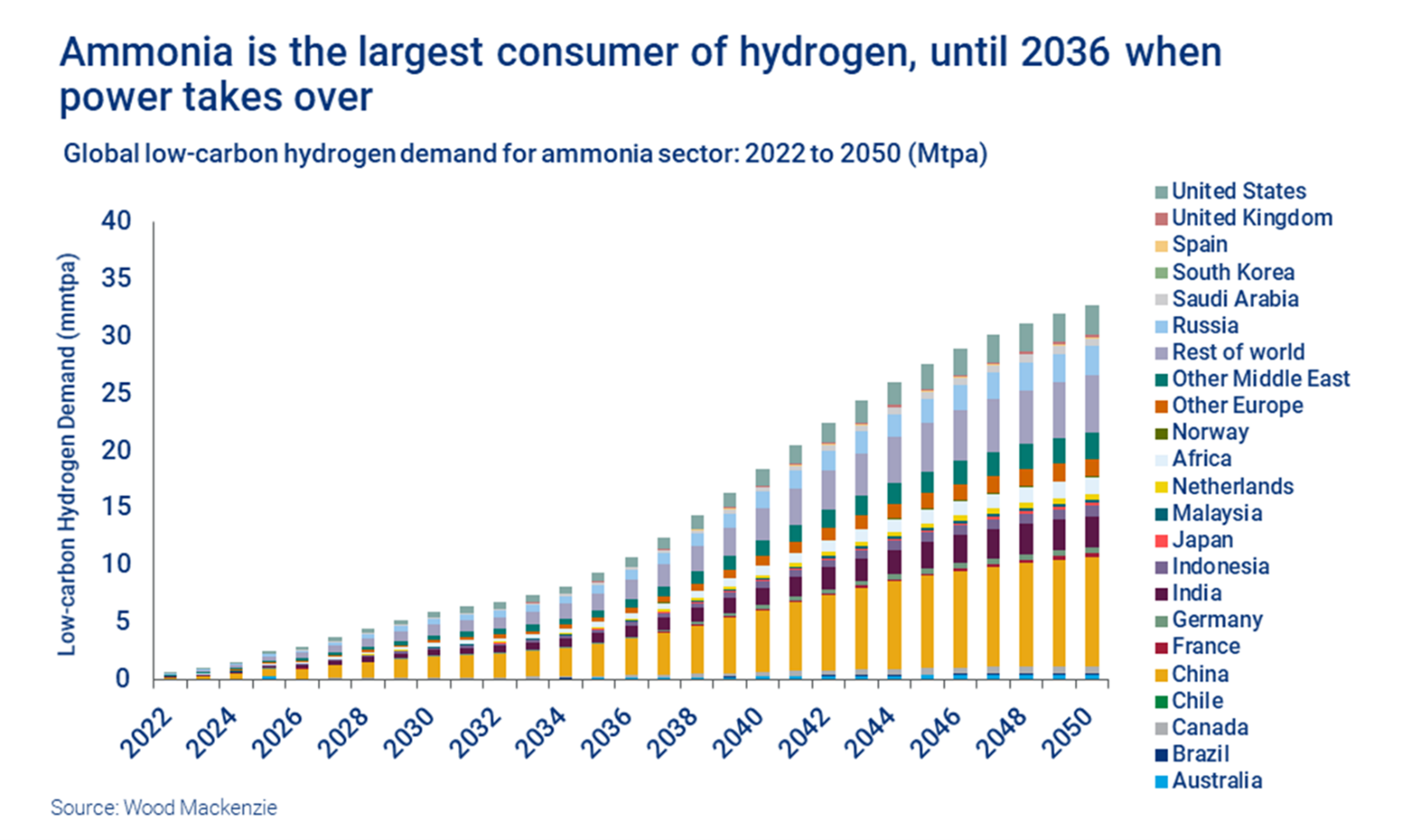
Hydrogen Is Likely Not Happening Fast Enough For The IPCC
Apr 6, 2022 12:36:34 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, LNG, Green Hydrogen, Renewable Power, Ammonia, hydrocarbons, solar, renewable energy, renewables, wind, energy transition, waste, hydro, geothermal
One of the concerns that the IPCC has in its report issued this week is that things are not happening fast enough and the Ammonia analysis in the chart below would support this view. Most of the capacity addition comes post-2030 in large part because project planners cannot see a way to enough cheap power to generate the green hydrogen needed until that time. In our view, since COP26 the transition part of the energy transition has been overwhelmed by advocates of green technology and renewable pathways without much thought about how practical they might be today. Those suggesting transition options are being given very little airtime and as a consequence, we see broad hostility towards anything that is not truly green, regardless of whether the costs or time frames make any real sense. If we do not embrace bold transitionary steps including the use of hydrocarbons with aggressive abatement targets we will not meet any of the shorter-term goals that the IPCC highlights and we are putting hope in renewable and technology development which may come up short. Related to this we see the LNG dilemma in Europe, with the current and medium-term needs very apparent, but a reluctance to sign up for longer-term supply because of an expectation that if all things renewable come to pass, the LNG might not be needed. The Europeans will need to make the longer-term commitment if they are to persuade the US and other potential exporters to build new export terminals.
Polymer Producers Have Waste And Carbon Footprints To Consider
Feb 9, 2022 12:25:43 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Recycling, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, decarbonization, hydrocarbons, polymer producers, climate, chemical producers, Covestro, waste, carbon footprints, fossil fuels
The linked Covestro headline from today's ESG & Climate report is a reminder that the chemicals and polymer makers are dealing with more than just recycling and product lifecycle management. Customers are equally focused on the carbon footprint of the products they buy and the green hydrogen move by Covestro (assuming that affordable green hydrogen is possible) would replace hydrogen made from fossil fuels and replace other fuels for heat in some cases. Germany has some considerable issues with decarbonizing, as the blue hydrogen route will be challenging in a country that will likely not allow onshore CCS. Covestro and others may have little choice but to buy green hydrogen and/or green power, even if supplies come up short of plan and costs are higher as a result. This is a good illustration of why we believe that the right policies in the US could drive some additional competitive edge while meeting climate objectives. Cheap hydrocarbons coupled with cheap CCS may only be matched in some parts of the Middle East.
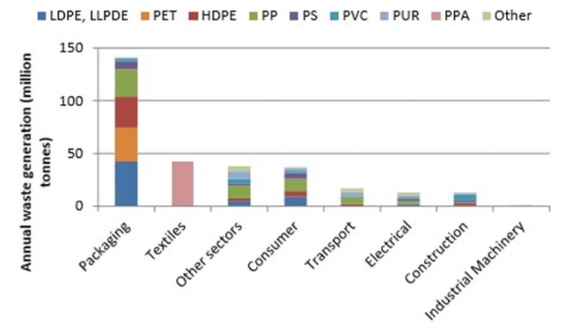
Packaging Waste Disposal May Not Mean Packaging Waste Recycled
Dec 17, 2021 1:59:37 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Sustainability, Pyrolysis, packaging, chemical recycling, renewables, climate, waste, carbon footprints, polymer recycling, waste disposal, recycled waste
We have spent a lot of time over the last few weeks talking about polymer recycling and renewables and the chart below is another look at where plastic waste is coming from. Packaging is the big piece and it is also the area where customers, i.e. the packagers, are looking for the largest increase in the use of recycled materials quickly. As we noted in our ESG and Climate piece this week, increasing volumes of this packaging waste is moving into different use applications, such as building products and durables, and even more could potentially flow into chemical recycling – note that there are 7 headlines on chemical/advanced recycling in today's daily report. The packagers have little chance of meeting their near-term recycling content goals in our opinion, but they have zero chance if they do not accept chemical recycling as part of the mix. It will be important to accurately audit the chain of custody of chemical recycling to avoid double counting. The separate challenge with chemical recycling is the now increased focus on carbon footprints, as the pyrolysis process is energy-intensive, whether direct heat from burning fossil fuel or electric power-based heat.
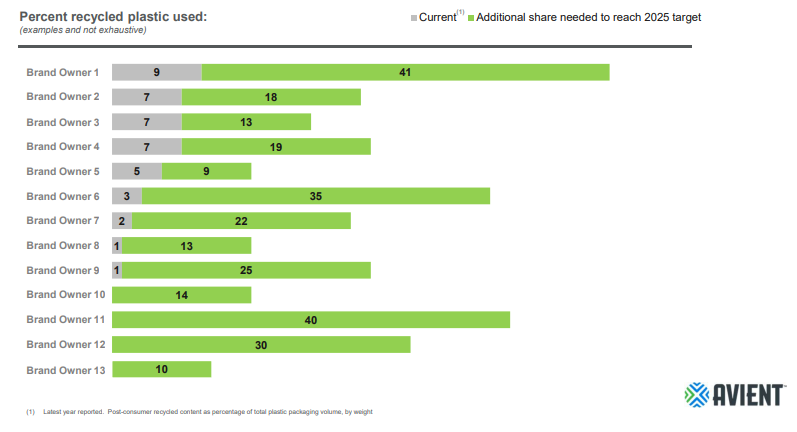
Challenging Recycle Targets Suggest High Prices & Opportunities For Renewables
Oct 28, 2021 1:57:50 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Sustainability, PET, polymer producers, renewable polymers, renewables, climate, recycled PET, virgin material, bio-polymers, waste, recycled material
The Avient chart around where brand owners sit with recycled content versus 2025 goals is quite scary. There are not enough initiatives collectively to address the needs, as the demand extends beyond the 13 brand owners listed. In our ESG and climate report yesterday we talked about the challenges with recycled PET and the complicating factor around recycled material heading into different applications, and consequently not being available to bottlers. We also have the issue of PET bottle pre-form capacity being overweight in Asia versus PET bottle demand and waste – setting up an imbalance between where the waste is and where the recycled material is needed. The gaps in the Avient chart and the slow and challenging recycling progress lead to a couple of conclusions. The first is that recycled material is likely going to rise in value versus virgin material – simply because of competition and the PR, IR, Social cost of not meeting targets for many brand owners. The second conclusion is that the renewably sourced polymer producers have a huge potential opportunity to step in and fill the gap. The challenge will be the ability to have enough capacity up and running to meet demand in 2025.