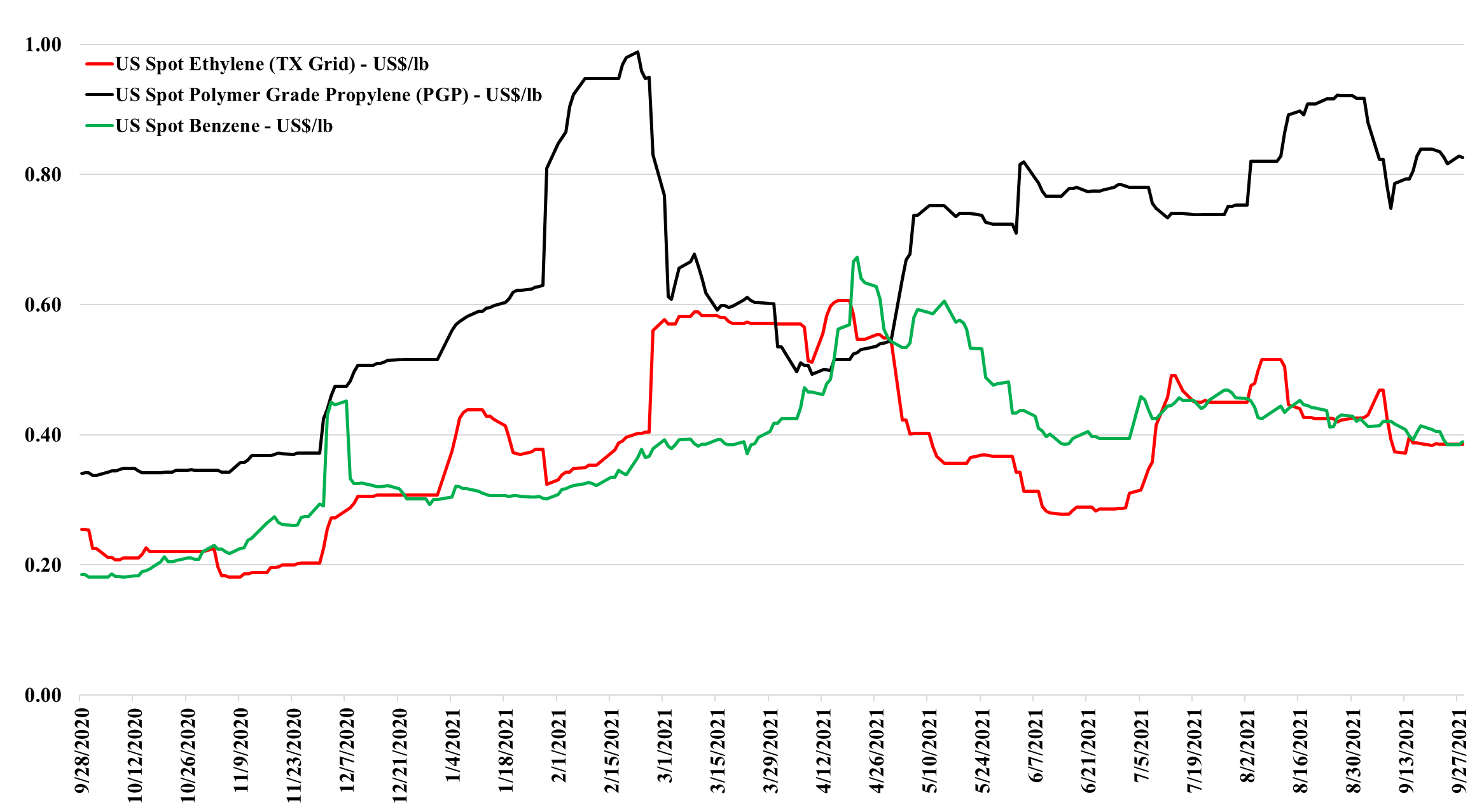
We have a fairly stable week for US olefins so far – no new production disruptions, but the industry is still recovering from the storm-related shutdowns over the last 4 weeks. We still believe that there is a downside to ethylene and propylene in the US as production recovers and as demand normalizes (especially for propylene). With another month of hurricane season to go, however, it probably does not make sense to force surpluses into an export market where prices are much lower – especially for ethylene. As we have noted in the past, the right strategy in 2020 was to store the ethylene at this time rather than sell it. Inventories would likely have to rise further before those with surpluses were willing to take the cut needed to export. At the same time, rising natural gas and NGL prices are another reason to hold on to products as what you have today did not cost that much to make and costs may rise near term. See more in today's daily report.
A Stable Start To The Olefins Week
Sep 28, 2021 12:48:24 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Propylene, Ethylene, Export, olefins, natural gas, NGL
Polypropylene Should Be Traveling
Aug 17, 2021 6:16:09 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polyolefins, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Export, arbitrage, polymer
The chasm between US and Asia polyolefins prices remains wide, close to a 5-year high for polyethylene and setting new highs for polypropylene. The polyethylene arbitrage is not large enough to encourage US imports – first Exhibit below – largely because of the very high container rates from China.
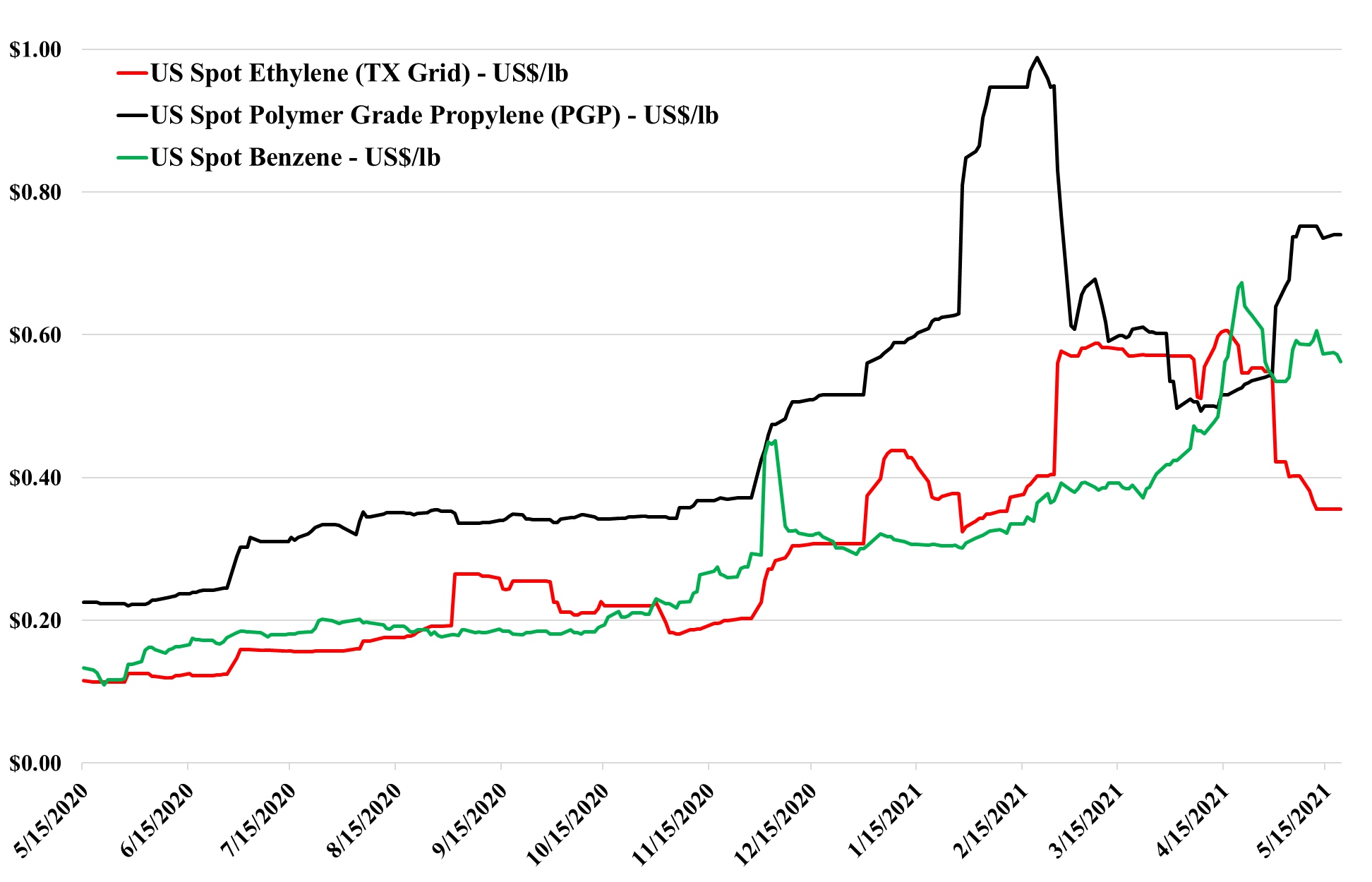
US Ethylene Looks More Precarious Than Other Basic Chemicals
May 20, 2021 12:11:06 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Ethylene, Monomer, Prices, Surplus, Export
Pessimism in the Asia ethylene market is a bad sign for ethylene vs. other US monomers. Those in the US with ethylene surpluses may need to fight a bit harder to find homes for the excess product in the US. We have not focused on the cost curve for a while as markets have been tight and global costs have not been an influence in the market for some time. The US has plenty of dry powder, in that export prices can fall significantly before they approach ethane-based costs, and can fall below production costs outside the US – especially in Asia – and still generate a margin for the US sellers. But that would mean more downside for US spot pricing and it may be enough to create some surpluses and some downward pressure on US derivative pricing. The caveat, of course, is that we had the same setup last year, albeit with less new capacity in Asia, and the summer hurricane season quickly wiped away any US surplus. A better understanding of the current cost curve and relative regional pricing can be found in our Weekly from Monday.