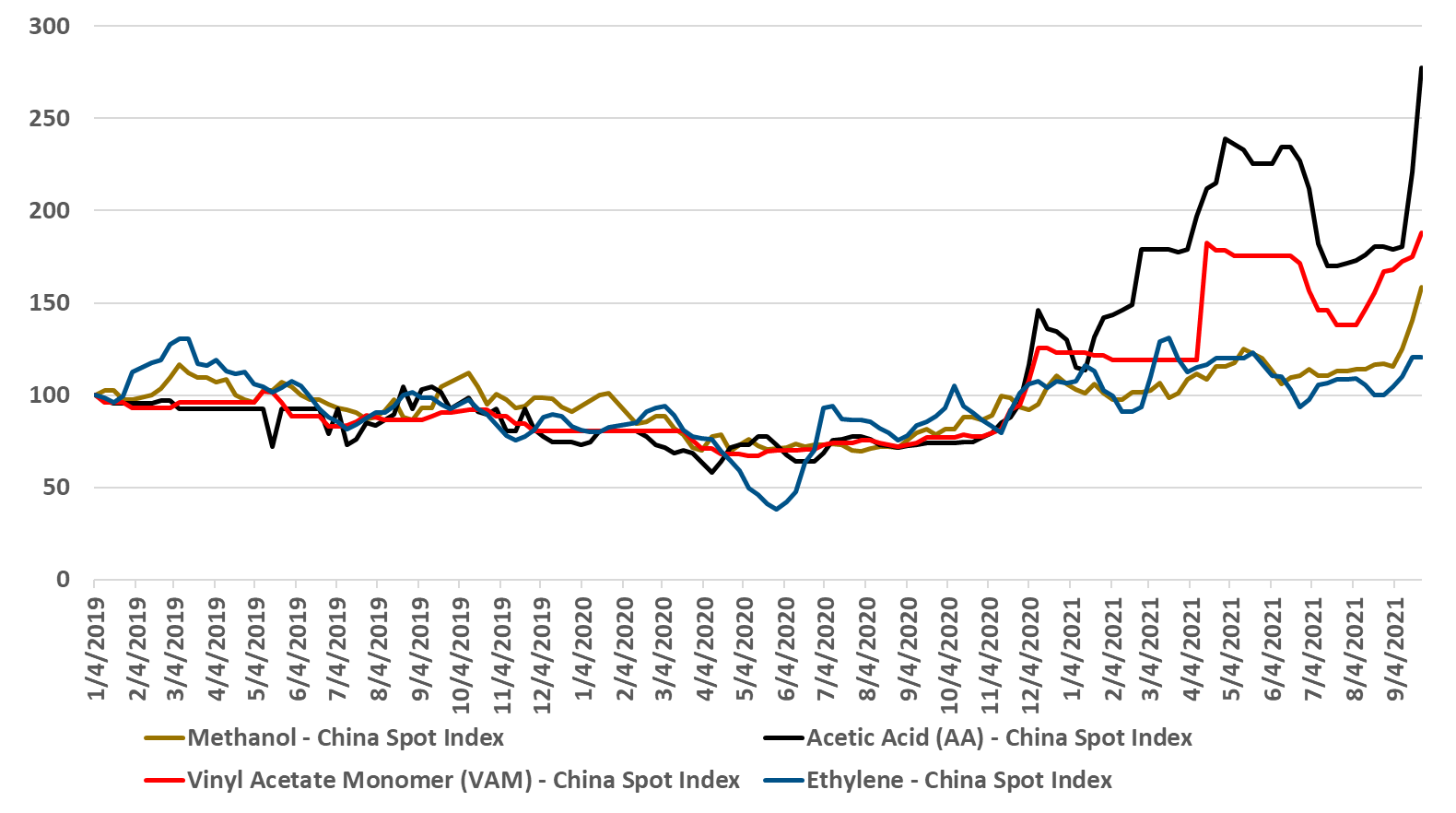
The move by China to reduce overall energy consumption is an effort to make progress on emissions but also to curtail energy demand where there is either a shortage or an over-dependence on coal-based power generation. The immediate impact in the acetic acid chain is clear from exhibit 1 in today's daily report.If these moves in China become more widespread they could reduce the significant near-term surpluses that the country has in polyolefins, PTA and PET. Why consume either expensive or high carbon power to make products that you currently cannot sell and that are either being sold at a loss or flowing into inventory? China has the structure to make decisions like this. Should this happen we could perhaps see a recovery in polyolefins pricing and PET pricing in China – as seen for the acetic chain in the exhibit below. Keeping production in line with the demand in China is important in the very near term as the fall out from the Evergrande collapse suggests that demand into the property market has been inflated and will likely correct negatively – increasing surpluses. China can force material into the export market, if it can find containers and if it is willing to operate at break-even margins. Better to curtail production.
Energy Issues In China Hurting Some Chemical Production
Sep 24, 2021 2:42:46 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polyolefins, Energy, Emissions, PET, PTA, Acetic Acid, Monomer, China, vinyl acetate, ethylene chain
2Q-2021 Likely To Be The Polymer Profits Peak, Weather Permitting
Apr 30, 2021 1:54:54 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Propylene, PVC, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Ethylene, Styrene, PET, PTA, Acetic Acid, Polyurethane, Glycol
We still believe that there is a good chance that 2Q 2021 is the peak for polymer profits in the US and Europe, but it very unclear how severe the downside could be, given the growth potential. Seasonal turnaround will keep markets more balanced in 2Q, and the major uncertainty beyond that will be weather in the US. A series of storms like last year could hold the market up through 3Q and into 4Q, but an absence of any weather events could expose US surpluses quite quickly, especially for ethylene and derivatives. The new builds in China have focused on ethylene and polyethylene (and some glycol), propylene and polypropylene, and PTA and PET, and this is where the potential weakness will emerge. There has been some new styrene capacity and that is also a vulnerable segment in our view. PVC, acetic acid, and large parts of the polyurethane chains look much more balanced to us and we have more faith in the projections being made by companies like Celanese, Olin, and Orbia than we do the major polyethylene producers. See today's daily report for more details.