Last week, and in our dedicated ESG and climate report this week, we talked about the challenges of shipping hydrogen, and the linked bp project for Western Australia will have the same problem to solve – choosing ammonia according to the announcement over the very inefficient toluene/cyclohexane option we discussed last week. The appeal of Western Australia is the unpopulated available land that has little alternative use and sees abundant sunshine. The bp project assumes that the facility can buy attractively priced renewable power from third parties, but the company must have a specific power project in mind for the bulk of the electricity needed. The stumbling block here will likely be when the power project(s) bid out the solar module contract, find out that the suppliers are sold out and are asking higher prices to cover reinvestment and higher material prices, and then have to go back to bp with a much higher than expected cost of power. The advantage of solar and wind projects is that inflation only impacts upfront capital costs, which can be amortized over the life of the project – feedstocks are free! That said, most of the announced projects have declining capital costs per megawatt in their planning assumptions today.
Green Hydrogen: Not So Good If Power Prices Do Not Come Down
Sep 3, 2021 1:14:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Methanol, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Ammonia, bp, feedstock, carbon dioxide, solar, wind, electrolysis
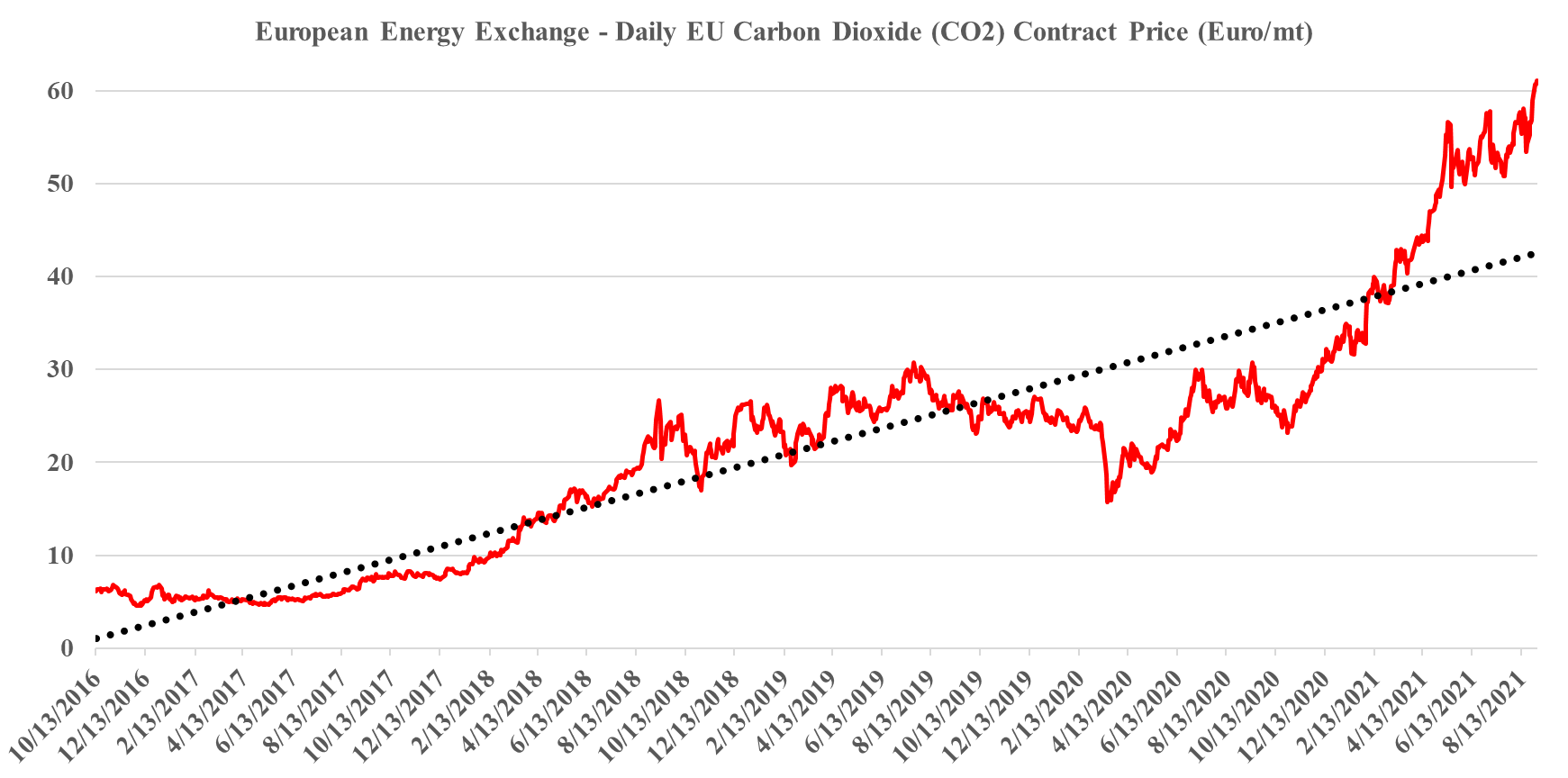
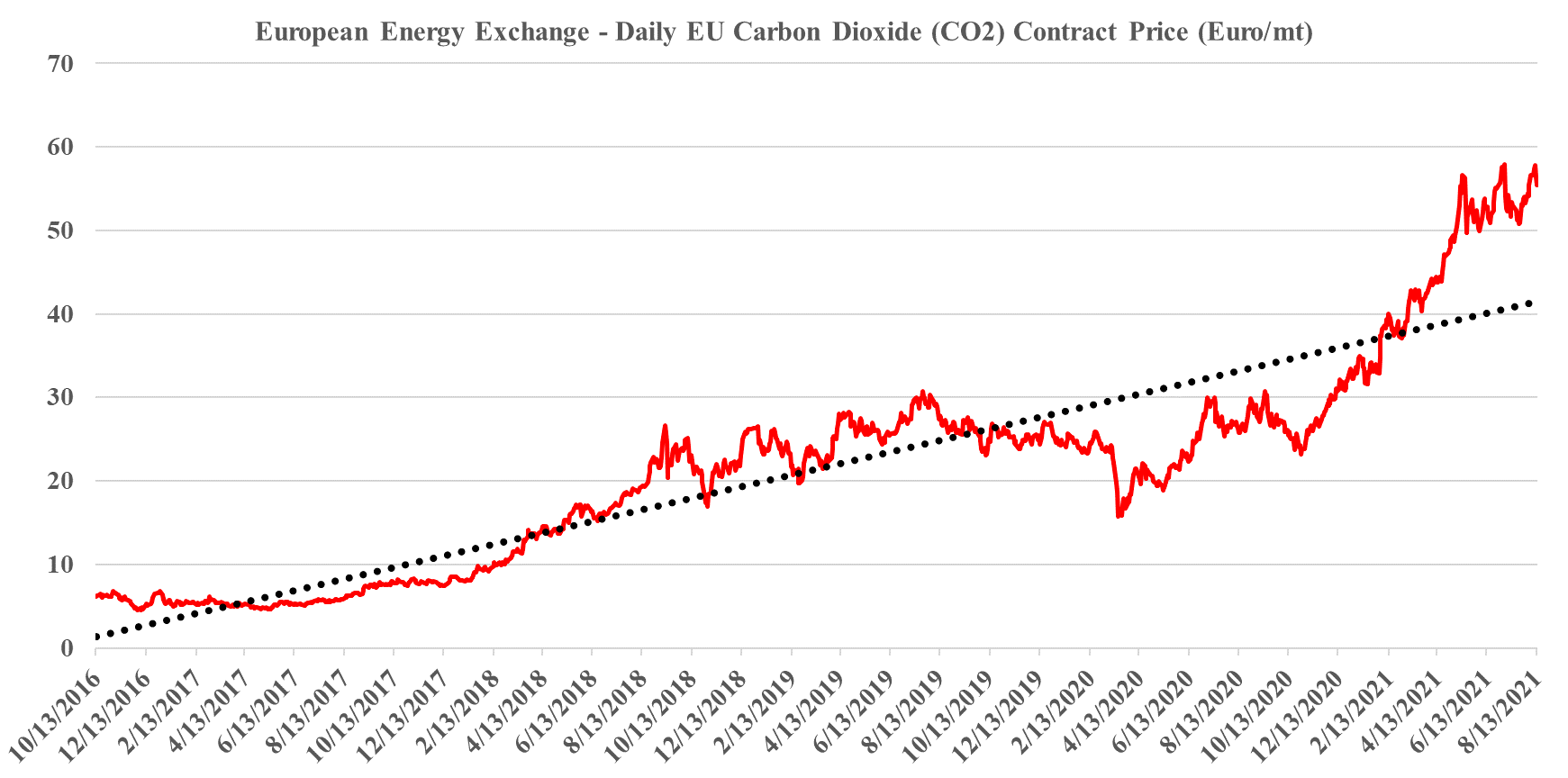
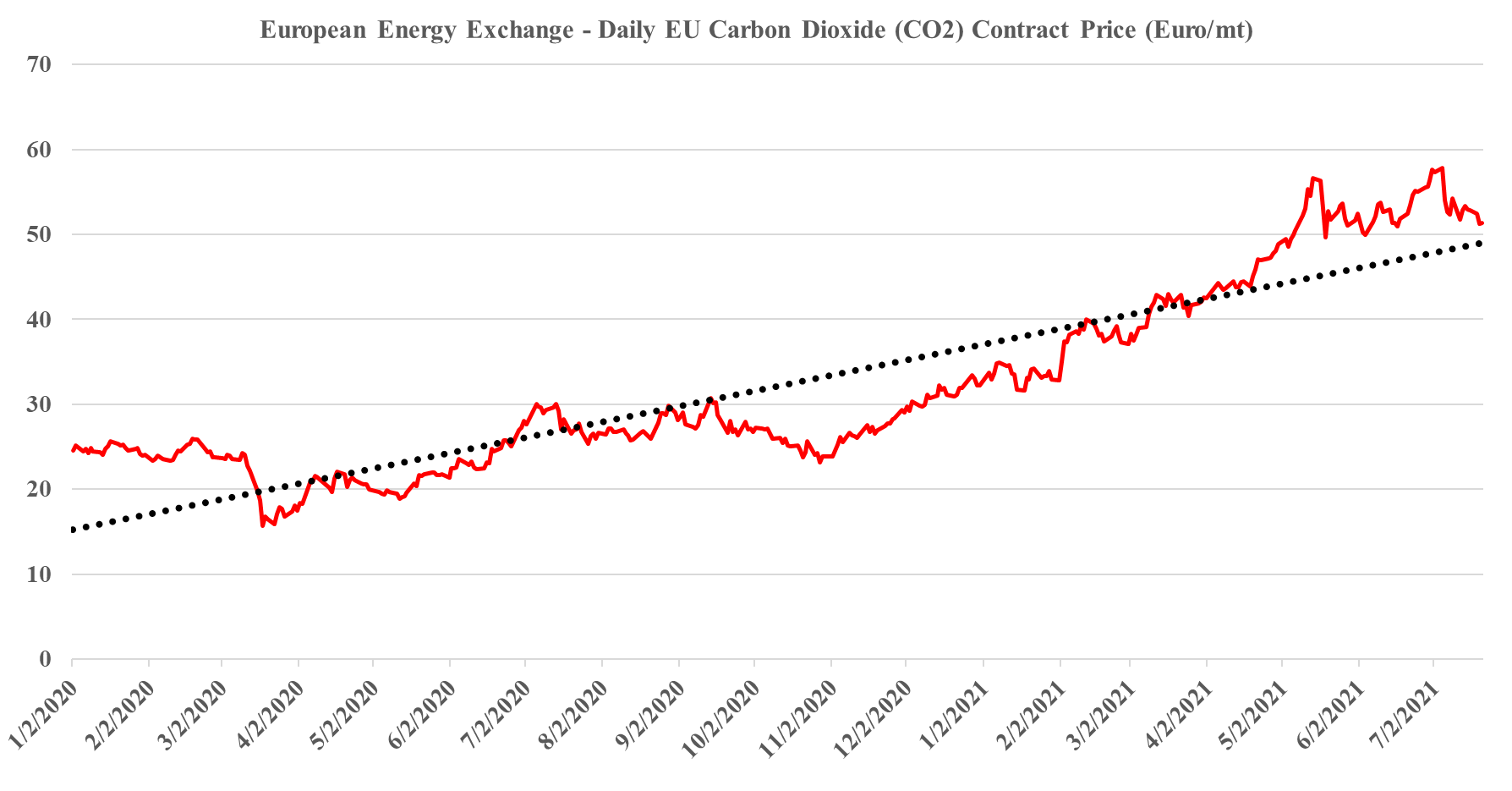
Europe's Record Carbon Prices: Not High Enough Yet
Sep 1, 2021 12:54:34 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, CCS, Carbon Price, ESG Investing, carbon dioxide, carbon value, carbon abatement, renewable power investments
We have maintained all year that the strength in the European carbon price is sustainable and that it should go even higher and consequently, we are not surprised by this week’s move, even if much of the impetus is speculation. The European price is still not high enough to justify unsubsidized CCS or widespread renewable power investments to replace carbon-heavy energy sources, especially as renewable power costs rise. We estimate that a price in the €85-100 per metric ton range would be needed to stimulate investment, but because of the structure of the European market prices could overshoot this level meaningfully and be quite volatile until the level of abatement spending accelerates. When we start seeing investments in Europe to lower carbon that are not highly subsidized by local governments (in addition to the incentive of the carbon price) we will have a better guide around where 45Q needs to go in the US (or other mechanisms) to get investments rolling. Our analysis suggests that the US has some lower-cost abatement opportunities than Europe, especially on the CCS front, but not by much. For more on carbon costs and prices see today's ESG & Climate report.
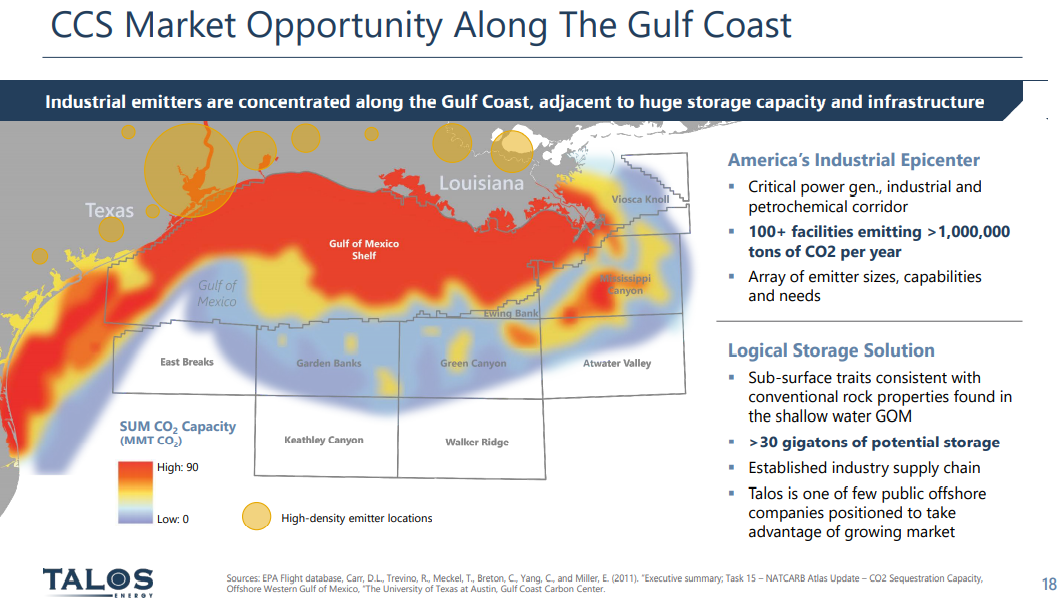
Offshore CCS Is Good: But Onshore CCS Should Be Cheaper
Aug 27, 2021 12:49:53 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, CO2, Sequestration, carbon abatement, Offshore CCS, Talos, Onshore CCS
The Talos release and the map shown in the Exhibit below, highlight some of the potential for offshore CCS along the US Gulf Coast. We will likely see some of this developed over time, in our view, but the question of cost is important, not because the US Gulf is likely to be more expensive than some of the offshore locations that are proposed for Europe, but because the same offshore geology on the US Gulf exists onshore, and the onshore opportunities will likely be much lower cost. Given that one of the overriding concerns around carbon abatement is cost and how it will be paid for, who will pay for it ultimately, and what it means for the competitive landscape, finding the lowest cost solutions will be key. This is something that we have covered at length in our dedicated ESG and climate research. Building high-pressure pipelines is expensive, and high relative to the onshore cost of sequestration. Talos might find interest from CO2 suppliers but may be undercut by onshore projects – assuming these get the green light from regulators – not giving them the green light would likely be imposing further unnecessary costs on industry.
Everyone Wants A Hydrogen Project: Some Strategies Less Risky Than Others
Aug 18, 2021 12:20:35 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Renewable Power, Emissions, Ammonia, natural gas, Neom
It is hard to ignore the number of headlines on hydrogen initiatives, today, highlighted in our ESG and climate report, as well as the acceleration in project announcements over the last several months. In the 80s in the UK, it was trendy to drive a VW Golf GTI – everyone had to have one – hydrogen has the same feel today – everyone has to have a project. The projects vary and fall into a handful of categories:
Will The Climate Frenzy Leave Plastic Waste Ignored For Now?
Aug 13, 2021 11:46:37 AM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Climate Change, Plastic Waste, Plastics, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Carbon Price, carbon abatement, climate, IPCC, Plastics producers, COP26, virgin plastic, plastic tax
As we sift through the positioning for the upcoming COP26 meeting and the attention focusing report from the IPCC this week, it is a reasonable question to ask what this means for the plastic waste issue. If governments, lobbyists, and activists are likely to be more focused on climate change action over the next few years, which seems to be a reasonable conclusion, will there be the bandwidth for plastic waste? The plastic waste issue is less open to interpretation than the climate change issue and is a visible problem for all, but if governments need to prioritize where they spend their incremental dollar, and/or where they provide incentives of penalties, the climate is going to be pushed to the front of the line in our view. Plastics producers will have to deal with emissions, like any other industrial user of power and heat. The risk is that local governments, looking for revenue to support climate initiatives see taxing virgin plastic (or unrecycled plastic) as a way to both push plastic waste initiatives forward and raise revenue. Adding a plastic tax in the US to the superfund proposal in the infrastructure bill would be hitting the chemicals industry from two sides and would give bodies like the ACC far more grounds for pushback. For more on the IPCC analysis see our ESG & Climate Change report from this week.
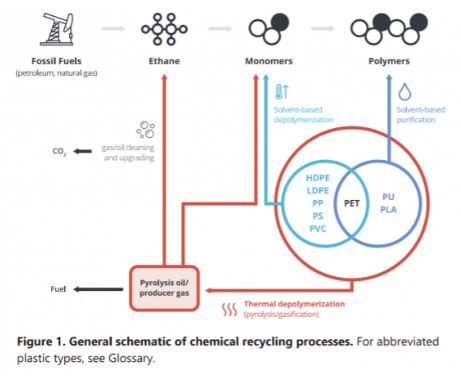
Chemical Recycling Is Good, But So Is Blue Hydrogen
Aug 12, 2021 2:02:17 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Climate Change, Plastics, Methane, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, CO2, carbon abatement, natural gas, chemical recycling, NGL, plastics industry, methane emissions, CO2 footprint
We believe that the plastics industry is right to get as much state backing for chemical recycling as it can – see Louisiana headline and diagram below. While chemical recycling is not as neat as mechanical recycling, it has far more chance of dealing with the core issue, which is the disposal of plastic waste – see report linked here. Our support for chemical recycling stems from the view that it will be very hard to get the behavioral change needed to ramp up mechanical recycling quickly and to a level that will impact waste.
Carbon Capture: Front and Center & Enabling Hydrogen Growth
Aug 5, 2021 1:17:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Carbon Capture, Polymers, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Emissions, Emission Goals, natural gas, carbon emissions, CBAM, NGLs, gray hydrogen
The primary reason for the flurry of carbon capture related headlines in the US over the last few weeks – and our analysis shows a significant step up – is because it looks like this will be the one technology/route to lower carbon emissions that will get a real boost from the infrastructure bill. There is bipartisan support for CCS because the fossil fuel industry sees it as a way to stay in the game and the unions believe that it will create jobs. This combination should garner enough votes to push it into the bill and get it passed, although the details around how CCS would be supported remain unclear. The infrastructure bill has very few real sources of income in it to offset the very high costs – something we will discuss on Sunday – and consequently giving a bigger tax break, through the 45Q program would create an even larger funding gap than we have today. The value/cost dynamic has to rise to get the activity that everyone is looking for and maybe that could be achieved by overlaying a carbon credit onto the program. Anyone exporting to Europe and concerned about the CBAM extending to natural gas, NGLs, chemicals, and polymers would likely consider CCS if they were eligible for 45Q and could also claim an offset on their exported products to neutralize the CBAM tax/fee.
Carbon Offsets: Direct Air Capture Is Not The Only Option
Jul 28, 2021 12:55:50 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, carbon abatement, carbon values, carbon offsets, direct air capture, methane emission, DAC
There has been a lot of press over the last couple of months around carbon offsets – not least because of Mark Carney’s efforts to legitimize the idea. Mr. Carney’s focus is to create a robust trading platform for the buying and selling of legitimate offsets so that a carbon market can operate efficiently. He believes that without accurate and realistic carbon values, and the ability to buy and sell them, the capital markets around emission reduction will be inefficient and that less money will be attracted into the area. On this, he is probably correct, but in our view, the carbon offset markets have a long way to go.
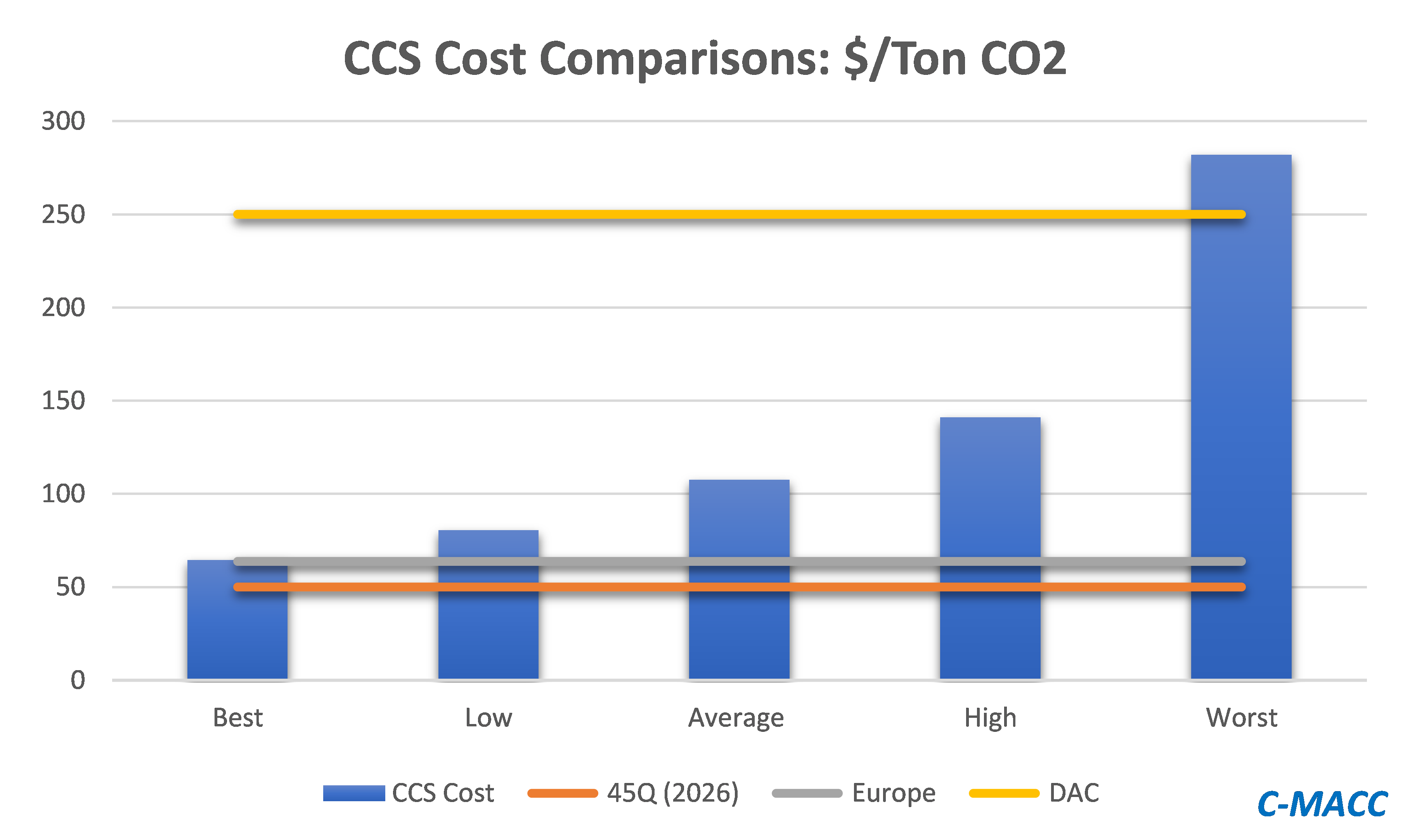
Carbon Capture (If Supported) Will Create Competitive Dislocations
Jul 21, 2021 1:08:19 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, CO2, fossil fuel, carbon footprint, carbon abatement, renewables, European Carbon price, climate
In our ESG and climate piece today we focus on Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) and the likely very steep cost curve between the mega projects and those less fortunate. But as we discuss CCS, we should not forget that the World is still not convinced about CCS as part of the solution set for carbon abatement, as the headline linked discusses. The naysayers are focused on the lifeline that CCS offers to the fossil fuel industry, but always fail to offer an economic rationale for the quick elimination of fossil fuels and their replacement by renewables. Few of the proponents of CCS see it as an alternative to a long term path to alternative means of abatement, but all recognize that relying on renewable power investments will likely leave the World with a much larger CO2 footprint from 2030 to 2050 than what could be achievable with CCS – note that the 45Q incentive in the US has a finite lifespan as there is an expectation that eventually CCS will be unnecessary because of fossil fuel replacement. Chevron has not helped the CCS proponents with its missed targets in Australia as it adds fuel to the argument that CCS has not lived up to its potential. While the European carbon price trend has stalled in recent weeks – chart below – the trend remains distinct and it would be foolhardy to ignore the likelihood of prices rising to a level that makes CCS attractive – especially for the mega-projects.
Carbon Abatement – A Multi-client Analysis
Jul 7, 2021 1:01:06 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Carbon Tax, Carbon Fuels, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Carbon, Carbon Neutral, Emission Goals, Net-Zero, decarbonization, carbon footprint, ESG Fund, carbon dioxide, carbon credit, carbon value, carbon abatement, power, carbon cost, carbon offset, offsets, ESG investment, carbon emissions, clean energy, climate
A major initiative by C-MACC in collaboration with the Power Research Group