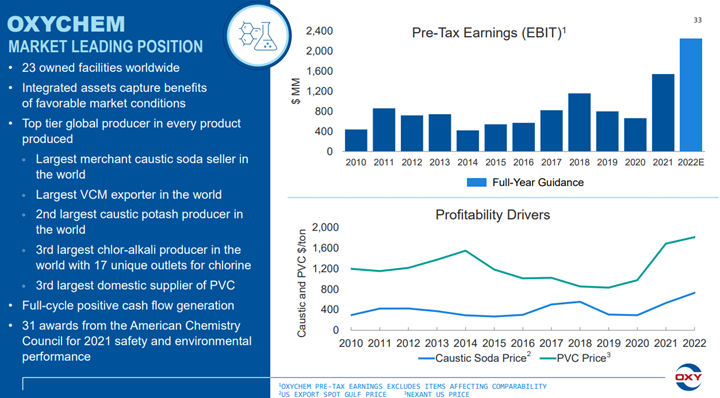
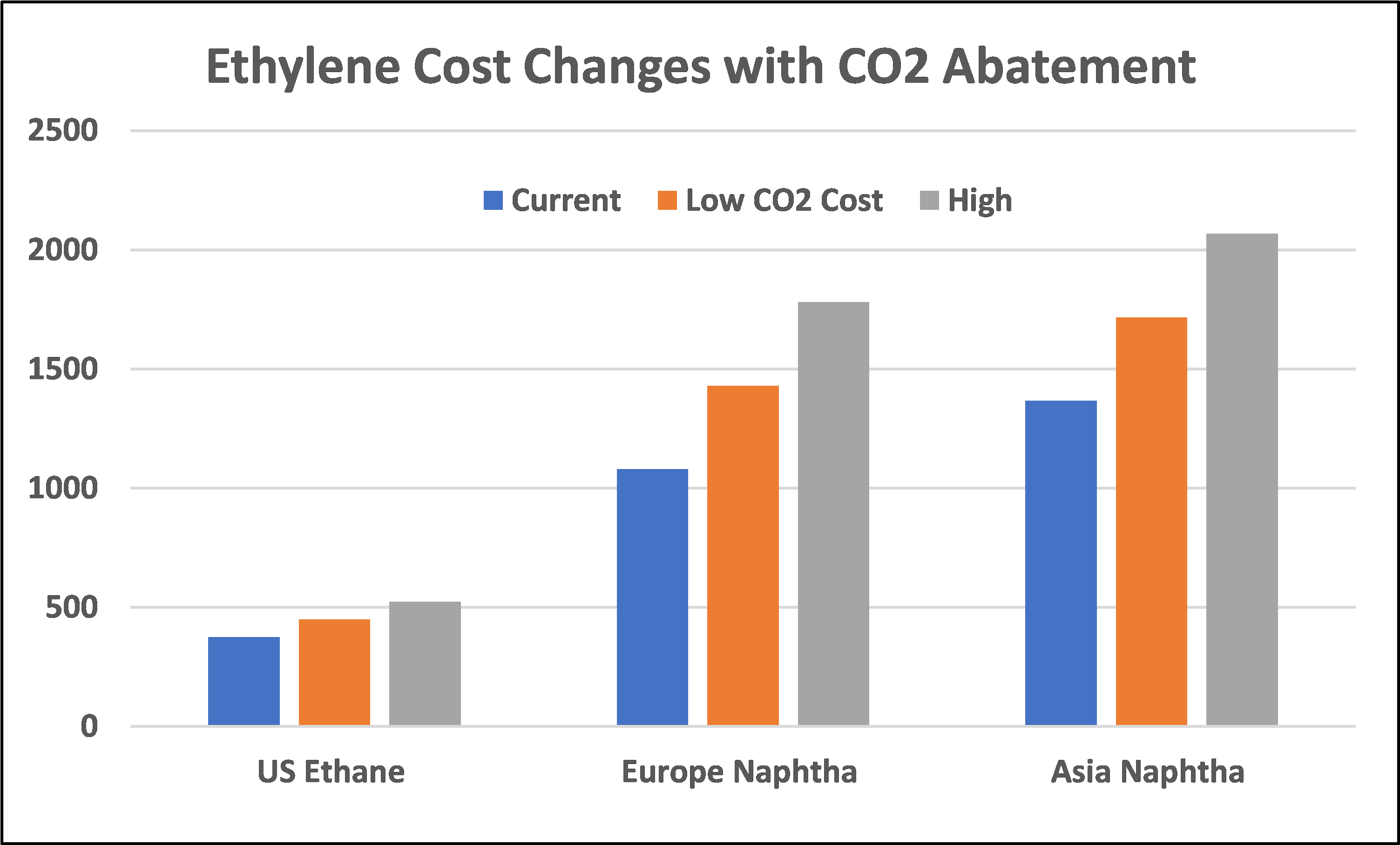
For those who are too young to remember, OxyChems’ 30-year comment is because the company owned ethylene capacity in the late 80s and early 90s and would have made more during that extreme ethylene peak. This is likely the most money that the stand-alone vinyls business has made. The strength in the PVC could see some reversal if the inflation pressure remains high and housing-related spending slows, but the strength in the caustic market could persist, regardless of economic growth because of structural shortages and the challenges with imports.
The Vinyls Chain Shines, Elsewhere We See Warning Signs
May 11, 2022 1:11:52 PM / by Cooley May posted in PVC, Polyethylene, LyondellBasell, Inflation, polymer, ethylene capacity, shortages, ICL, Oxy, vinyls
Refinery Propylene Remains A Cheap Source, If You Can Find It...
Dec 15, 2021 2:09:46 PM / by Cooley May posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Polymers, Propylene, Polypropylene, Emissions, CP Chemical, carbon footprint, ethane, PDH, ethylene capacity, polypropylene demand, refinery, Refinery Propylene, ethylene demand, surplus refinery propylene, polymer recycling, propylene splitter
The CP Chem propylene splitter announcement linked suggests that CP Chem expects surplus refinery propylene to be around for the long-term, and likely has supply lined up from the parent companies. However, this is still a bit of a gamble unless both parents see a scenario where they would change catalysts on FCC units longer-term and run at higher severity for more propylene and more hydrogen. This project looked a lot better only a few weeks ago than it does today – based on the spread in the Exhibit below, but propylene demand continues to grow faster than ethylene demand in the US and with all incremental ethylene capacity based on ethane, propylene consumers either have to choose the path from refineries or invest in on purpose PDH. PDH is an energy-intensive process with a large carbon footprint, and splitting refinery propylene likely looks far less problematic from an emissions perspective, especially if there is surplus process heat on-site. In our ESG report today we talk about polymer recycling into new end markets, but polypropylene may see more direct substitution, especially if we see consumables related polypropylene recycled into durable polypropylene markets. This might dent demand growth for polypropylene going forward, but probably not meaningfully.
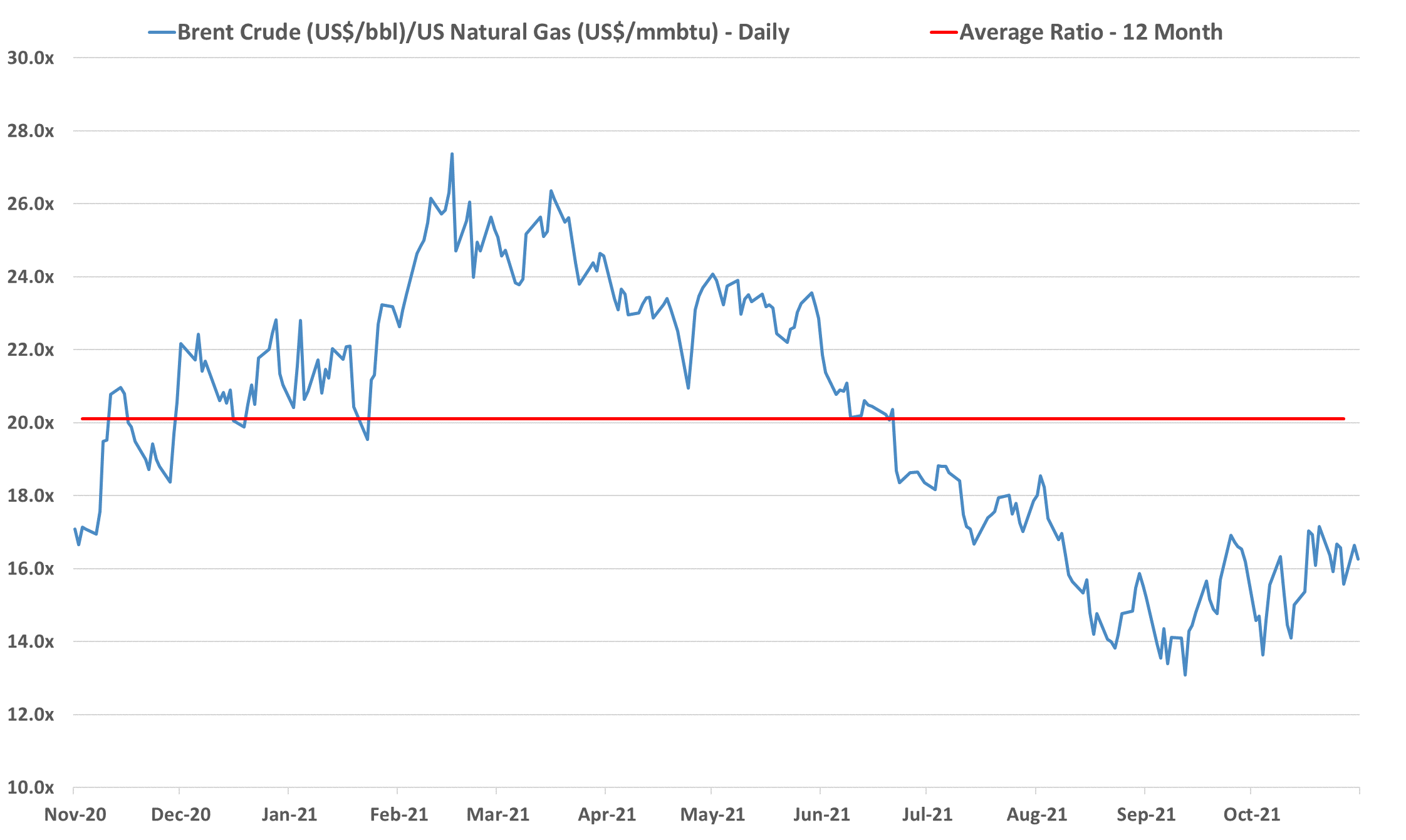
Is A Feedstock Shock In The Cards For US Chemicals?
Nov 23, 2021 1:39:28 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Crude, LNG, Energy, Emissions, petrochemicals, propane, carbon footprint, feedstock, ethane, natural gas, ethylene capacity, E&P, NGLs, exports, shortages, chemicalindustry, Brent Crude, butane, Mexico, fuels
We remain concerned that natural gas E&P investment in the US remains too low to meet expected demand increases, especially for natural gas-fired power stations and LNG, but also possibly for NGLs, especially ethane, given new ethylene capacity and a fresh export market in Mexico. Near-term, natural gas prices are showing some easing relative to crude, albeit a very volatile trend – Exhibit below – but we see medium and longer-term shortages unless E&P spending increases. The new power facilities shown in the bottom Exhibit will all need incremental natural gas, and the international LNG market is so tight that as new capacity comes online in the US we would expect it to run as hard as is possible. This sets up for a market where the clearing price of natural gas in the US is at risk of being set by the marginal exporter. The price jump for domestic consumers would be dramatic and it would cause all sorts of headaches in Washington and probably intervention. We showed the incremental natural gas price in the Netherlands in our Daily Report on November 18th, and if the US price were to reflect the netback from this level, they would rise close to $30 per MMBTU. The natural gas industry needs some sort of global blessing to continue to operate as what will likely be the core transition fuel. It will be necessary to clean up the emissions footprint of natural gas, but the industry should be encouraged to invest on this basis. For those who doubt whether the US natural gas price can rise to $30/MMBTU – note that the Europeans did not think $30 was possible either.
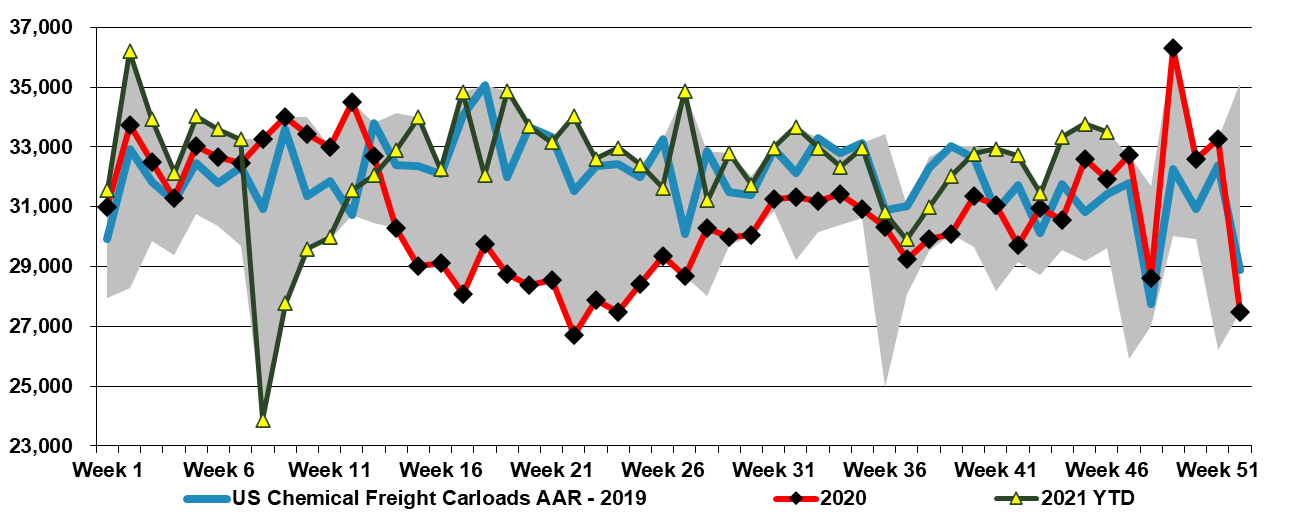
Chemical Supply Increases And US Prices Weaken
Nov 19, 2021 12:35:27 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, PVC, Polyethylene, Plastics, Polypropylene, ExxonMobil, polymer buyers, railcar shipments, Supply Chain, Dow, propane, PDH, ethylene capacity, US polymer prices, US Polymers, propylene prices, energy prices, chemicalindustry, plasticsindustry, spot market, cost arbitrage
US rail data for chemicals remain at the 5-year highs and have been there for almost 2 months. This is working its way into the supply chain and we are seeing weakness in US polymer prices across the board, except for PVC. US spot polymer prices are in a bit of a “no man's land” right now as they would need to drop significantly to find incremental demand offshore, given US premiums to the rest of the world. We believe that most of the volume leaving the US is doing so within company-specific businesses – ExxonMobil supplying ExxonMobil customers, Dow supplying Dow customers, etc, and consequently, these shipments do not show up in the spot market.
Relative To The Chemical Inflationary Cycle Of The ’70s, Present Times Reflect Similarities But Some Major Differences
Nov 17, 2021 2:47:40 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, LNG, Plastics, Ethylene, ExxonMobil, raw materials inflation, Inflation, feedstock, Borealis, ethylene capacity, crude oil, shortages, chemicalindustry, plasticsindustry, Adnoc, OPEC+, oil prices, Investments
The linked article looks at the chemical inflationary cycle of the 70s, which has some relevant indicators for what we are seeing today, but there were also some stark differences. Rising raw material prices is a common theme and while it is convenient to blame OPEC+ this time, the group is not nearly as much to blame today as it was in the 70s. Consumers were facing not just higher oil prices, but also genuine shortages because of the OPEC cutbacks and the multi-year lead times that it took non-OPEC producers to ramp up E&P and ultimately production. This time the oil is there and relatively easy to get to, especially in the US, but the capital spending decisions of the US oil producers – mostly because of ESG related pressure – are holding back the production.
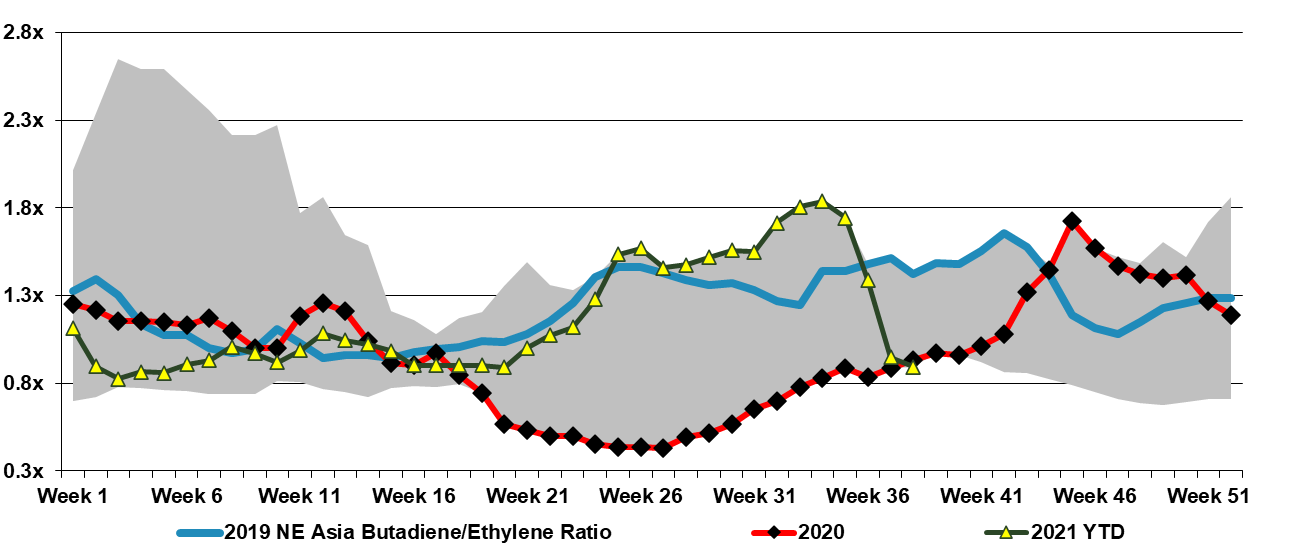
Butadiene in Asia: Too Much Supply & Not Enough Demand
Sep 23, 2021 1:32:20 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Butadiene, Asia prices, ethylene capacity, butadiene supply
The recent collapse in Asia butadiene prices, as implied in the charts below is likely mostly supply-driven, given all the new heavy feed ethylene capacity that has been added in China and its impact on associated butadiene supply. On the demand side, there are negative impacts both from the overall slower growth in China and from the forced cutbacks in auto production because of the semiconductor shortages – ultimately this feeds back into tire demand. Further, with the Delta variant slowing consumer activity in Asia this has likely resulted in below trend tire replacement. See more in our daily report.
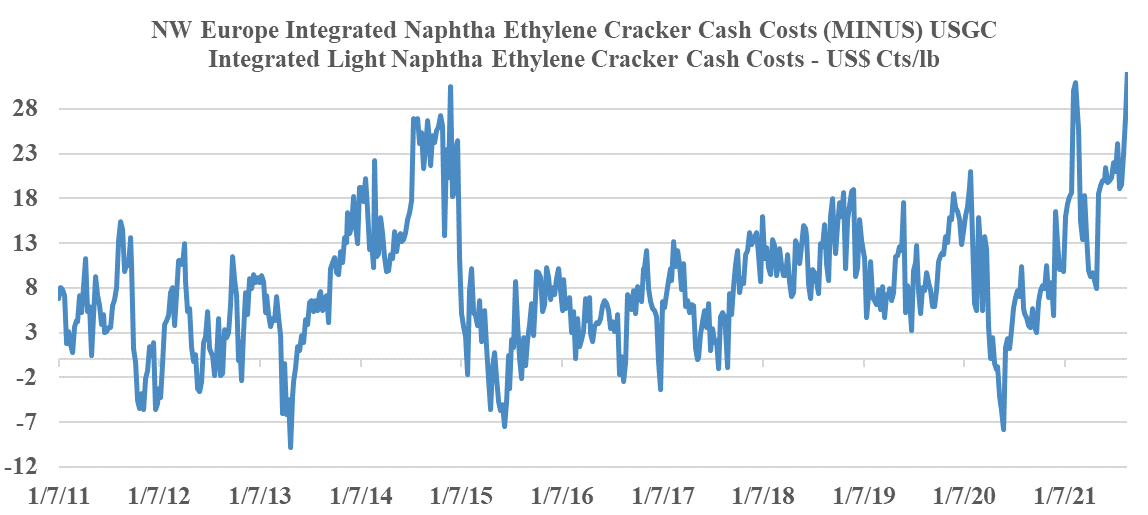
US Ethylene: Flexibility Has Lessened, Despite More Funds Available
Aug 24, 2021 12:59:27 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Ethylene, Butadiene, LyondellBasell, Dow, feedstock, ethane, US ethylene, naphtha, ethylene capacity, light naphtha
Before the wave on new ethylene capacity came online in the US there were several low-cost expansion projects all of which added the ability to crack ethane and some of which brought constraints around feedstock flexibility. Consequently, it is less clear than it used to be just how much US ethylene capacity can flex to exploit the very attractive light naphtha economics today. Very conservatively, we would estimate that 5-6 million tons of capacity can flex easily and about the same again with some planning and some logistic adjustments. Among the public companies, both Dow and LyondellBasell are well placed, and likely have at least 1 million tons each of flexible capacity – in both cases, there is a need for propylene and LyondellBasell has significant butadiene/C4s capacity. For context, at current prices, both companies are likely looking at an additional ethylene margin benefit in the US of $2.5-3.0 million per week for as long as this opportunity exists. This would be 0.3 cents per share per week for Dow and 0.7 cents per share per week for LyondellBasell – a rounding error in current earning but more free cash regardless. The chart below shows the unprecedented benefit in the US and see our daily report for more.
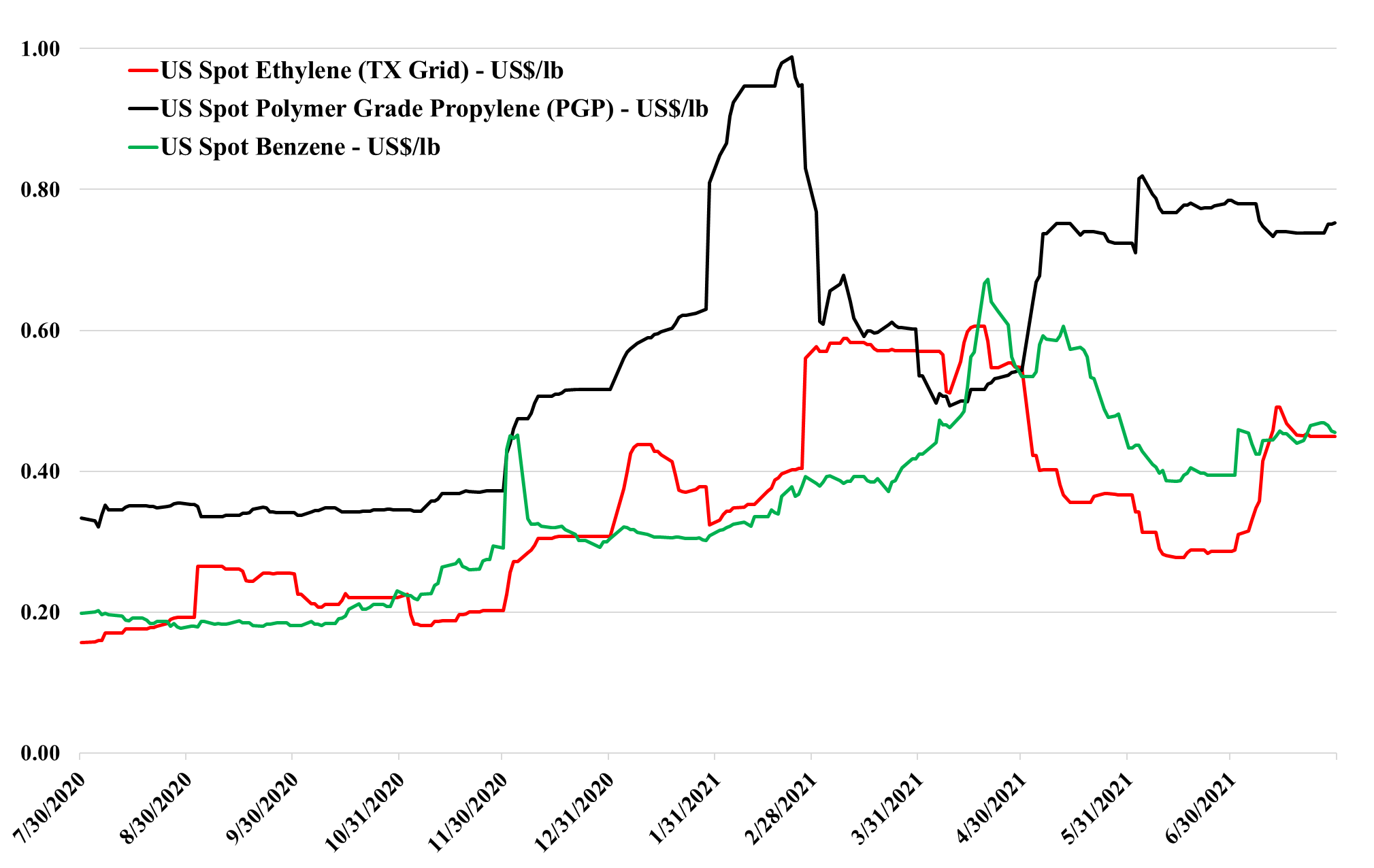
Ethylene To Stay Volatile: Sizable Price Swings Likely
Jul 30, 2021 3:15:12 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Ethylene, feedstock, ethane demand, ethylene capacity
We focus on ethylene price trends today, as we discuss it’s movement and related ethane tightness in today's daily report – more operating ethylene capacity means more ethylene (depressing prices) but it also means more ethane demand, inflating its price. Margins remain robust, even with the feedstock increase and the price decline and it is important to remember that any decline in US ethylene prices would be stopped at a level that allowed increased exports, which would still be well above US costs. With the full ethylene fleet operating in the US, there is a surplus (i.e. more ethylene than there is consuming capacity) so we expect export economics to drive spot pricing under “normal” circumstances. Abnormal production outages over the last year have seen that export surplus come and go a couple of times and the price volatility the Exhibit below shows that.