While we would generally avoid quoting work from a company that we might consider a peripheral competitor, we are happy to do so when it backs up one of our central themes – in this case, inflation in renewable power costs. The quote is taken from the Wood Mackenzie report flagged article linked here and discusses a view on how challenges that renewable power installers have faced in 2021 will extend into 2022. The quote talks about shortages of renewable power equipment, and the obvious consequence will be higher prices for that equipment, especially as raw material prices for components remain high and possibly move higher. In our ESG and Climate report today, we talk about the need for some commonsense oversight such that impractical ESG investing targets do not limit the ability of producers of critical fuels and materials to operate.
Renewable Power Bottlenecks = More Fossil Fuels
Dec 22, 2021 1:44:32 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Sustainability, LNG, Coal, Renewable Power, ESG Investing, raw materials inflation, solar, renewable energy, wind, climate, shortages, fuels, renewable power inflation, oil production, Permian basin, coal demand, electricity, LNG supply
Investment Constraints On Solar Before We Even Start With Hydrogen
Dec 14, 2021 1:17:04 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, Renewable Power, ESG Investing, Materials Inflation, Inflation, solar, ESG investment, climate, solar energy, material shortages, product shortages, onshore wind
Much of the core focus of both our chemical industry and ESG and Climate research recently has been on inflation and materials shortages; we would point you to: Inaction, Caused By Inflation Fears, Is Driving More Inflation! and Coming Up Short: Materials Availability To Limit Climate Progress. This linked article suggests that, as we have predicted, cost and availability pressures are taking a toll on solar installation plans for 2022 in the US. While the inflation piece is real and the product shortages highlight some of the capacity constraints for materials and panels, the broader conclusions that can be drawn from the headline are more concerning. These shortages (and higher prices) are coming well before we see any step change in attempts to increase renewable power installations associated with all of the green hydrogen projects that have been announced over the last 6-9 months. All of these investments are relying on the deflationary trends continuing, especially for onshore wind and solar.
Are We Asking Too Much Of The Renewable Power Industry?
Dec 1, 2021 12:19:53 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Sustainability, Renewable Power, Emissions, Materials Inflation, Emission Goals, Inflation, Net-Zero, IEA, solar, wind, climate, renewable power inflation, commodity pricing
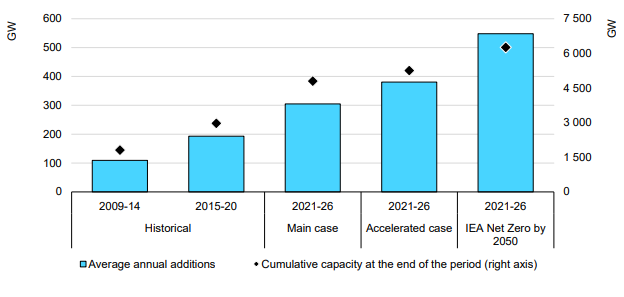
The core message of the IEA analysis published today is around how renewable power rates of investment remain far too low and need to more than double immediately to meet net-zero goals – see below. This analysis is very supportive of our renewable power inflation thesis, as none of the renewable power component manufacturers can double production either cheaply or quickly, and none of their suppliers has that much spare materials capacity. On the solar front, we may have the additional problem of regional production concentration. China has the largest share of capacity for solar module capacity and now has much more aggressive plans for solar power domestically. We could see China-based components stay in China, exaggerating shortages outside China. The IEA has an accompanying report today on the possible impact of commodity pricing on solar and wind pricing and it is also linked here – these reports were published this morning and we will cover them in more detail in next week's ESG and Climate report. More on this in today’s ESG and Climate report.
More Evidence To Suggest Material Shortages For Energy Transition
Nov 30, 2021 1:34:42 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Coal, CCS, Renewable Power, Energy, hydrocarbons, natural gas, solar, wind, energy transition, energy sources, fossil fuels, nuclear, bioenergy, hydro, geothermal, material shortages
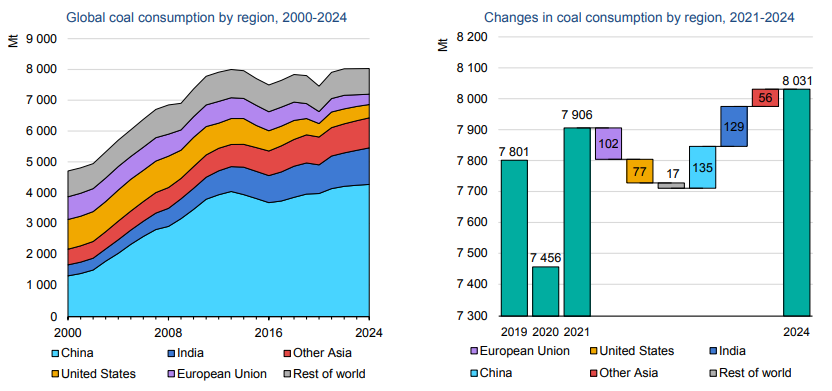
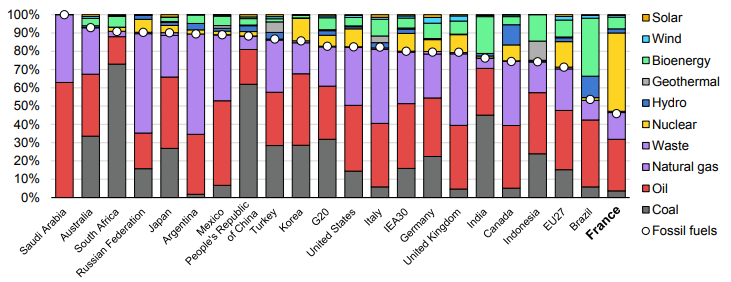
The fuel use data in the Exhibit below is very much a function of geology and the good and bad luck associated with it. The large hydrocarbon users' consumption patterns are a function of what they have – if you have a lot of coal, you use a lot of coal. The significant build-out of nuclear in France is partly because of Frances’ exceptional track record with the technology but also because the country does not have anything else to fall back on. Japan’s nuclear component was much higher before Fukashima. It is, however, worth noting the almost insignificant share of wind and solar anywhere, and then to put this into context with the collective ambitions, not just for 2050, but for the much shorter 2030 targets.
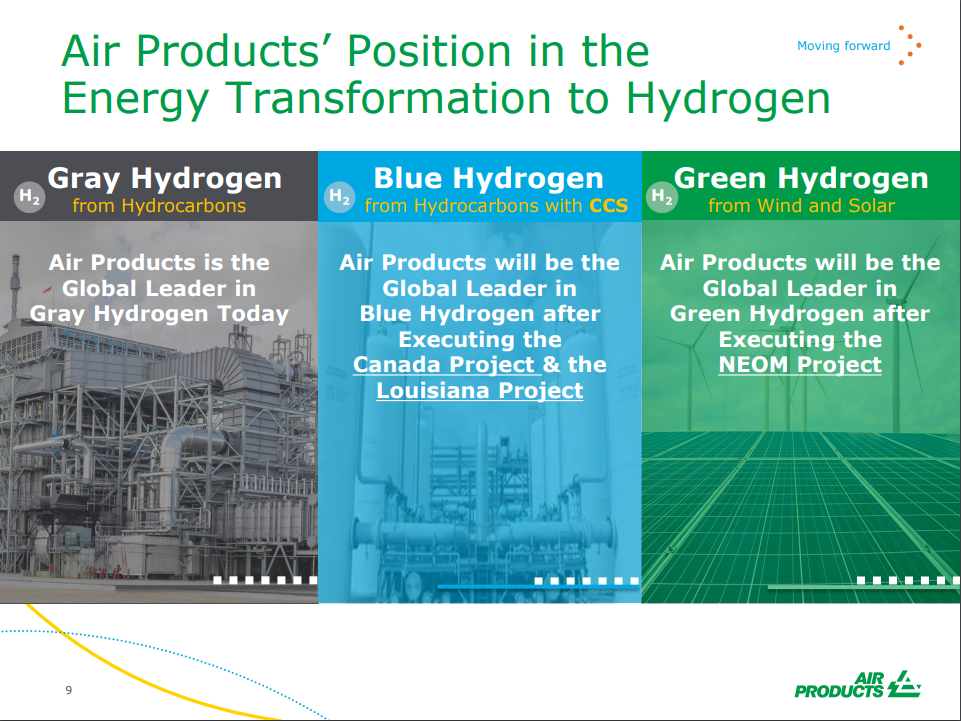
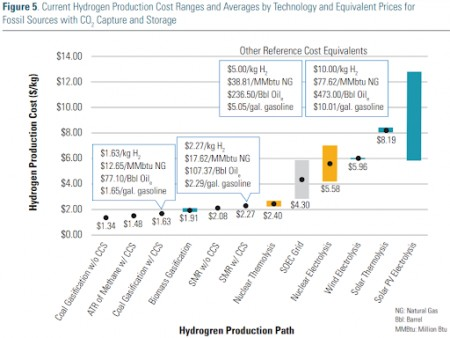
Green Hydrogen Plans Look Expensive, Blue Looks Easier
Nov 5, 2021 3:15:29 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Green Hydrogen, CCS, Blue Hydrogen, Energy, Air Products, Ammonia, carbon footprint, natural gas, solar, carbon pricing
If We Want Green Hydrogen, We Better Start Now
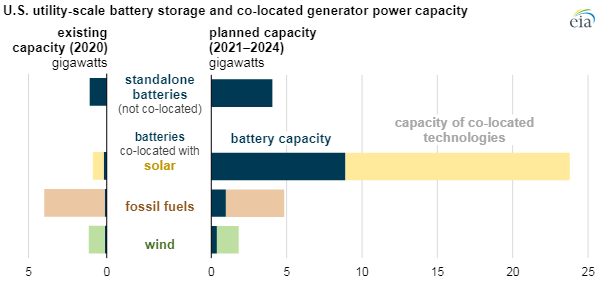
Sep 30, 2021 2:20:51 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, Green Hydrogen, power, solar, batteries, wind, clean energy, battery storage, green investments
The battery storage investment chart below is interesting in that it shows significant pairing with Solar facilities and less with wind. If we are to meet the green hydrogen goals that many are optimistically predicting over the next 10 years, then the new wind and solar investments need to be paired with hydrogen and hydrogen-based swing power generation capacity. This is the only way that countries will develop effective hydrogen grids. Simply having one or two large hydrogen facilities and/or import facilities will result in very inefficient distribution models either for fuel cell vehicles or for heating and swing power generation. A distributed network for hydrogen makes much more sense and modular electrolyzers coupled with modular hydrogen power generators is a more holistic model, with much more flexibility than adding batteries. Granted, the battery technology is tested and available today, but the broader ambitions for hydrogen will not be met if we do not get out of the blocks soon.
Green Hydrogen: Not So Good If Power Prices Do Not Come Down
Sep 3, 2021 1:14:52 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Methanol, CCS, CO2, Renewable Power, Ammonia, bp, feedstock, carbon dioxide, solar, wind, electrolysis
Last week, and in our dedicated ESG and climate report this week, we talked about the challenges of shipping hydrogen, and the linked bp project for Western Australia will have the same problem to solve – choosing ammonia according to the announcement over the very inefficient toluene/cyclohexane option we discussed last week. The appeal of Western Australia is the unpopulated available land that has little alternative use and sees abundant sunshine. The bp project assumes that the facility can buy attractively priced renewable power from third parties, but the company must have a specific power project in mind for the bulk of the electricity needed. The stumbling block here will likely be when the power project(s) bid out the solar module contract, find out that the suppliers are sold out and are asking higher prices to cover reinvestment and higher material prices, and then have to go back to bp with a much higher than expected cost of power. The advantage of solar and wind projects is that inflation only impacts upfront capital costs, which can be amortized over the life of the project – feedstocks are free! That said, most of the announced projects have declining capital costs per megawatt in their planning assumptions today.
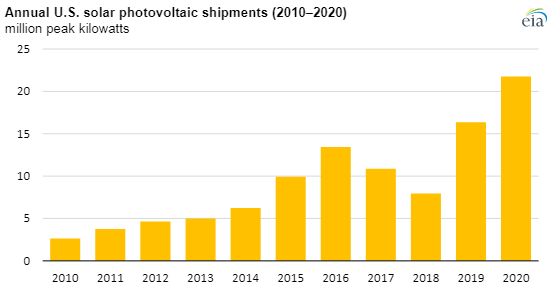
Solar Module Raw Material Costs Reversing Long Term Price Declines
Sep 2, 2021 1:57:21 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Renewable Power, Energy, Raw Materials, raw materials inflation, solar, renewable energy, renewable investment, solar energy, solar module
In our ESG and climate piece yesterday we discussed rising costs of climate-related actions, with a focus on some of the likely inflation in renewable power costs. The optimists are looking at the Exhibit below, and what were falling module costs through 2020, and concluding that solar installations can grow and that costs can still fall. While the module shipment growth in 2020 was impressive at 33%, some of the forecasts of what will be needed call for a much more dramatic rate of module growth than we saw in 2020.
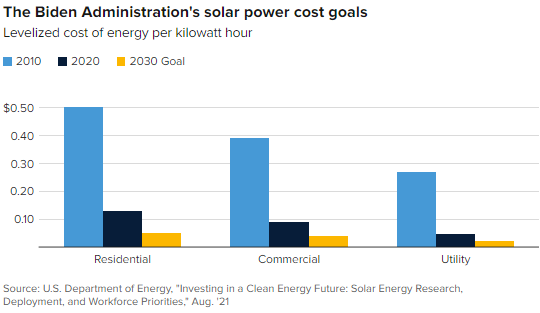
It's Hard To Bet On Deflation When You Are Dependent On Commodity Pricing
Aug 19, 2021 11:57:02 AM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Climate Change, Sustainability, Renewable Power, Raw Materials, solar, copper, silver, wind, Lithium, solar energy, steel, basic polymers, semiconductors, renewable power goals, aluminum, EV batteries, rare earths
We are back on one of our pet topics today which is the reasonableness around some of the assumptions around the future cost of renewable power. We reference, work done by the US Department of Energy in the Exhibit below, and see two potential pitfalls with the assumptions around continuous improvement in solar, wind, and hydrogen costs, although there is a slight twist for hydrogen. The first is around the dynamics of learning curves. As the exhibit shows, in the early stages of any product development, there are huge leaps in cost improvements, driven by scale, better know-how, more efficient manufacturing, and in the case of solar power, both better processes for installation and some technology improvements. However, as you drive costs lower, the cost of raw materials becomes a much larger component of overall costs, and your ability to lower costs further can be overwhelmed by moves in material costs. Any inability to pass on the costs will result in economics that do not justify additional capital and you find yourselves in a commodity cycle. This is something that we have seen in basic polymers for decades, and no buyer of polyethylene today can claim that they are benefiting from a learning curve improvement. Closer to home for solar, we are seeing the same issue today in semiconductors – not enough margin to invest as everyone has been trying to push costs lower. The expectation in the DOE study and highlighted in the CNBC take on the study below is that annual solar installations in the US need to rise by 3-4X to meet some of the renewable power goals the Biden Administration is looking for by 2030, while similar growth is expected in other markets – the solar panel and other component makers have to be making good money to achieve this.
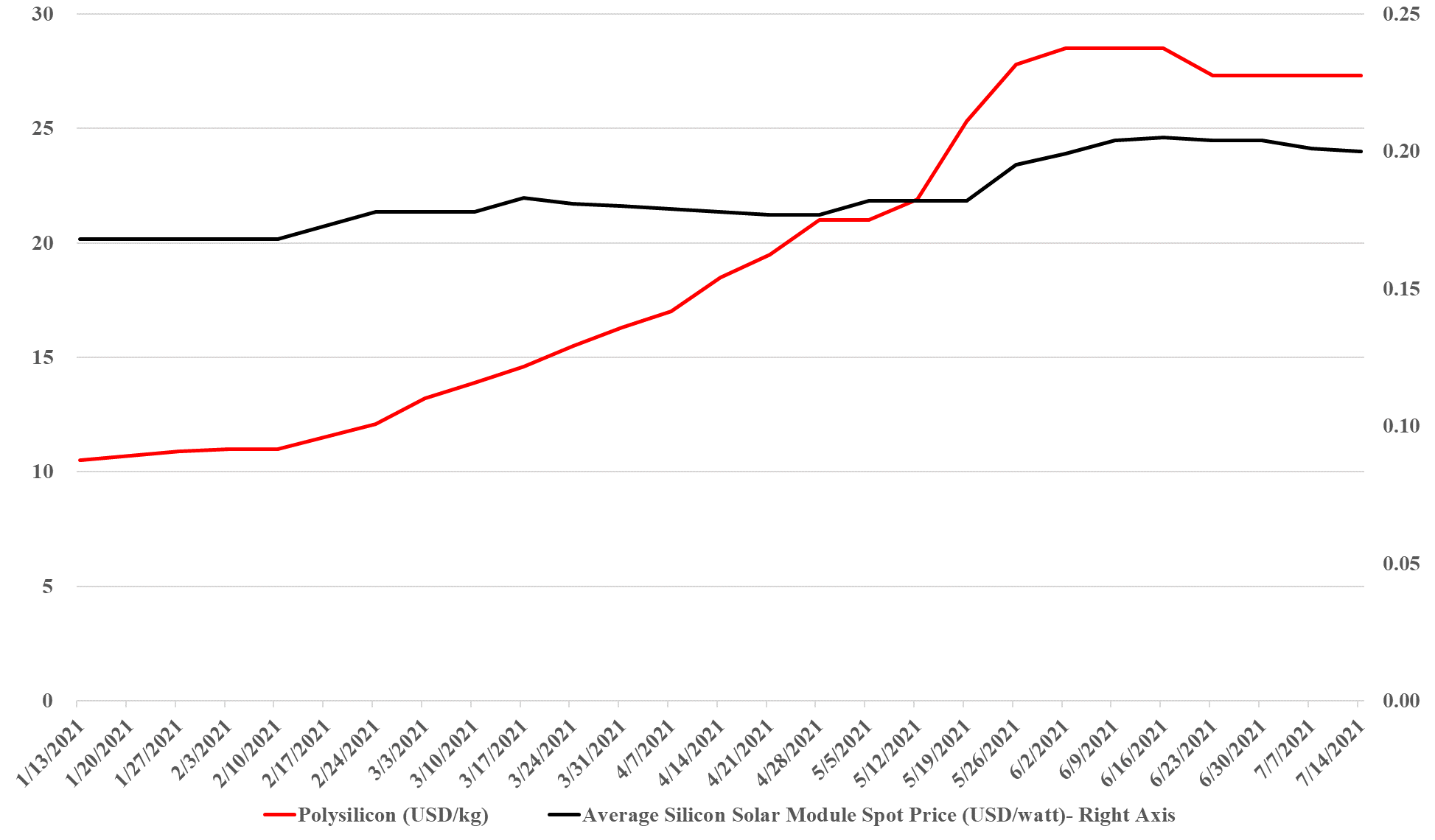
Here Comes The Sun... But Not Cheaply
Jul 16, 2021 1:50:56 PM / by Graham Copley posted in ESG, Hydrogen, Renewable Power, Raw Materials, carbon abatement, solar, solar energy
While the escalation in solar panel material costs has plateaued over the last couple of months, the increase has been enough already to reverse the decline in solar module pricing as we have noted previously (see charts below). While the increase in module pricing is not that significant there are three points to note: