ExxonMobil is seriously upping its lower-carbon game with the CCS announcements over the last few weeks and the release this week that states the company will spend $15 billion over the next 6 years on lower carbon initiatives. In this linked headline ExxonMobil states that it will meet its 2025 emission goals this year – we are assuming that this must be correct as the company would not want to risk the accusation of greenwashing. Either way, the critics will weigh in, either claiming “greenwashing” or suggesting that the targets were not high enough, to begin with. The ExxonMobil focus is very much on CCS, which makes sense for an oil and gas-centric company whose only real play right now is to lower the carbon footprint of its fuel portfolio. In the release linked above, ExxonMobil also talks about biofuel and hydrogen initiatives, but again calls for supportive policies from governments and we suspect that the underlying push here is towards the US government. ExxonMobil and others have indicated that $100 per ton is the right incentive to drive CCS and other carbon abatement strategies and we would agree with this estimate as it backs up much of the work that we have done over the last year. See - Carbon: Trading, Offsets, and CCS as a Service – It’s All Coming! and - Carbon Games – Appetite, But Not Enough Hunger Yet. The other reason why ExxonMobil and others would like to see the US act is because other jurisdictions in which they operate will likely take a lead from the US.
ExxonMobil: Going Heavy On CCS (The Right Move), But Pushing For Support
Nov 12, 2021 2:07:37 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, CCS, Carbon, Emissions, ExxonMobil, Emission Goals, carbon footprint, carbon abatement, biofuel, carbon offsets, carbon trading, greenwashing
Global Hydrogen Ambitions Will Fail Without CCS: The US Needs A Plan
Nov 11, 2021 1:36:40 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Renewable Power, Energy, Emissions, CCUS
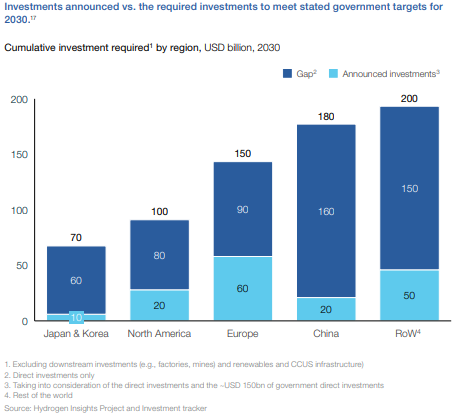
The hydrogen council chart below drags us away from 2050 and back to the more concerning near-term goals of 2030. The chart shows a significant gap in the current planned spend for hydrogen by region and the spending required to move far enough towards 2050 targets. This chart makes assumptions about the share of energy transition that will be met by hydrogen and given that it is the industry producing the chart, it is probably on the high side, but it is inclusive of both blue and green hydrogen. We have serious concerns about these totals being reached in general, but we see the target as completely unreachable without significant blue hydrogen (because of renewable power and electrolyzer capacity limits and we cannot rely on Canada to do all of the “heavy lifting” for blue hydrogen - see company section in today's daily report. The Biden administration may make more progress on emissions if the next order of business was just on CCUS rather than an omnibus bill that included CCUS but which could get held up in negotiations for months if it even gets passed.
Agriculture, A Big Part To Play In Emission Abatement
Nov 10, 2021 2:06:41 PM / by Graham Copley posted in CO2, Emissions, carbon footprint, offsets, fertilizer, renewable natural gas, Agriculture, Emission abatement
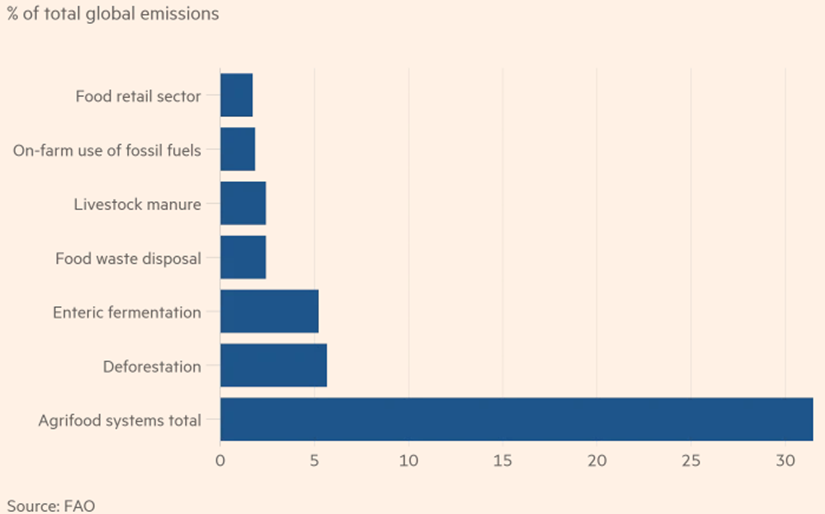
We have not spoken much about the agriculture industry and its emissions footprint – but it is significant and the sector is coming under greater focus as a consequence. It is not clear to us that the chart below is complete as it does not appear to include the carbon footprint of the fertilizer used in farming unless it is included in the fossil-fuel category, which seems unlikely. Much of the renewable natural gas planning in the US is relying on farm-based production, and there are initiatives to increase the amount of “low-tillage” farming as it has the effect of releasing far less CO2 from the soil than heavy tilling/plowing. Some of the categories listed below can be addressed through better land and waste management, but others will require offsets, another reason why the offset market needs work. For more on carbon offsets see today's ESG and Climate report.
If Ammonia Can Offset Coal In Power Plants, Demand Estimates May Be Too Low
Nov 9, 2021 1:45:47 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Sustainability, Coal, CCS, Ammonia, Power Plants, demand
One question we would have concerning the IEA ammonia projections in the charts below is whether the absolute demand assumption for 2050 is too low. If Japan has success co-firing its coal-based facilities with ammonia over the next 6-7 years, we could see a step-change in ammonia demand. The chart likely reflects expectations in Japan, but we would expect other coal-heavy economies to follow Japan's lead. If this were the case, we would expect the share of hydrocarbon-based ammonia to rise with accompanying CCS.
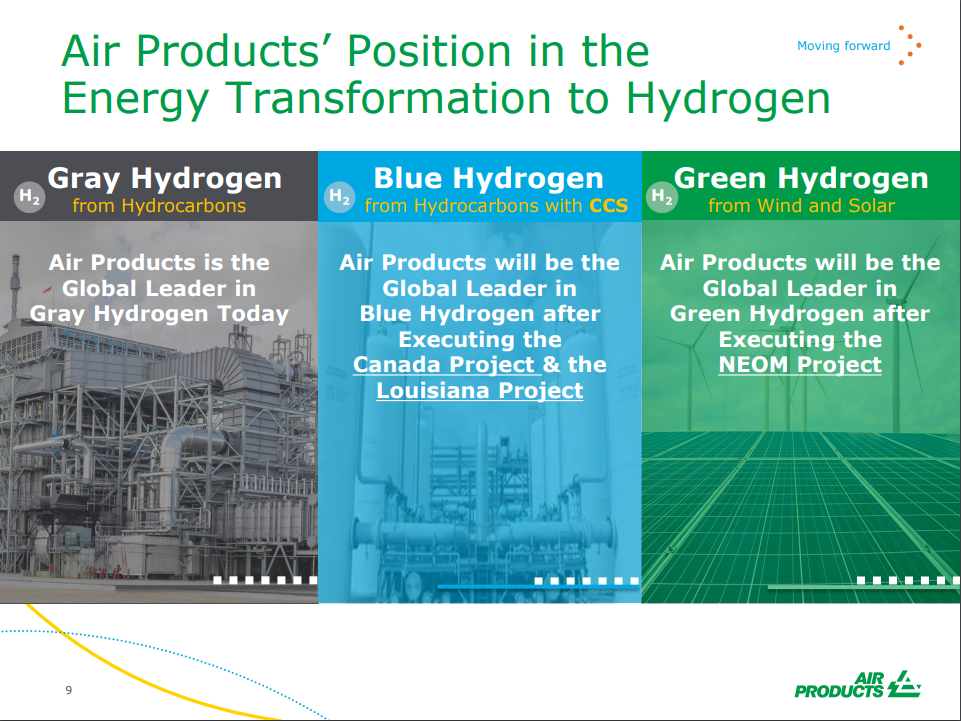
Green Hydrogen Plans Look Expensive, Blue Looks Easier
Nov 5, 2021 3:15:29 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Energy, Air Products, Ammonia, carbon footprint, natural gas, solar, carbon pricing
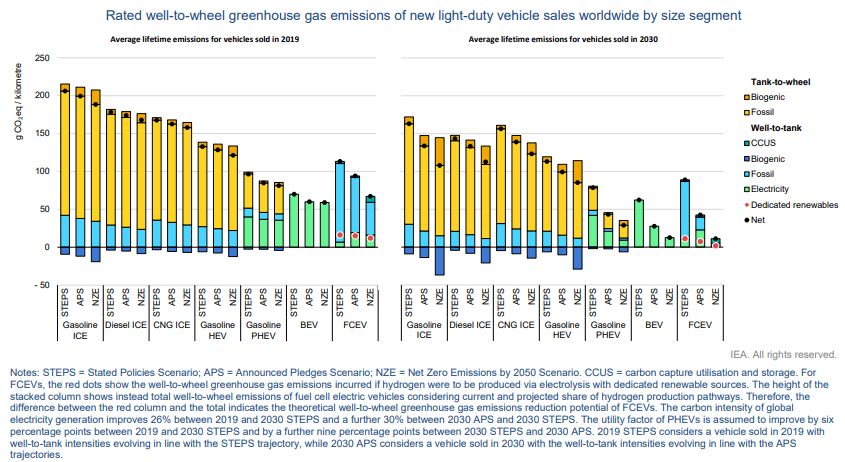
Hey Mr. President/Prime Minister, Will You Buy My Car?
Nov 4, 2021 1:58:06 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Electric Vehicles, Net-Zero, IEA, climate, EVs, ICE, carbon footprints
We highlight more from the IEA on the importance of EVs versus other vehicles to bring down “well to wheel” carbon footprints and the second (not unexpected) “kick in the pants” chart that shows the World woefully short in terms of its projected EV adoption rate. There are – probably expensive – hurdles to reaching the IEA net-zero goals with respect to EVs. The first is going to be the need to pay or tax consumers enough for them to give up a perfectly good ICE vehicle long before the end of its natural life.
The US Remains Divided On How To Price Carbon
Nov 3, 2021 1:34:59 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, LNG, CCS, CO2, Energy, Emissions, Carbon Price, carbon credit, renewables, LCFS credit, COP26
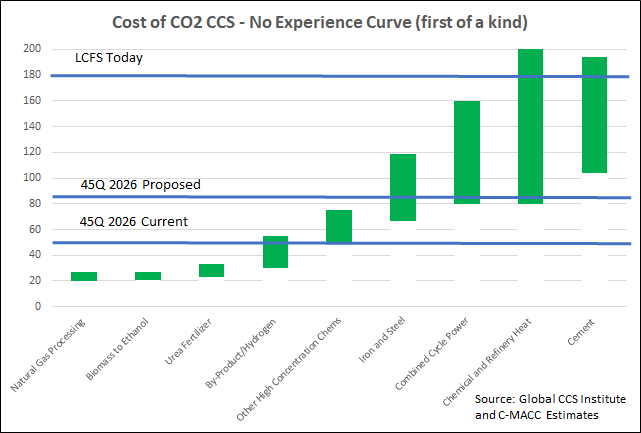
We want to focus today on the headlines around the possible increase in the 45Q CCS credit in the US and discuss the false logic of those that are objecting to it. There is no scenario where the US can move to a lower emissions power and transport profile while avoiding runaway inflation and social disorder without the continued use of fossil fuel-based power and transportation fuels for decades. The reliance on these fuels should and will decline over the years, but it is unreasonable to expect a transition that causes it to stop overnight. In the meantime, CCS is a mechanism that would allow fossil fuels to play a part with a much lower emissions footprint, and given that the CO2 impact on global warming is cumulative, if we can capture and store several billion tons of CO2 underground over that transition period it should be a good thing. Members of the Sierra Club and others would do well to look at the energy inflation problems in Europe and the move this week to put natural gas and nuclear back in the energy transition mix (too late in our view) because the move to renewables cannot keep pace with demand, which will grow faster as more EVs hit the road. The proposed 45Q credit is shown in the chart below vs. the current credit, the LCFS credit, and estimates of CCS costs.
COP26: Potential Unintended Consequences & Greater Clarity Around Action Needed
Nov 2, 2021 3:34:04 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, natural gas, climate, methane emission, COP26, materials, ESG messaging, ESG objectives
In our dedicated ESG and climate piece tomorrow we will focus on the progress and lack of progress at COP26 and discuss some of the likely consequences (intended and unintended) for the energy and materials industries. One of the subjects we touched on in the energy section of today's daily report, is how to craft a methane emission initiative that does not result in a decline in natural gas production before we see a needed recovery as the last thing the world needs now is more limited natural gas availability. Methane emission reduction looks like it is one subject on which there appears to be broad global agreement.
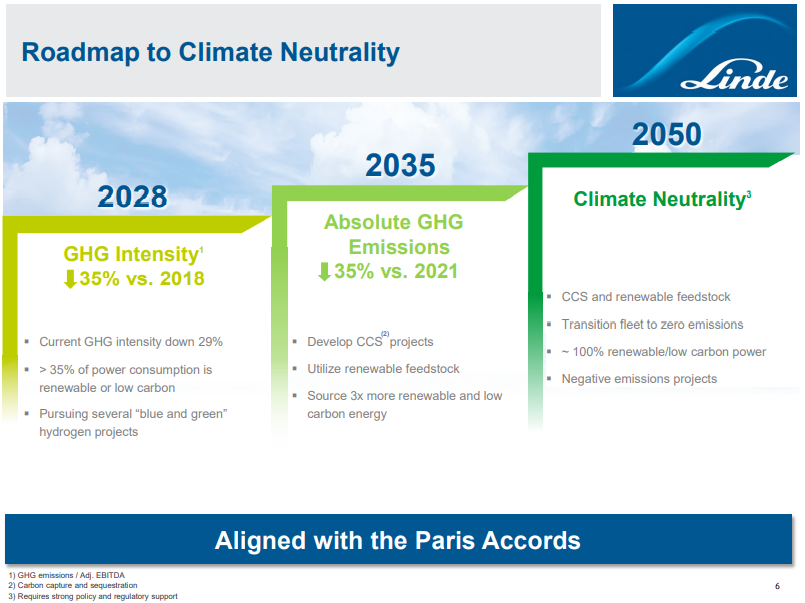
Net-Zero Goals Need Stronger Action Plans
Oct 29, 2021 1:56:53 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Energy, Air Products, Industrial Gas, LyondellBasell, Net-Zero, Dow, carbon footprint, carbon emissions, climate, COP26, materials, low carbon polyethylene, Linde
It is interesting to contrast Linde and LyondellBasell with Air Products and Dow. Air Products and Dow have transitioned away from the more generic messaging around broad objectives, and while they still have them, have started talking about concrete plans and spending aimed at lowering carbon emissions. Dow has a project on the books that will lower the emissions of existing capacity while Air Products is talking about greenfield low carbon investments at this point. Many of the commentators and climate activists are calling for concrete plans as opposed to broad objectives and we suspect that most of the narrative will move that way across energy and materials.
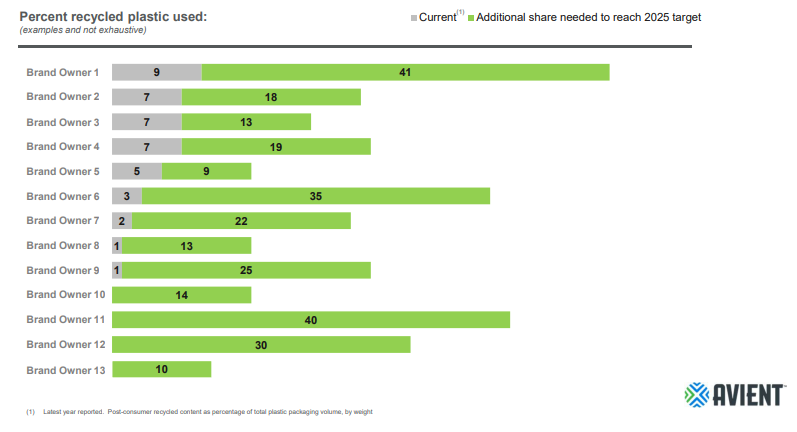
Challenging Recycle Targets Suggest High Prices & Opportunities For Renewables
Oct 28, 2021 1:57:50 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Recycling, Sustainability, PET, polymer producers, renewable polymers, renewables, climate, recycled PET, virgin material, bio-polymers, waste, recycled material
The Avient chart around where brand owners sit with recycled content versus 2025 goals is quite scary. There are not enough initiatives collectively to address the needs, as the demand extends beyond the 13 brand owners listed. In our ESG and climate report yesterday we talked about the challenges with recycled PET and the complicating factor around recycled material heading into different applications, and consequently not being available to bottlers. We also have the issue of PET bottle pre-form capacity being overweight in Asia versus PET bottle demand and waste – setting up an imbalance between where the waste is and where the recycled material is needed. The gaps in the Avient chart and the slow and challenging recycling progress lead to a couple of conclusions. The first is that recycled material is likely going to rise in value versus virgin material – simply because of competition and the PR, IR, Social cost of not meeting targets for many brand owners. The second conclusion is that the renewably sourced polymer producers have a huge potential opportunity to step in and fill the gap. The challenge will be the ability to have enough capacity up and running to meet demand in 2025.