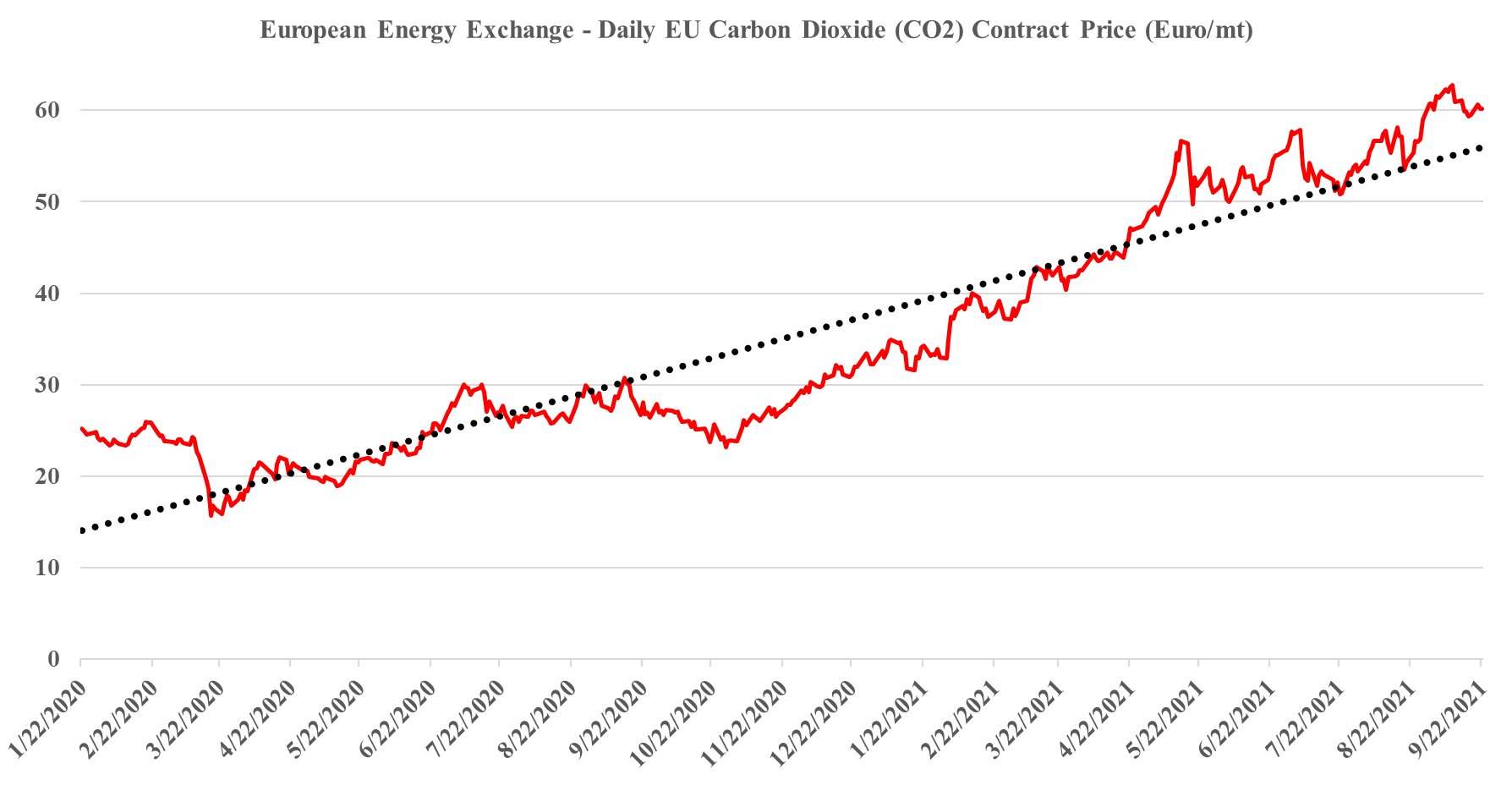
It is worth a short explanation of what is going on with European CO2, given the mixed signals of shortages in headlines today and then the slight weakness in pricing shown in the image below. These are two very different markets, with the food, beverage, medical and nuclear industries looking for pure streams of CO2 rather than the contaminated streams that make up the bulk of emissions. Historically, the food and beverage industry looked to fermentation – so alcohol production – as its source of a pure CO2 stream, but as demand grew, the next best place became ammonia production, which also has a pure CO2 stream as a by-product. Most ammonia is further converted into urea, which is a consumer of CO2 and there is not enough CO2 produced in a natural gas-based ammonia plant to convert all of the ammonia to urea. You sometimes see urea facilities also selling ammonia, but more frequently they take the carbon monoxide by-product of the syngas reaction and convert that to CO2. The result is enough CO2 to convert all of the ammonia to Urea and surplus CO2 to sell. Because of this more dominant supply of food and beverage grade CO2, and shutdowns caused in this case by runaway natural gas prices, have an immediate impact on the industries that rely on the CO2.
How Can We Have Too Much & Too Little CO2 At The Same Time?
Sep 22, 2021 2:04:48 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Carbon Capture, Climate Change, Sustainability, CCS, CO2, Emissions, Carbon Price, Inflation, Ammonia, natural gas, European Carbon price, urea, CF Industries
Higher Costs Likely To Undermine Some Clean Energy Timetables
Sep 21, 2021 1:37:55 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Wind Power, Renewable Power, Metals, raw materials inflation, Inflation, renewable energy, solar energy, EVs
The charts below both support our view that we will see continued inflation in renewable energy costs, rather than the deflation that is baked into all of the forward models. It is easy to forget that some of the early solar installations are coming to the end of their useful lives and are retiring – these are gaps that new solar will need to fill. Wind power has the same issue, as many of the original wind farms need equipment replaced and the introduction of recyclable wind turbine blades has been in recent manufacturers' announcements. When we see analysis of who is going to use which tranche of new renewable power for which new hydrogen project we see major gaps in the power demand analysis, in part related to power demand growth at the domestic consumer – because the more rapid introduction of EVs – and in part because or retirement of facilities and the need to replace them.
Inflation Challenges In Europe; Overall Challenges In China
Sep 8, 2021 2:02:16 PM / by Graham Copley posted in LNG, Emissions, Carbon Price, Emission Goals, Inflation, China, carbon values, carbon emissions, COP26
Europe is likely to be a test case of how much inflation a country or region is willing to bear on its path to clean energy. Costs are rising in Europe, as LNG markets tighten and as carbon prices rise. The net result is increased power prices, with reports of unhappiness in many countries – this is a topic we have discussed at length in our dedicated ESG and climate work and was a focus of last week's report – linked here.
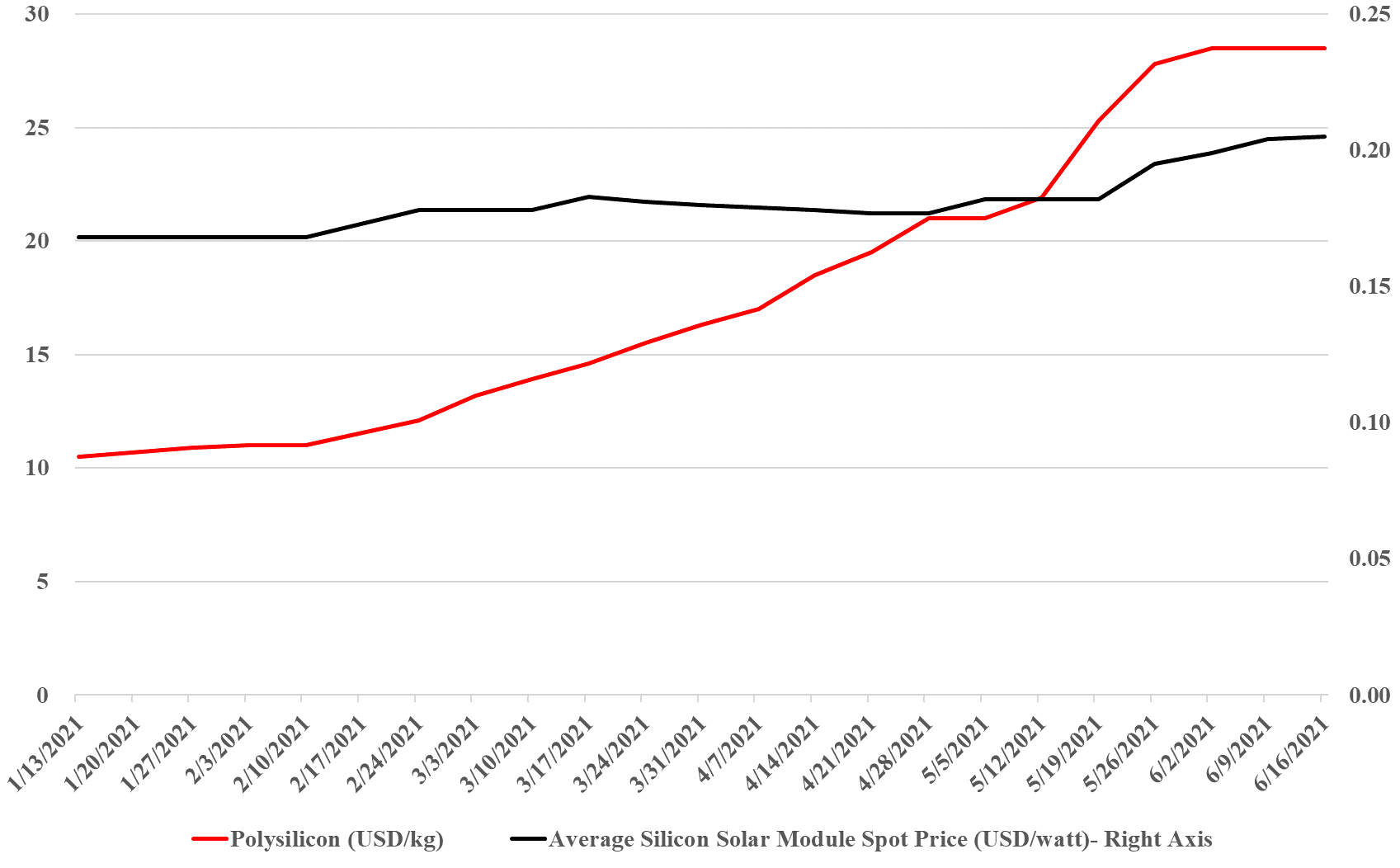
Solar: A Clear Example Of Potential Renewable Energy Inflation
Jun 17, 2021 1:32:30 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Biofuels, Polymers, ESG Investing, Electric Vehicles, Raw Materials, LyondellBasell, Inflation, Gevo, solar, polysilicon, Wacker, copper, silver, Aemetis, renewable energy
The exhibit below summarizes well one of the primary concerns that we have with some of the very ambitious goals for decarbonizing power grids, EV introduction, the further electrification of industry, and hydrogen. While the solar module price increase does not look that significant (yet), to put it in context, solar module prices have collapsed from over $1.80 per watt in 2010 to below $0.20 in 2020, and many of the expectations around cheap hydrogen require the cost to keep falling. The bigger concern is the polysilicon price, which is up 160% this year, good for the polysilicon producers like Wacker (see the headline here), but bad for the solar module producers, who are seeing major margin squeezes, especially given the rise in copper and silver as well this year. The raw material pressure should drive further increases in solar module pricing and while the higher margins for polysilicon will likely drive expansion investment, the metals are harder to call, given the ESG views on mining. We remain firmly of the view that raw material availability and price inflation, as well as module and wind turbine manufacturing capacity, will be the rate-determining constraint in terms of the growth in renewable power and this is why we question all of the near-term cheap power and cheap hydrogen goals that are being suggested by potential producers and government agencies.
More From The IEA; Expensive Hydrogen & Carbon Capture
May 19, 2021 1:44:48 PM / by Graham Copley posted in Hydrogen, Carbon Capture, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Inflation, IEA, Ammonia
We discussed the IEA report yesterday at some length, but in such a comprehensive report we missed a couple of things that are probably worth noting today. See more in our ESG Report today.