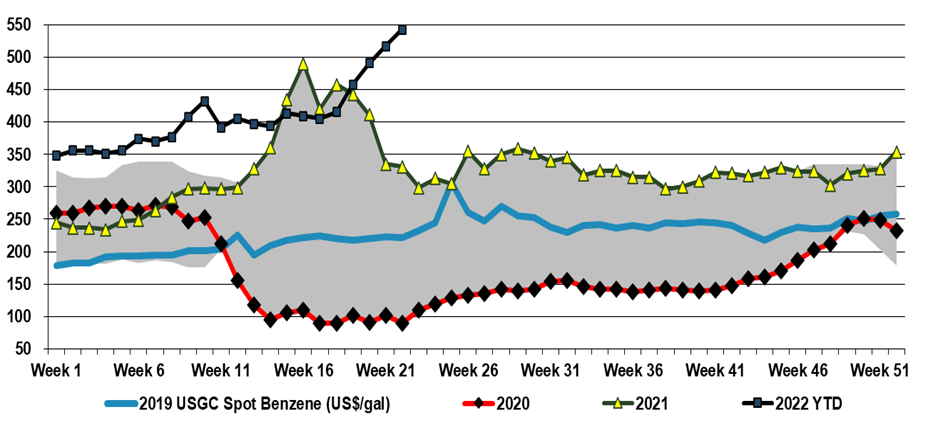
US benzene prices reflect both the net short market in the US but also the alternative value of reformate as a gasoline feed. While benzene is very limited in terms of how much can be left in fuel streams, its refinery-based feedstock, reformate, is a key component in gasoline – albeit low octane – prior to reforming and even during reforming the benzene conversion can be limited if the gasoline value is higher and volumes are constrained. In the US, as well as in many other parts of the world, we are facing gasoline shortages and today more than 13 US states have gasoline prices above $5 per gallon. While that may be shocking to Americans, the car ride from Heathrow yesterday was in a very popular make in the US that currently costs more than $200 to fill up in the UK! So benzene is getting squeezed – its feedstocks are more expensive and some of the alternatives to making benzene currently offer better netbacks. While we see all polymer costs rising in the US and elsewhere, this US benzene surge is not good for US polystyrene producers at a time when the industry is trying to justify polystyrene’s existence in a “circular” world, and it is also inflationary for the epoxy businesses, and other consumers of both styrene and phenol.
Benzene: Tightness Persists, Derivatives Mixed
Jun 7, 2022 2:47:09 PM / by Cooley May posted in Styrene, Benzene, Inflation, feedstock, polystyrene, polyurethanes, gasoline, US benzene, MDI, gasoline shortage, epoxy, phenol
Runaway Trains Into Weaker Demand?
May 13, 2022 1:40:50 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Propylene, Ethylene, Styrene, Benzene, US Chemicals, natural gas, manufacturing, EDC, ethylene glycol, demand, US chemical rail, ethylbenzene
The US chemical rail volumes should be considered in the context of some of the slowing demand that has been indicated by companies downstream of chemicals, and we see this as further evidence for possible inventory build through the chain. Earlier in the year these builds would have been justified by supply chain issues that have plagued all segments of retail and manufacturing for close to two years, but today we should be at or above inventory comfort levels. We are calling for weakness in demand and some margin erosion in US chemicals and polymers in 2H 2022, before a strong rebound as early as 2024, but if buyers of polymers and chemicals and their customers look to reduce inventories more quickly, the landscape could change quickly. While this is possible, with the threat of higher energy prices very real, we would be surprised in anyone was interesting in dramatically lowering inventories today.
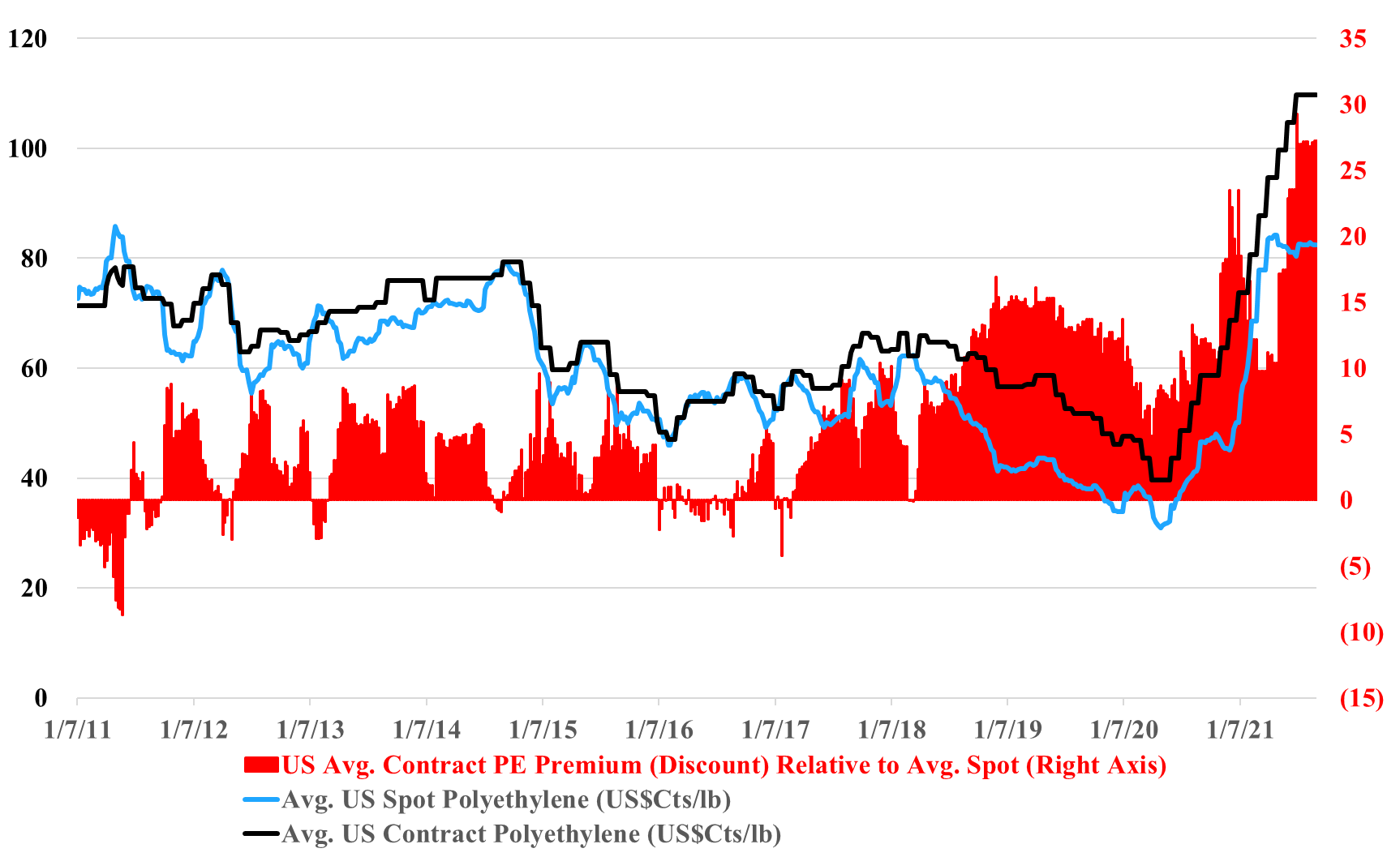
US Ethylene and Polyethylene: Instability From Many Directions
Sep 10, 2021 1:54:53 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Ethylene, Styrene, Dow, arbitrage, US ethylene, US polyethylene, ethylene glycol
The gap between the US contract and spot price for polyethylene in the exhibit below looks wrong, and it could be wrong in absolute terms but the trend alone makes a statement. In the past, we have seen a couple of instances where reported contract settlements have drifted further from net transaction prices, either because of larger agreed discounts or because of contract formulae that reflect spot pricing to a greater degree. This tends to work for a while, but ultimately smaller buyers with more limited purchasing power become more disadvantaged and there is a breaking point at which the “contract” price is adjusted downwards by the price reporting services to better reflect what is really going on. The current market feels like the times in the past when an adjustment has been needed.
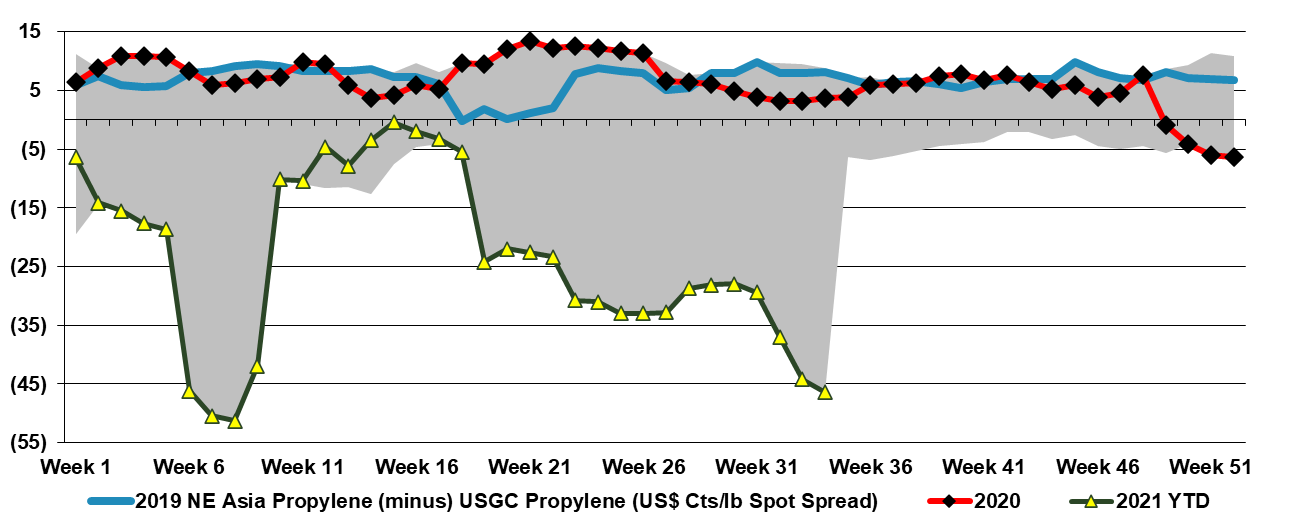
The Tale Of Two Regions: Asia Loose, US Tight
Aug 26, 2021 12:49:40 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Polyolefins, Propylene, Styrene, PET, Surplus, polymer producers, US Polymers
China trade data for chemicals and polymers points to a dramatic swing in net imports, partly due to the new capacity added over the last 12 months. Imports are down, and exports are up. Despite the logistic challenges of moving the products and the powerful pull on consumer durables from China driven by US and European demand – much of which consume significant volumes of polymers and chemicals locally. The trade swings talk to the significant capacity additions and the relatively sluggish consumer within China, where spending patterns remain subdued because of the Pandemic. Even with a recovery in domestic spending, China has probably added 2 to 3 years of demand growth in current capacity adds – most notably for polyolefins and PET, but also for styrene, where we believe demand growth could be slowing. If logistics improve and container rates come down, the surpluses in China will have a severe negative impact on international prices. This development will likely be seen in either polymer quantities flowing faster/more freely around the globe or because the export rate of consumer durables will pick up even further at the expense of durable producers in the US and Europe.
ExxonMobil, SABIC JV Petrochemical Project Runs Ahead of Schedule
Jul 27, 2021 3:41:21 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polyethylene, Ethylene, Styrene, ExxonMobil, petrochemicals, petrochemical capacity, Dow, Sabic, Gulf Coast Growth Ventures, Aramco, Motiva, NPV, chemical plant, ethylene plant
ExxonMobil Chemicals has announced that its Corpus Christi JV project with SABIC is ahead of its original schedule – ExxonMobil is now targeting a start-up in 2H21, ahead of its previously targeted 1H22 expectation. It is unusual for projects in the US to be ready ahead of schedule these days, and start-up delays tend to be the norm. We also take a positive view of this development upon comparison to the Shell Pennsylvania project, which still has a vague 2022 start-up expectation though its construction began before ExxonMobil. One could argue that the remoteness of the location – well away from petrochemical infrastructure has been a constraint for Shell, but the Corpus Christi location is also a greenfield project for ExxonMobil/SABIC. This will be the largest ethylene plant built in the US, though it is likely that the recent 1.5 million ton units (Dow, ExxonMobil, CP Chem) are expandable to 2.0 million tons. Dow is already discussing such a move with a new polyethylene facility at Freeport. It will be interesting to see what impact this ExxonMobil/SABIC facility has on both the USGC ethane market and the polyethylene market – 1.3 million tons of polyethylene is a large increment and SABIC will have half of the capacity and will be a new market entrant with on-shore production. Aramco has ethylene, through Motiva’s purchase of Flint Hills, and SABIC owns half of the Cosmar styrene plant in Louisiana.
The Wrong Time To Build Styrene Capacity
Jul 2, 2021 12:22:35 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Styrene, polystyrene, packaging polymers, durables markets, styrene derivatives, Kraton
We think the India styrene plan is ill-advised. The styrene market has had a brief moment in the sun over the last couple of years, but we believe that it has another leg down ahead, based on the recycling complications of polystyrene versus other packaging polymers. New capacity in China and likely weaker demand in the US and Europe should push the global market into oversupply for a prolonged period (if not permanently). This is bad news for styrene (or polystyrene) producers but very good news for the non-integrated producers of styrene derivatives targeting the durables markets – such as Kraton.
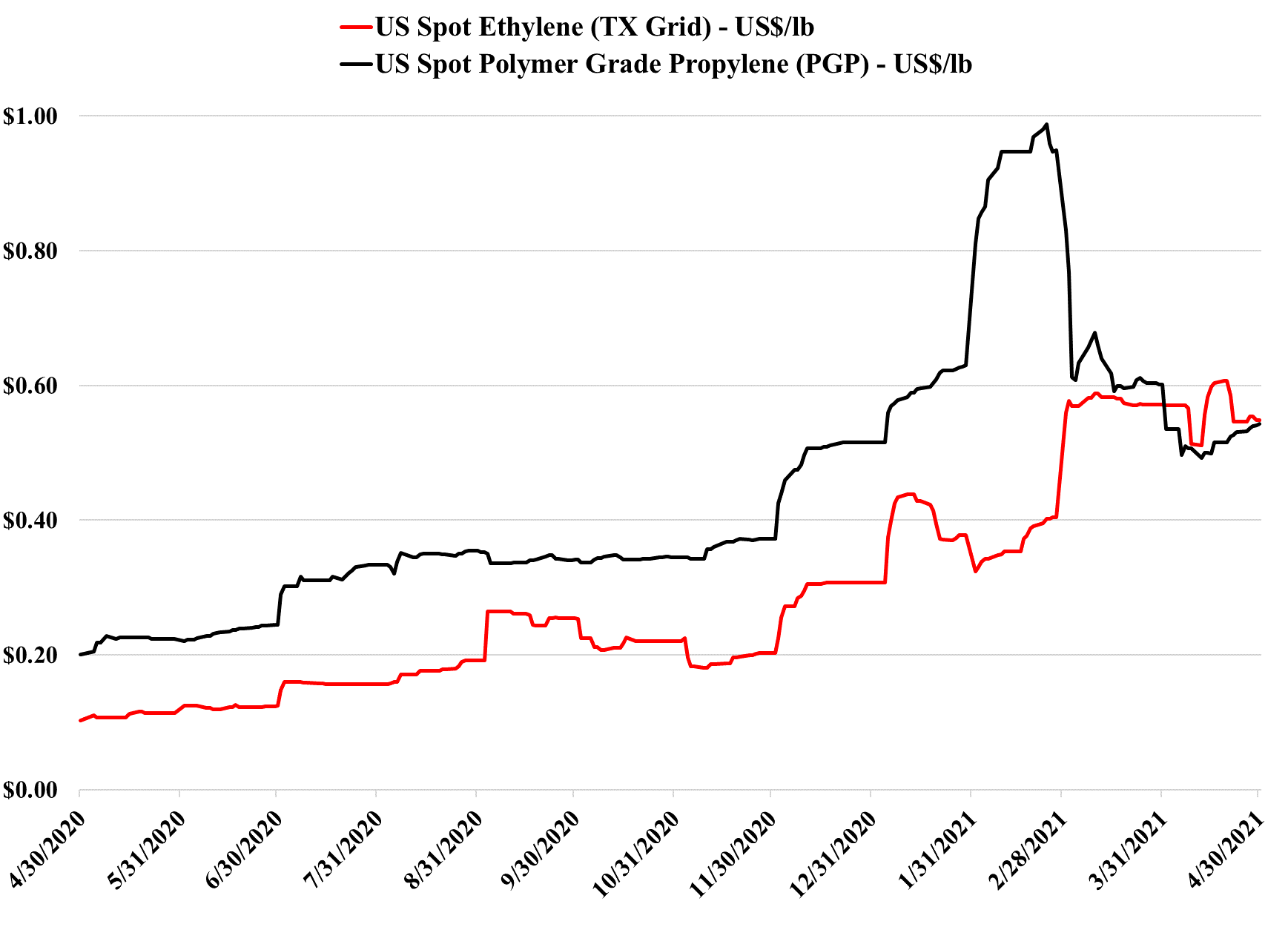
2Q-2021 Likely To Be The Polymer Profits Peak, Weather Permitting
Apr 30, 2021 1:54:54 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Propylene, PVC, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Ethylene, Styrene, PET, PTA, Acetic Acid, Polyurethane, Glycol
We still believe that there is a good chance that 2Q 2021 is the peak for polymer profits in the US and Europe, but it very unclear how severe the downside could be, given the growth potential. Seasonal turnaround will keep markets more balanced in 2Q, and the major uncertainty beyond that will be weather in the US. A series of storms like last year could hold the market up through 3Q and into 4Q, but an absence of any weather events could expose US surpluses quite quickly, especially for ethylene and derivatives. The new builds in China have focused on ethylene and polyethylene (and some glycol), propylene and polypropylene, and PTA and PET, and this is where the potential weakness will emerge. There has been some new styrene capacity and that is also a vulnerable segment in our view. PVC, acetic acid, and large parts of the polyurethane chains look much more balanced to us and we have more faith in the projections being made by companies like Celanese, Olin, and Orbia than we do the major polyethylene producers. See today's daily report for more details.
BASF Makes Industry Standard ESG Pledges While Styrene Heads for a Brick Wall
Mar 26, 2021 12:00:26 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Styrene
A couple of headlines stand out today but the BASF capital markets day is probably not one of them. This is now becoming the norm; to provide an investor update tailored at focusing on clean energy and sustainability goals, and BASF’s expectations are not much different from others – there is a bold claim about 2050 and some harder targets by 2030. So far we have yet to see one of these presentations where the math is believable, and the investment targets in dollar terms all seem too low to meet a net-zero goal. To be fair, it is hard to know what will happen in 5 years, let alone from 2030 to 2050, and we would doubt that anyone has a good estimate today. BASF and others will likely end up spending multiples of what they currently project, but this may not be a bad thing – much of the spending will be backed by incentives (or encouraged by penalties) and all of the spending will be good for jobs and economic growth.