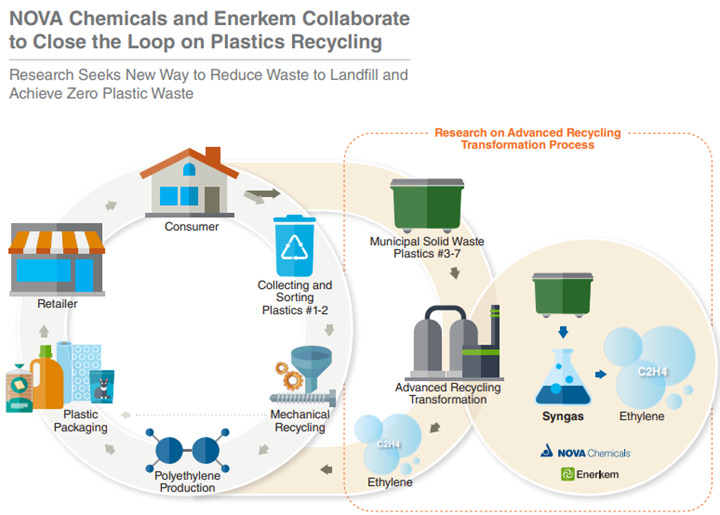
As we look at the news flow on recycling, we see many initiatives to collect, sort, and reuse polymers, whether for like-for-like applications, pyrolysis, or energy. What we do not see enough of, in our view, are initiatives to increase the pool of recycled plastics through packaging standardization or the elimination of compounds or colors that make recycling more challenging. Recycling can be improved by better collection and sorting methodologies and technologies. Still, the rate-limiting step will eventually be the pool of materials fit for recycling, and this is particularly important for like-for-like mechanical recycling. The ironic piece here is that the consumer staples and beverage companies call for higher recycled content and are primarily responsible for the amount of recyclable material in the market. If the packagers were to focus on sustainability rather than the unique look and feel of their packaging, we would see a material change in the volumes of recyclable polymers. This might come at the expense of some of the compounders, especially those with an extensive packaging component to their customer base, but it might also impact specific polymers and we would highlight polystyrene as a particularly vulnerable material as almost any application for which polystyrene is used today could be replaced with PET, polyethylene and/or polyethylene – all of which are larger volume polymers that are easier to recycle. The polystyrene industry is doing a good job of promoting recycling initiatives, but this may not be enough.
More Standardization In Packaging Is Needed To Boost Recycling
Apr 14, 2022 3:59:49 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Climate Change, Sustainability, packaging, standardization
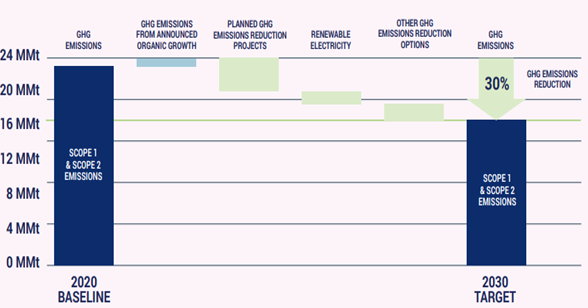
Many Of The 2030 Climate Targets Will Not Come Much Before 2030
Apr 13, 2022 3:14:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Emissions, ExxonMobil, LyondellBasell, Dow, carbon abatement, renewable fuels
Given the lead time to get some of the emission abatement projects in place – whether it be renewable power or hydrogen with carbon capture – many of the 2030 goals that we see, like the LyondellBasell chart below – are likely to be just that – plans for 2030, with not much in the years in between. We see very little CCS coming online in the US over the next 5 years because of permitting and because of the lead time for any large hydrogen or power project that might be associated with the CCS. Not too many companies seem interested in cleaning up existing CO2 streams and are more interested in building alternative capacity that generates easier to capture CO2 – such as hydrogen from an ATR. These are expensive and long lead-time projects. LyondellBasell, ExxonMobil, Dow, and others might meet their 2030 targets but it might all happen in 2029/30.
Green Hydrogen Ambitions Too Aggressive: CCS Is The Answer
Apr 8, 2022 1:04:23 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Renewable Power, renewable energy
The two charts below today are interesting bedfellows as while one talks about yet more, likely impractical, hydrogen ambitions, the other talks about a possible solution.
A Plastics Tax In The UK That Very Few Will Be Able To Avoid
Apr 7, 2022 12:39:13 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Climate Change, Sustainability, Plastics, plastic tax, recycled resin
Our recent work on recycling - Recycling: Beware Of The Misleading PR – would suggest that the UK treasury will raise quite a bit of money from the plastics tax. We see very little chance of most packaging meeting a 30% recycled content goal any time soon, and possibly ever. We could see an odd dynamic where UK packagers import recycled resin from the EU to meet the minimums. This would then be at odds with EU recycled content goals and would need the EU to do something similar on the tax front to avoid the trade. The EU has a plastic tax in the works and its net effect will be similar to the one in the UK – any trade arbitrage for recycled resin would not likely last long.
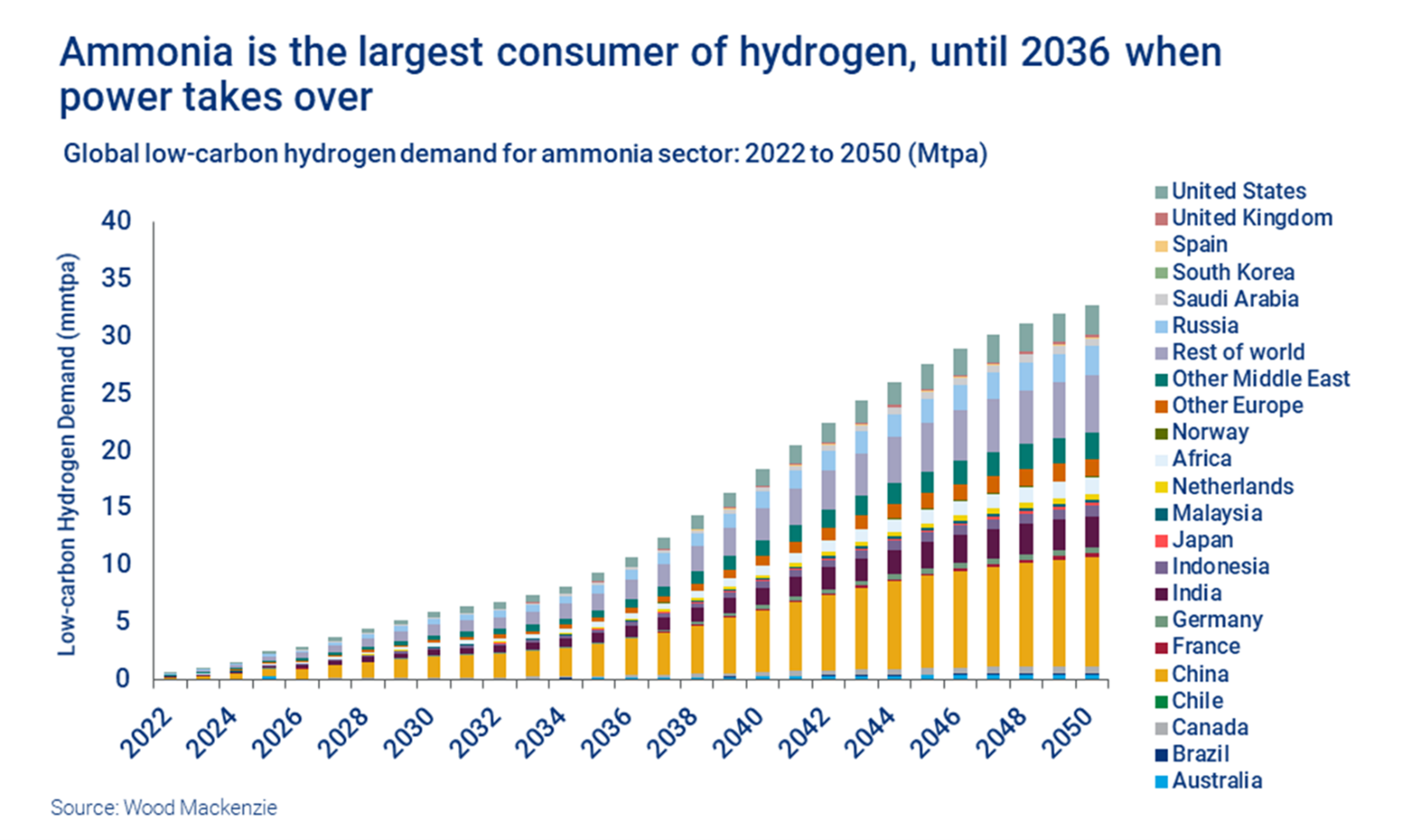
Hydrogen Is Likely Not Happening Fast Enough For The IPCC
Apr 6, 2022 12:36:34 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, LNG, Green Hydrogen, Renewable Power, Ammonia, hydrocarbons, solar, renewable energy, renewables, wind, energy transition, waste, hydro, geothermal
One of the concerns that the IPCC has in its report issued this week is that things are not happening fast enough and the Ammonia analysis in the chart below would support this view. Most of the capacity addition comes post-2030 in large part because project planners cannot see a way to enough cheap power to generate the green hydrogen needed until that time. In our view, since COP26 the transition part of the energy transition has been overwhelmed by advocates of green technology and renewable pathways without much thought about how practical they might be today. Those suggesting transition options are being given very little airtime and as a consequence, we see broad hostility towards anything that is not truly green, regardless of whether the costs or time frames make any real sense. If we do not embrace bold transitionary steps including the use of hydrocarbons with aggressive abatement targets we will not meet any of the shorter-term goals that the IPCC highlights and we are putting hope in renewable and technology development which may come up short. Related to this we see the LNG dilemma in Europe, with the current and medium-term needs very apparent, but a reluctance to sign up for longer-term supply because of an expectation that if all things renewable come to pass, the LNG might not be needed. The Europeans will need to make the longer-term commitment if they are to persuade the US and other potential exporters to build new export terminals.
Carbon Prices Rising, Wind & Solar Costs Also
Apr 5, 2022 12:32:08 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, CO2, Energy, Net-Zero, carbon abatement, solar, renewable energy, wind, carbon prices
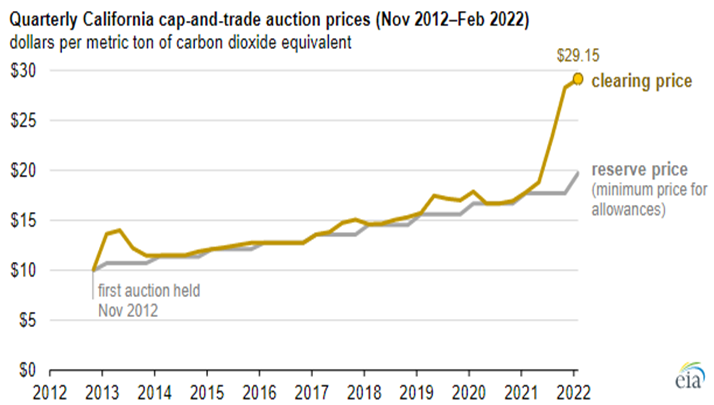
We have written extensively about carbon prices over the last two years and followers of our dedicated ESG and Climate service will know that our expectation is for all CO2 markets to see prices rise to levels that justify large investments to avoid CO2 production or sequester it. We see that price closer to $100 per ton than the $50 per ton that 45Q will rise to by 2026. The California price shown below has much more upside as credits demand rises. Many of the net-zero pledges made by manufacturers and energy producers today cannot be achieved without buying some sort of credit and we expect demand to rise relative to supply through the balance of the decade and possibly quite quickly.
The Cost Of Reshoring May Push Energy Transition Investments Offshore
Apr 1, 2022 3:29:55 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, Sustainability, LNG, Energy, Dow, energy transition, Canada, Mexico, reshoring, Sempra
Looking at the Sempra chart below, we reflect on some research that we wrote several months ago that talked about a lost opportunity in the US because of the lack of cooperation and coordination in Washington. Energy demand is growing, the demand for materials is growing and the demand for re-shoring is growing, and if the US political and permitting system is either too hostile towards new investment or too cumbersome companies will look for workarounds. The Dow investment in Canada was partly justified by the easier regulatory environment as well as the proposed carbon price. Sempra is looking at Mexico because the ease of permitting for LNG is advantageous and we note Mattel's “near-shoring” in Mexico rather than reshoring. The opportunities for both Mexico and Canada are very significant if we remain mostly directionless in the US. For more see today's daily report.
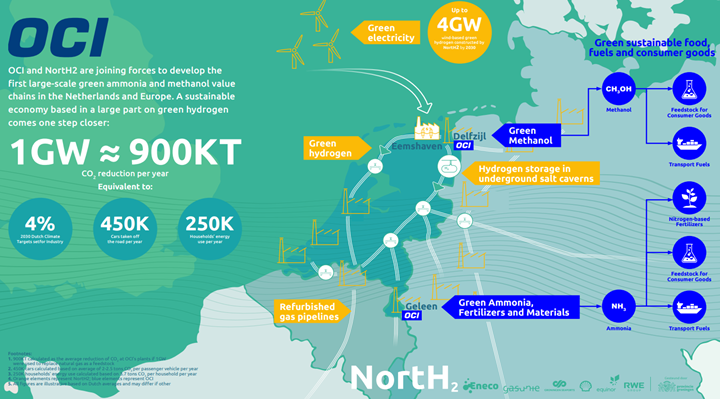
Strong Challenge In Canada And Collaboration In Germany
Mar 31, 2022 2:27:55 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Renewable Power, Emissions, BASF, renewables, EV, materials, Shortage, Canada, renewable, materials costs, Germany, Henkel, GHG
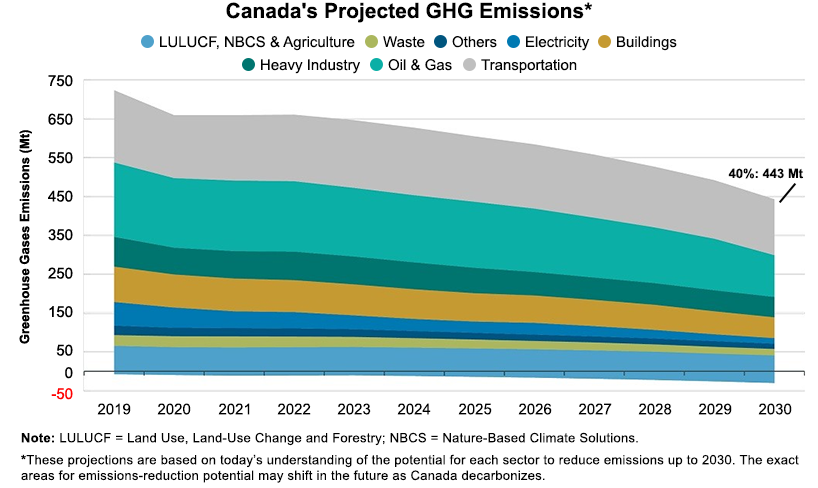
The Canadian targets highlighted below are ambitious and will likely not happen without the significant CCS projects planned for Alberta. The CCS opportunity will drive down energy and chemical (heavy industry) based emissions meaningfully and could also be the basis for new power generation capacity to allow the transport industry reductions that the country is looking for – either through EVs or hydrogen-based transport.
It's Not Just Packaging That Needs To Be Recycled
Mar 30, 2022 11:55:43 AM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Polymers, Climate Change, Sustainability, Plastic Waste, Plastics, Emissions, packaging, durables, carbon footprint, polymer, recycle, materials, Building Products, construction, life cycle, greenfield, building industry, recycled materials
We tend to focus on recycling conventional plastic waste, but there are growing initiatives to look at the longer life cycle of durables and while this has mostly been focused on the automotive space, it is interesting to see the building industry looking at building life cycles. Many of the alternative use mechanical recycling initiatives are directed toward substituting building products such as concrete and wood and while this will help the construction sustainability story, the end of life cycle issue is less clear. The majority of commercial real-estate emissions are associated with operations (around 70%) and this is the greater focus for owners today, but the life cycle question is increasingly important for building tenants. In the UK for example there are redevelopment projects proactively advertising how much of the original building will be retained – i.e. not demolished and landfilled. Ultimately this might lead to lower demand for commercial building products where developers are looking at existing buildings, but it will not impact new greenfield builds unless you get a steep increase in recycled polymer use. The offset would likely be concrete as this is the high carbon footprint material that most are targeting. See more in today's ESG and Climate Report.
Is Your Recycling Really Green?
Mar 29, 2022 2:19:24 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Recycling, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, Emissions, Pyrolysis, carbon footprint, Offshore CCS, gasification
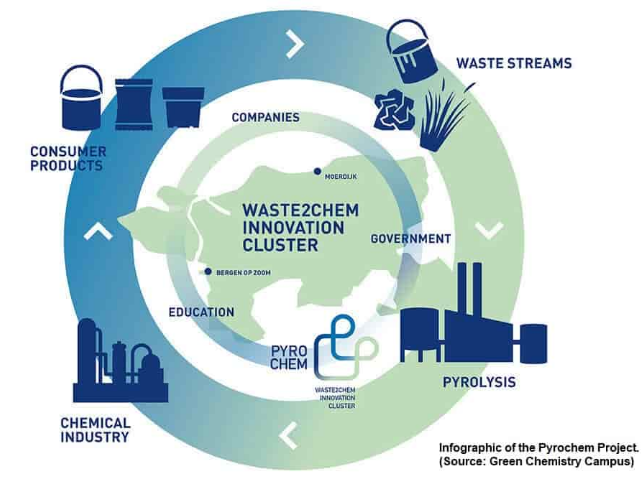
The focus of our ESG and Climate report tomorrow will be on recycling and the challenges associated with each proposed solution. The piece that most chemical recycling projects, like the one highlighted below, fail to mention is that the heat required for pyrolysis is significant, and the carbon footprint is very high unless you can heat through renewable power or you can capture the carbon associated with the heat. Given the location of the facility shown below, it could have access to offshore wind-based power and/or could tie into one of the offshore CCS projects that have been proposed. Both pyrolysis and gasification processes have very high emissions.