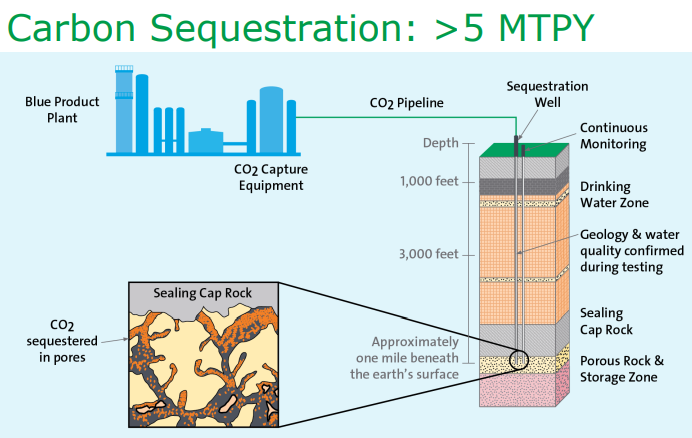
In our ESG piece yesterday we talked about the competitive edge that Canada now has with respect to both natural gas (because of lower prices versus the US) and CCS, both because of relatively low costs but also because of the clear value on carbon. Yet today we see an announcement in the US!
Air Products Claiming The Hydrogen Highground
Oct 14, 2021 3:04:12 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Air Products, Ammonia, natural gas, carbon values, blue ammonia, Carbon Sequestration
Net-Zero Pledges Remain Well Below What Is Needed: 2030 Particularly Worrying
Oct 13, 2021 12:27:36 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, Energy, Net-Zero, fossil fuel, IEA, clean energy, COP26, Climate Goals, energy technologies
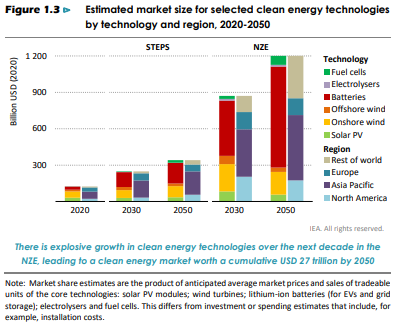
The IEA chart in the exhibit below is another stark reminder of how far away stated policies for clean energy are from what will be needed, and the 2030 gap is the most significant in our view as there is little time to correct it. The IEA has presented several studies over the last year that presents a series of “straw men” examples around how the World and, most recently China, might meet their respective net-zero targets, and the chart below is intended to show how far adrift we are, comparing what is needed to what has been stated. As we have mentioned a couple of times, it would be unusual for companies and countries to have firm plans for 2050 that sum to what the IEA is looking for as there are new technologies under development and the incentive/penalty landscape is still uncoordinated and very unclear. The latter is also a problem looking forward to 2030, but closing the gap between the STEPs scenario and the NZE scenario by 2030 looks almost insurmountable today, without a much tougher and more globally coordinated regulatory landscape, which looks unlikely given some of the low expectations for COP26 specifically. Note that how under the Net-Zero scenario discussed by the IEA, fossil fuel would peak by 2025 and compare this with the EIA analysis that we discuss in today's daily report – there is a huge disconnect.
Chevron Joins The Club, But The Focus On Cleaning Up Its Fossil Fuel Footprint Could Be Important
Oct 12, 2021 2:05:37 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Biofuels, Climate Change, Sustainability, LNG, Methane, CCS, Renewable Power, Carbon, Net-Zero, fossil fuel, carbon abatement, natural gas, carbon trading, offsets, EIA, Chevron, methane emissions, CO2 footprint, COP26, low carbon, methane leakage, carbon credits
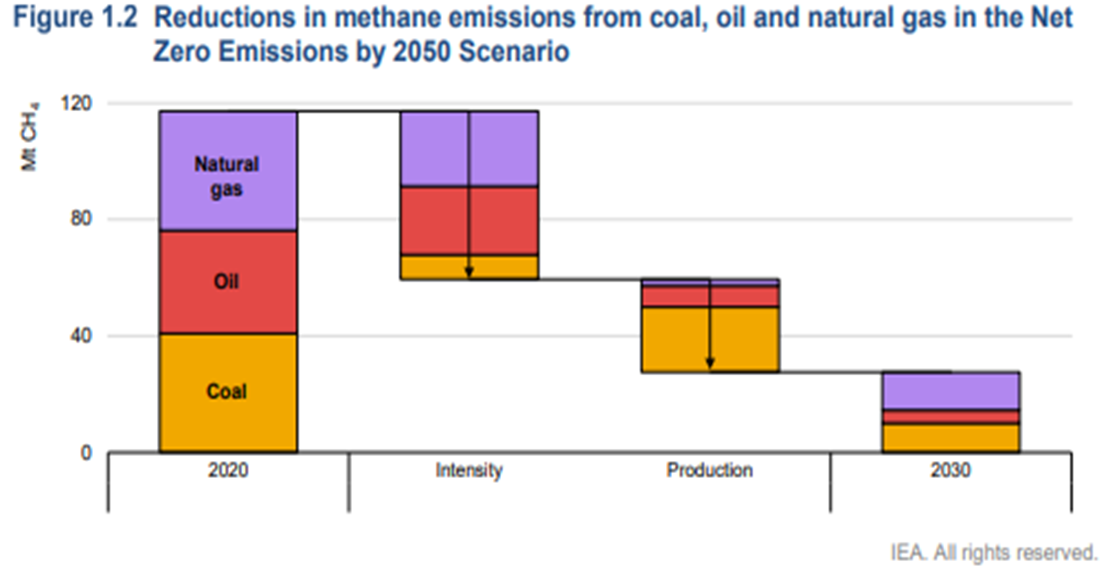
A couple of things worth highlighting in today's daily report – the first being Chevron’s move to join the net-zero club – focusing all eyes now on ExxonMobil in particular but also the rest of the US E&P crowd. Chevron will have some major challenges getting to net-zero and will likely face much of the same skepticism that bp, Shell, and TotalEnergies attracted in Europe initially and still face today. The Europeans have placed a lot of their bets on moving into renewable power – for the moment, Chevron is focused on moving to net zero in its own operations, which we read as biofuels and a lot of CCS. Given the acute shortage of international natural gas, it would make the most sense for the independent natural gas E&P companies and the LNG sellers to jump on the same boat. By promising low carbon natural gas and LNG, the industry is much more likely to gain support for the expansion that the world needs to counter some of the EIA assumptions around coal and petroleum product use from 2030 to 2050. Of course, it would be a whole lot easier for the US industry to do this if they had a value on carbon to work with! The chart below looks at one of the core clean-up issues, which is methane leakage. This is a subject we cover extensively in our ESG and Climate service linked here.
Carbon Capture Supportive Of LNG, But You Need Somewhere To Put The Carbon
Oct 1, 2021 1:46:17 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, LNG, CCS, CO2, decarbonization, ethanol, natural gas, 45Q
The carbon capture plans lacking a place to put the CO2, suggested in the two connected stories linked here (link 1, link 2), echo something that we have been highlighting for a while. There have been several press releases with respect to CCS – partnerships – plans to accompany new investments – gathering schemes for the ethanol industry, etc. but none have any specificity around where they will put the CO2. The Houston team, discussed in a recent report is talking about offshore Texas, and given both ExxonMobil and Chevron in the partnership, we do not doubt that there is a plan, but in general, the permit activity at the EPA is, we understand, quite limited today. To apply for a class 6 permit, applicants need to have a detailed analysis of the sub-surface that they plan to target, and once you have identified a location, there are likely at least 18 months of work to get into shape to submit the permit. Some of the oil majors may be able to move faster on acreage that they already have seismic models for, but it is a long process – we wrote about the need for 45Q to change in both value and duration in our recent ESG and Climate Piece.
How Can We Have Too Much & Too Little CO2 At The Same Time?
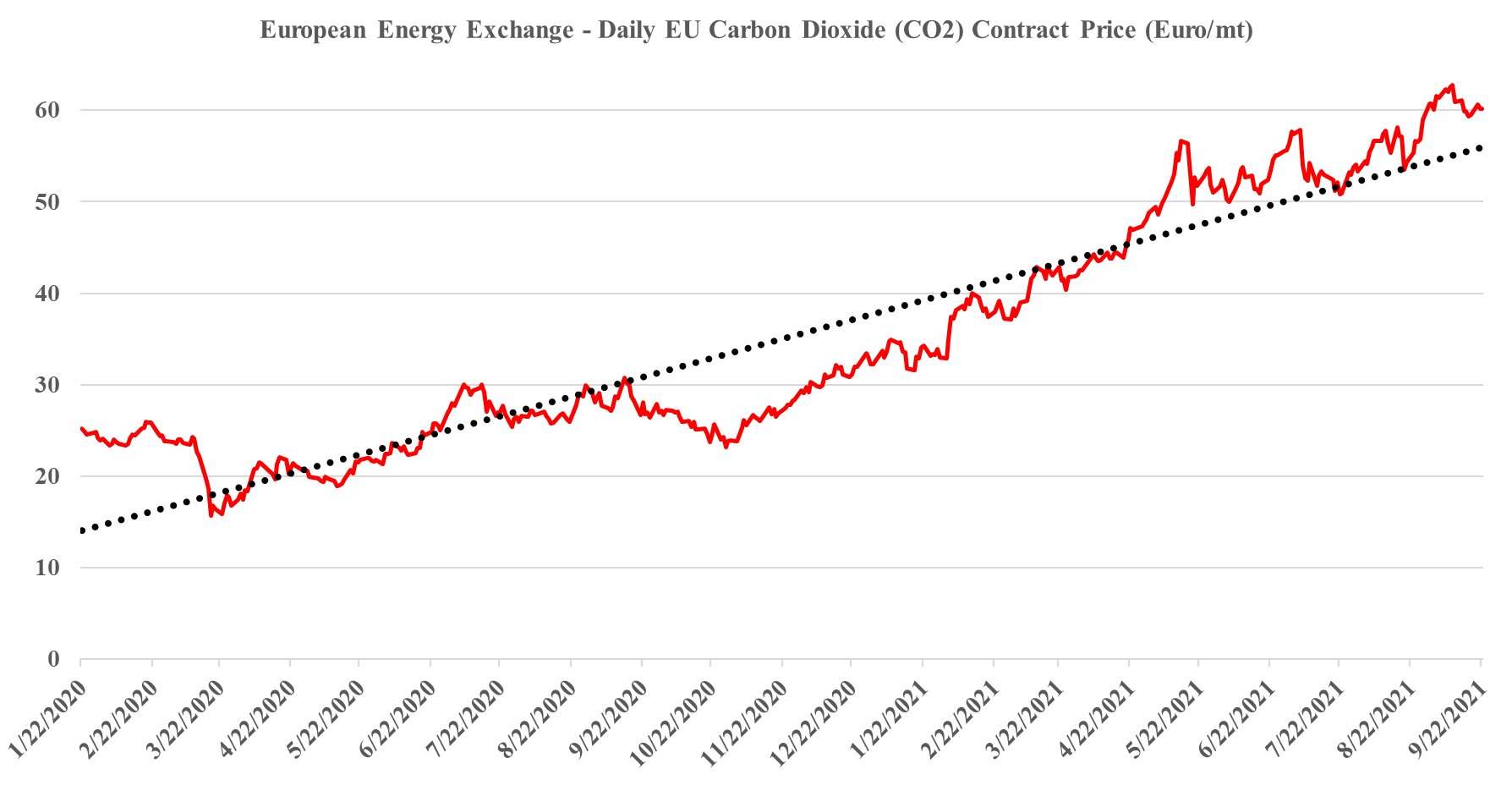
Sep 22, 2021 2:04:48 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Carbon Price, Inflation, Ammonia, natural gas, European Carbon price, urea, CF Industries
It is worth a short explanation of what is going on with European CO2, given the mixed signals of shortages in headlines today and then the slight weakness in pricing shown in the image below. These are two very different markets, with the food, beverage, medical and nuclear industries looking for pure streams of CO2 rather than the contaminated streams that make up the bulk of emissions. Historically, the food and beverage industry looked to fermentation – so alcohol production – as its source of a pure CO2 stream, but as demand grew, the next best place became ammonia production, which also has a pure CO2 stream as a by-product. Most ammonia is further converted into urea, which is a consumer of CO2 and there is not enough CO2 produced in a natural gas-based ammonia plant to convert all of the ammonia to urea. You sometimes see urea facilities also selling ammonia, but more frequently they take the carbon monoxide by-product of the syngas reaction and convert that to CO2. The result is enough CO2 to convert all of the ammonia to Urea and surplus CO2 to sell. Because of this more dominant supply of food and beverage grade CO2, and shutdowns caused in this case by runaway natural gas prices, have an immediate impact on the industries that rely on the CO2.
US CCS Clusters Gaining Momentum, As They Should
Sep 17, 2021 12:32:39 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, CO2, Sequestration, Emissions, ExxonMobil, Emission Goals
News that ExxonMobil has support for its large CCS hub in Houston should not be a surprise. According to the EPA data, for 2019, Harris and Galveston counties combined have more than 50 million tons of CO2 emissions and there are another 20 million tons in Brazoria county, which is close enough to be included. The devil will be in the details as the cost of building a high-pressure pipe network will be high, as will drilling wells with sufficient capacity offshore. We believe that this hub, or cluster (as they are called in Europe), approach will help drive CCS costs down, but we are concerned by the competitive disadvantage that this might cause for those without access to a hub or cluster – see our ESG report - Cluster F***ed: The Dangerous Scale Component of CCS – for more.
Chevron: Working Hard, But Will It Be Enough?
Sep 16, 2021 2:57:56 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, CCS, ESG Investing, ESG investment, Chevron, carbon storage
We focused on several aspects of carbon in our ESG and Climate report yesterday and we see several headlines today that focus on carbon and storage, whether it is the blue hydrogen project in France or the Chevron interest in CCS. Chevron has some experience with CCS with the Gorgon natural gas project in Australia and while the company has been criticized recently for falling short of its capture goals for the facility – we believe that all learning experiences are valuable, and what happened in Australia likely leaves Chevron better equipped than many to pursue successful projects going forward. The likely disappointment for Chevron will be the lack of investor appreciation that it may get for the initiatives, as the focus will remain on the scale of fossil fuel exposure – see our Sunday Piece from this week. The barrage of announcements from Chevron is likely in response to the investor pressure that the company (and the industry) is under, but as we discussed on Sunday, it may not make a difference – it did not for Shell in the eyes of the Dutch court.
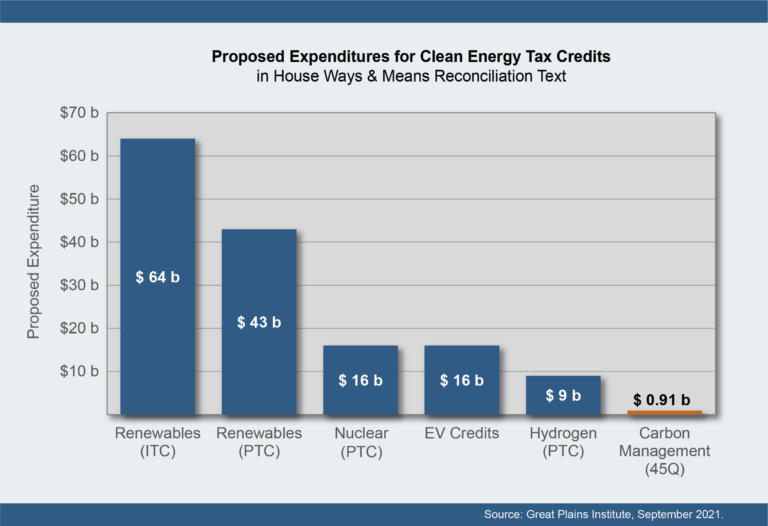
CCS: US Government Funding Expectations Seem Very Low
Sep 15, 2021 12:15:49 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, ExxonMobil, carbon credit, carbon value, 45Q
The tax credits suggested for 45Q in the budget reconciliation plan – see Exhibit below – would pay for roughly 18 million tons of CO2 sequestered or used in EOR over the life of the budget, assuming a credit value of $50 per ton of carbon. While this may seem huge in the context of the current levels of CCS in the US, the country had around 2.5 billion tons of emissions in 2019 that could be addressed with CCS (power and industrials), and if we assume 10% of that needs to be dealt with through CCS, the 45Q provisions in the budget reconciliation would cover less than 8% of the volume for one year and the percentage will be even lower if the “CATCH” act is successful in driving the 45Q value to $85 per ton of CO2. So the numbers are either inadequate, or the government is assuming that the levels of CCS in the US will be much lower than the potential – note that the ExxonMobil proposal for a hub in and around Texas talked about the maximum size for the one project being as much as 100 million tons per annum which should equate to $5 billion of tax credits – per annum. See our ESG & Climate report for much more on carbon markets today.
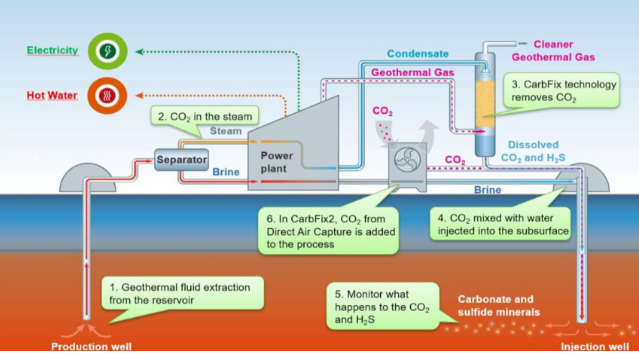
Direct Air Capture Is Expensive, But Demand Is There
Sep 10, 2021 1:43:32 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CO2, Emission Goals, carbon dioxide, carbon offsets, direct air capture, greenwashing, DAC, carbon neutral hydrocarbons
The most notable news from the Iceland CO2 direct air capture (DAC) project, illustrated in the Exhibit below, is not that it is working and how energy efficient it is, but that the CO2 capture costs are extremely high and yet all of the offsets are sold. One report talks about the costs per credit approximating $1000 per ton of CO2, which is likely accurate given that the facility is relatively small scale, at 4 thousand metric tons per year. The same report also states that the credits are almost sold out for the 12 years that they are being offered. We believe that this is indicative of the marginal demand for uncontestable carbon offsets, and this is a topic we have covered at length in our ESG and climate work. Shell, bp, and others are selling what they claim to be carbon neutral hydrocarbons around the world and are buying offsets to do so, but they are coming under quite a lot of “greenwashing” fire because of the less tangible/auditable nature of the credits they are buying – often related to agricultural or specific tree conservation/planting initiatives that are questioned because of the validity of the capture claim or the vulnerability of the credit to weather, fires, and forest maintenance years in the future.
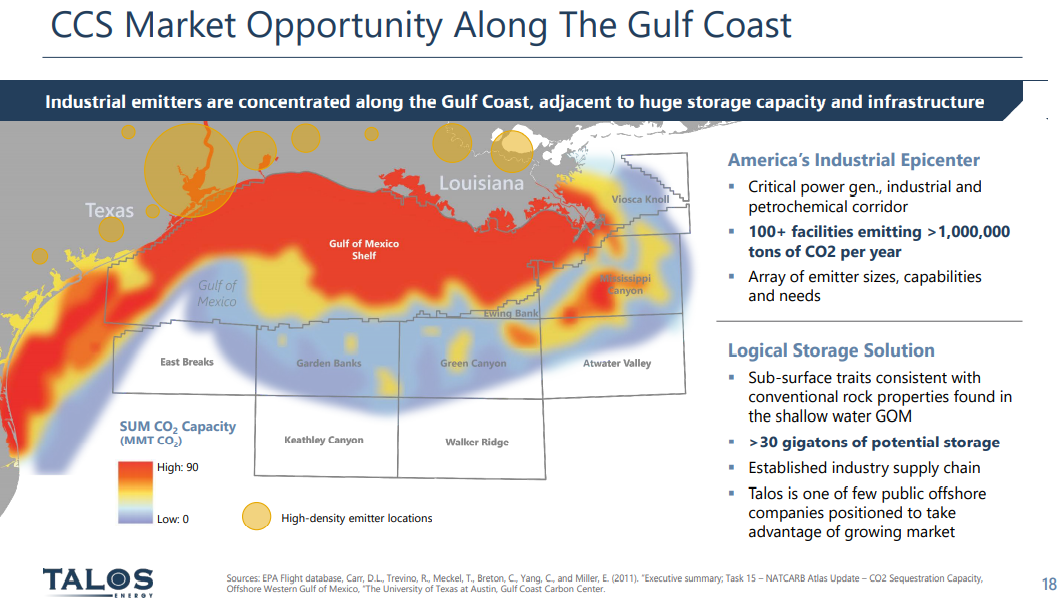
Offshore CCS Is Good: But Onshore CCS Should Be Cheaper
Aug 27, 2021 12:49:53 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, CCS, CO2, Sequestration, carbon abatement, Offshore CCS, Talos, Onshore CCS
The Talos release and the map shown in the Exhibit below, highlight some of the potential for offshore CCS along the US Gulf Coast. We will likely see some of this developed over time, in our view, but the question of cost is important, not because the US Gulf is likely to be more expensive than some of the offshore locations that are proposed for Europe, but because the same offshore geology on the US Gulf exists onshore, and the onshore opportunities will likely be much lower cost. Given that one of the overriding concerns around carbon abatement is cost and how it will be paid for, who will pay for it ultimately, and what it means for the competitive landscape, finding the lowest cost solutions will be key. This is something that we have covered at length in our dedicated ESG and climate research. Building high-pressure pipelines is expensive, and high relative to the onshore cost of sequestration. Talos might find interest from CO2 suppliers but may be undercut by onshore projects – assuming these get the green light from regulators – not giving them the green light would likely be imposing further unnecessary costs on industry.