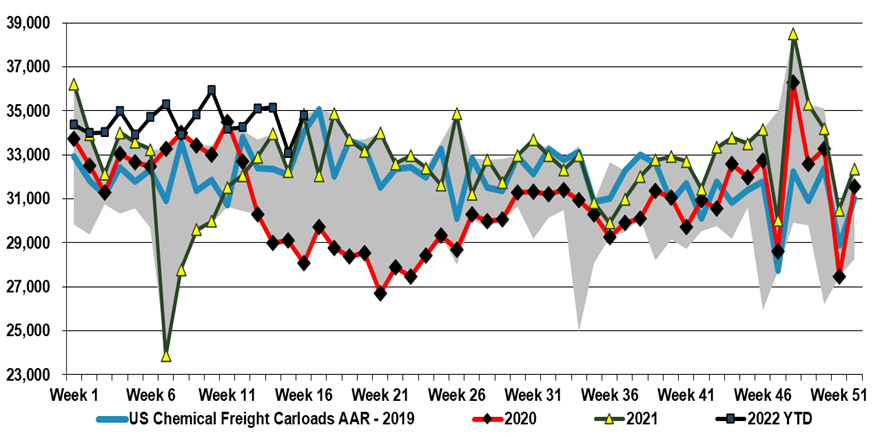
The US chemical rail volumes should be considered in the context of some of the slowing demand that has been indicated by companies downstream of chemicals, and we see this as further evidence for possible inventory build through the chain. Earlier in the year these builds would have been justified by supply chain issues that have plagued all segments of retail and manufacturing for close to two years, but today we should be at or above inventory comfort levels. We are calling for weakness in demand and some margin erosion in US chemicals and polymers in 2H 2022, before a strong rebound as early as 2024, but if buyers of polymers and chemicals and their customers look to reduce inventories more quickly, the landscape could change quickly. While this is possible, with the threat of higher energy prices very real, we would be surprised in anyone was interesting in dramatically lowering inventories today.
Runaway Trains Into Weaker Demand?
May 13, 2022 1:40:50 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Propylene, Ethylene, Styrene, Benzene, US Chemicals, natural gas, manufacturing, EDC, ethylene glycol, demand, US chemical rail, ethylbenzene
Overall Inventory Worries Hide Some Interesting Focused Upside
Apr 28, 2022 4:24:25 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Methanol, Energy, freight, US Methanol, US Polymers, Methanex
Chemical railcar volumes remain very strong in the US, despite some issues with exporting polymers, which has led to inventory builds on the coast, especially the Gulf Coast, and despite the implied consumer volume purchase decline in 1Q GDP estimates (sales grew but prices rose 500 basis points more than sales growth – suggesting an equivalent decline in volumes). As we noted yesterday, some companies closer to the consumer are indicating demand weakness and are more cautious about 2Q outlooks. If a higher than usual proportion of rail freight is moving into inventory, either at customers or stuck in rail cars – something Union Pacific has signaled – we could see a correction.
Some Prices Are Keeping Up With Costs But Shipping Remains Challenging
Apr 26, 2022 1:42:08 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Axalta, Inflation, Prices, shipping, specialty chemicals, basic polymers, container freight rates, logistic constraints, Costs, Mobility
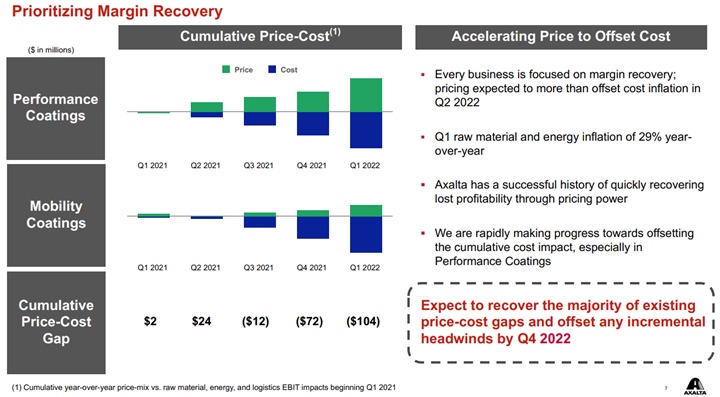
Axalta shows a helpful picture below of how pricing and costs are moving. All coatings producers are seeing the same cost inflation, some of it energy/hydrocarbon input related and some of it supply chain-related – either for inputs such as pigments or higher costs of getting products to markets. How pricing looks relative to costs is very customer dependent, as shown in the chart below. Auto OEM customers have long lead times on price adjustments and this is why Axalta is signaling the end of the year before prices will be aligned with costs. This of course assumes that costs do not rise again in 2H 2022 as they will also drive a lag in price increases and create a further gap as shown in the “Mobility” bar below. In the more consumer-facing coatings, it is easier to raise prices more quickly and Axalta and others have managed to keep pace with costs. We see the pricing versus costs issue as a much greater headwind for the specialty chemical companies than for the commodity companies and the industrial gas companies – the commodity chemical companies can raise prices more quickly and most industrial gas pricing is on a cost pass-through basis.
Industrial Products: Plastic Prices Reflect Support, Recycled Resin Prices Advance
Apr 13, 2022 2:44:51 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Industrial Sector, HDPE, plastic resin, materials, resins, polypropylene recycling
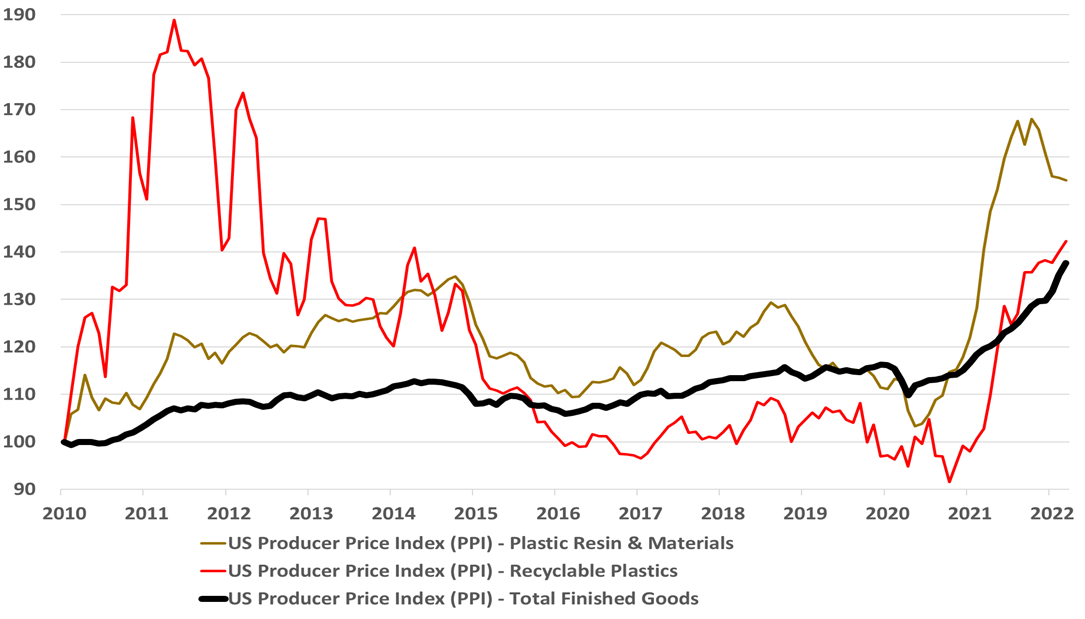
It is important to note from the chart below that the US plastic resin price index is out of phase with the overall industrial products markets as we saw a shortage driven peak in 2021 – largely weather and supply chain-related. The US on average continues to command resin price premiums relative to Asia. The China polymer surpluses are largely land-locked for now because of very high shipping costs and very high oil-based production costs, and the US surplus is also challenged because of logistic issues with exports. In the US, exporters are building inventory in anticipation of better logistics and on the basis that the surpluses for the most part have customers. If we do see a global slowdown in demand, triggered by inflation – see our most recent Sunday Recap – the inventories in the US and China could become a problem.
The PVC Market Is Compelling - One Of The Most Attractive Global Polymer Stories
Apr 7, 2022 1:39:50 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, PVC, Basic Chemicals, Westlake, US Polymers, mega-cycle
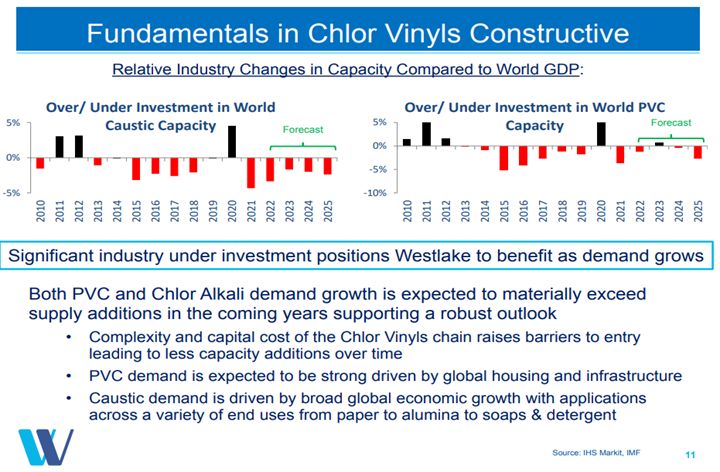
The margin weakness in PVC, as shown in Exhibit 1 from today's daily report, suggests that the market might be weakening, but higher prices would suggest that it is not. The integrated margin weakness is mostly the result of rising costs, and the US PVC market may be strong enough to allow producers to pass on these costs fully over time. We still see PVC as the least risky way to play the US polymers market as infrastructure and manufacturing investments should keep demand strong even if we see a decline in consumer durable related spending. The Westlake chart below highlights one of the primary drivers behind our mega-cycle view – no new capacity. The supply shortfalls that are implied in the chart will be mirrored in other basic chemicals in our view but PVC is likely the most acute example – creating what could be a prolonged period of strong margins for the industry.
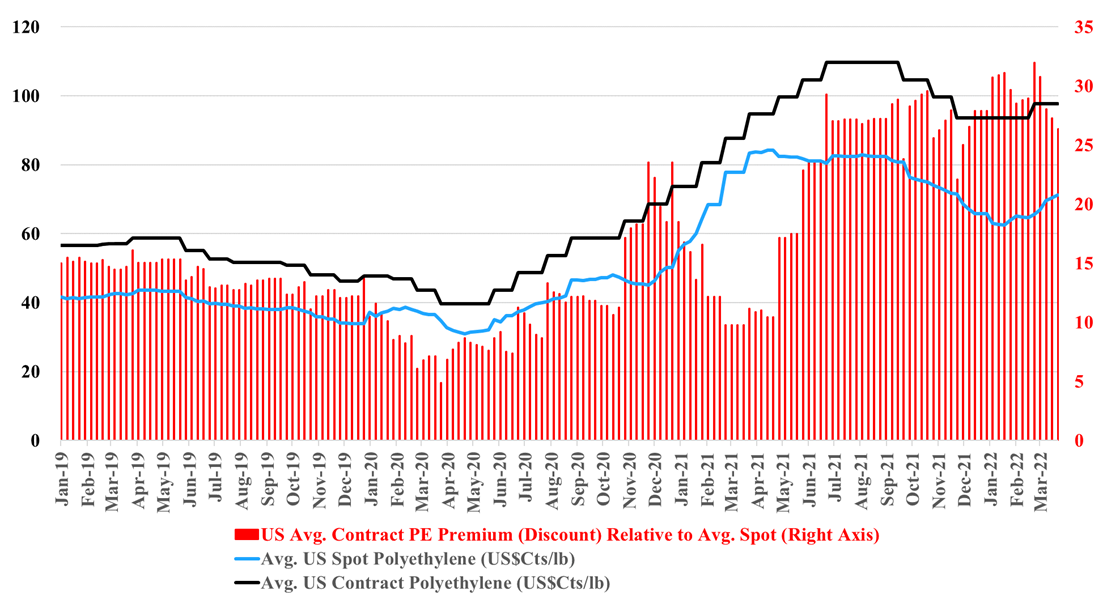
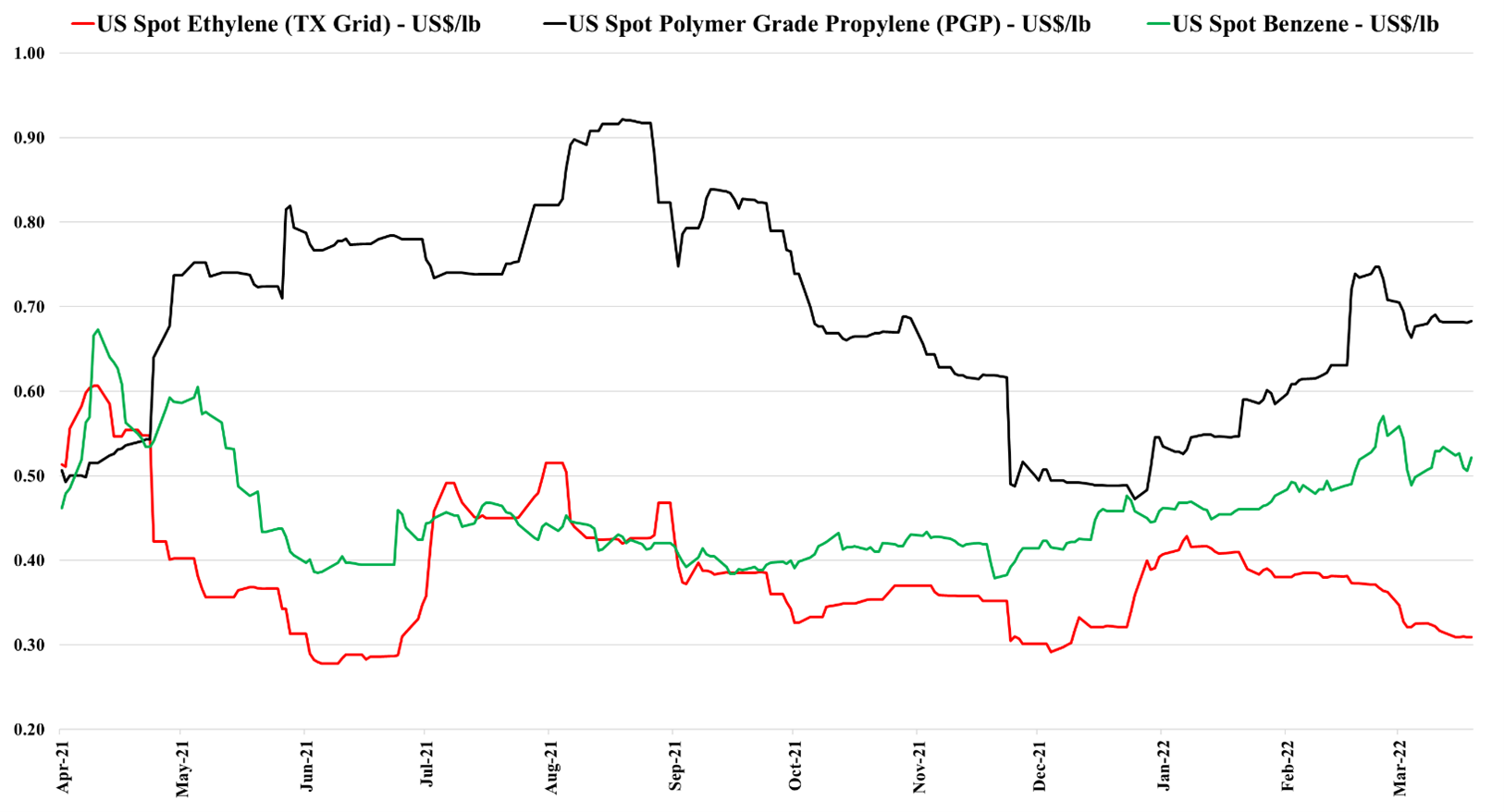
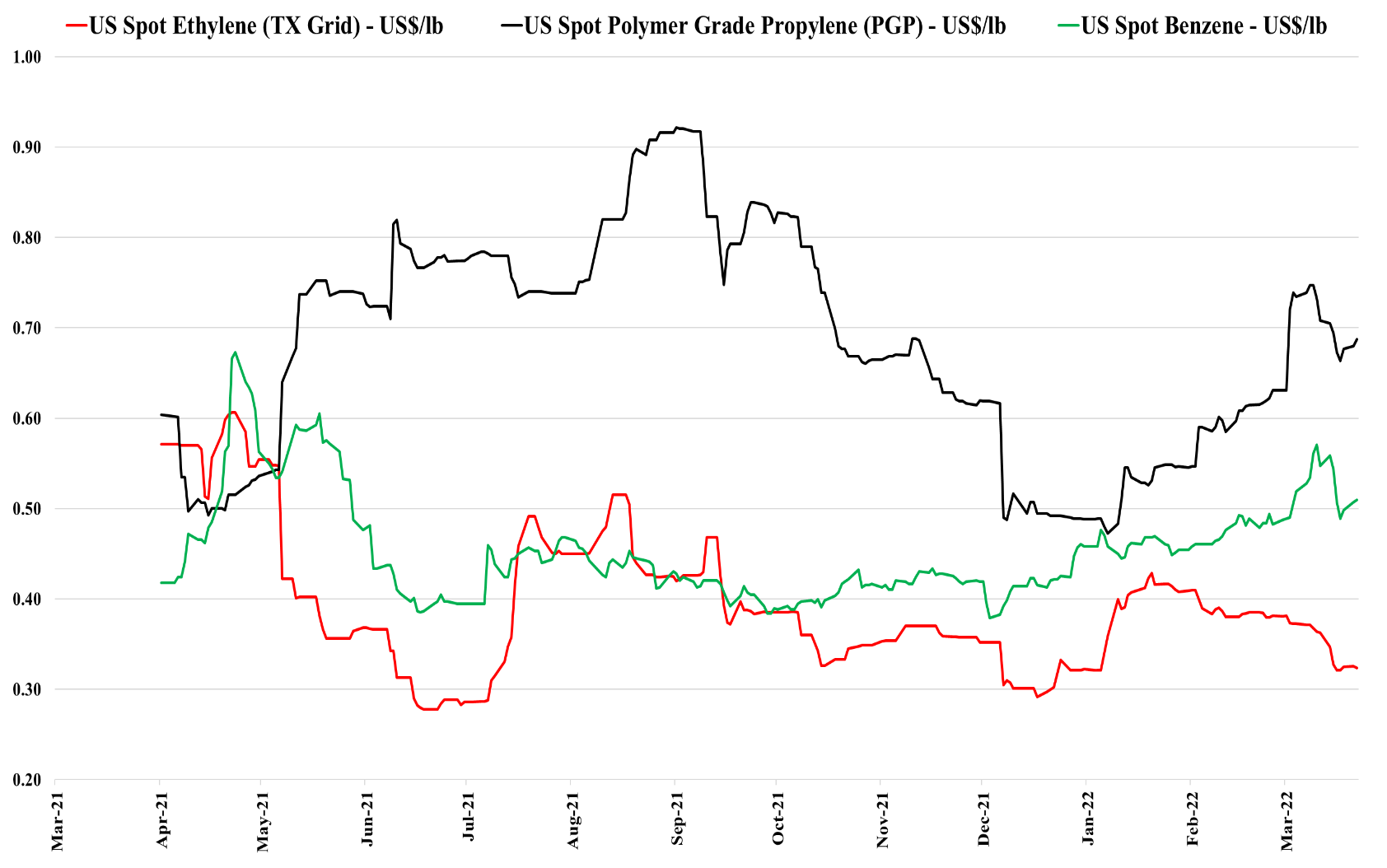
Polyethylene Back To The Future
Apr 5, 2022 1:03:31 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, Ethylene, Chemical Industry, PE, basic polymers
It's back to 2012/2013 for polyethylene, but with a potential twist. As we noted in today's daily report, international prices for polyethylene are being pushed up by oil prices, and even with higher prices in Asia, margins are still negative locally, which suggests that they will go higher. This margin umbrella is what generated windfall profits for US and Middle East producers in 2012, 2013, and half of 2014. The upward pressure remains high for international polyethylene prices because producers are not covering costs locally and in theory, the US should continue to benefit and we see domestic polyethylene prices rising again, both contract and spot. The risk for the US is local overcapacity of polyethylene and potential export challenges. The pricing arbitrage to export US polyethylene is huge and rising, but we are in a constrained trade world and we understand that export terminals are at capacity and warehouses are full. It is possible that the sharply lower US ethylene price is not just a function of new ethylene capacity, but also a function of integrated polyethylene producers choosing to limit production and looking for homes for the extra ethylene. If the polyethylene producers in the US try to push more volume domestically we could see local prices fall well below their export alternative – this is possible, but unlikely, in our view. Polypropylene does not have the same significant net export and the two plant closure in the US are likely enough to drive the price support that we are seeing this week.
Europe: Short Of Chemicals But Logistics Limit Help
Apr 1, 2022 3:34:45 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Ethylene, BASF, Logistics, energy costs, Europe
The BASF commentary about the impact of gas cuts in Europe should not be read as specific to BASF, but as we move out of the winter in Europe it is less likely that countries will directly restrict industry in favor of retail customers should gas supplies become limited. While many European countries will try to protect retail customers from hyperinflation in energy costs, their ability to do that for the industry might be more limited as they cannot find the additional gas, and subsidizing everything would be fiscally irresponsible. We expect to see more basic chemicals and derivatives moving from the US and the Middle East to Europe to displace uneconomic local production, but we understand that all shipping capacity is now constrained – liquids, gases, and containers – limiting the volumes that can move. The high end of the cost curve that Europe has occupied for decades in chemicals means that exports from Europe have been very limited and reducing exports is not a balancing act tool that Europe has to play with. We continue to see significant upward pressure on prices in Europe and the jump in inflation in the region, reported today, was dramatic but could accelerate as there are very few corrective levers that Europe can pull right now.
A Chemical Mega-Cycle Is Coming
Mar 22, 2022 12:55:58 PM / by Cooley May posted in Hydrogen, Chemicals, Polymers, Ethylene, polymer pricing, downstream, renewables, EV, Aramco, monomers, crude oil, fuels, mega-cycle
We have talked at length in today's daily and recent Sunday recaps about our expectation for a mega-cycle in chemicals because of an unwillingness to deploy capital as uncertainty rises. The exception is likely to be large oil producers looking at long-term downstream integration plans, with the primary objective of consuming captive crude oil. The Aramco ambitions in China bear some similarities to the ExxonMobil investment announced for China last year. While the crude oil market may be tight and prices may be high today, few oil producers believe that demand will not ultimately be hurt by renewable penetration and EV and hydrogen growth as transport fuels. Looking for captive crude oil demand is a logical step for the major and it is likely that the Aramco ambitions include refining as well as chemicals in China.
If You Are In The Right Place With The Right Products, Times Are Good
Mar 18, 2022 12:19:25 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Polyethylene, Polypropylene, LyondellBasell, Inflation, Dow, US Chemicals, natural gas, Basic Chemicals, Westlake, Braskem, US Polymers, commodity chemicals, demand strength, raw material, silicone
As we have been suggesting for some time, there are pockets of real strength in chemicals; identifying them is the hard part. It is not enough to have pricing strength in a market where raw material prices are volatile daily and we have seen plenty of examples of companies with very strong end demand dynamics missing earnings because of a cost squeeze. We continue to highlight the competitive strength in the US in basic chemicals because of the decoupled and relatively low natural gas price and this is likely a large piece of the Dow earnings strength – strong polyethylene demand against a backdrop of relatively stable and lower costs. While polypropylene (Braskem) remains extremely profitable in the US, it has seen more sequential weakness than polyethylene – as we show in Exhibit 1 of today's daily report. That said, both polyethylene and polypropylene margins in the US are significantly higher than was likely expected this year and certainly what has been reflected in stock valuations, even with the commodity chemicals rally. Dow is also seeing the benefit of a very strong silicones market – something that was covered in detail in Wacker’s release earlier this month.
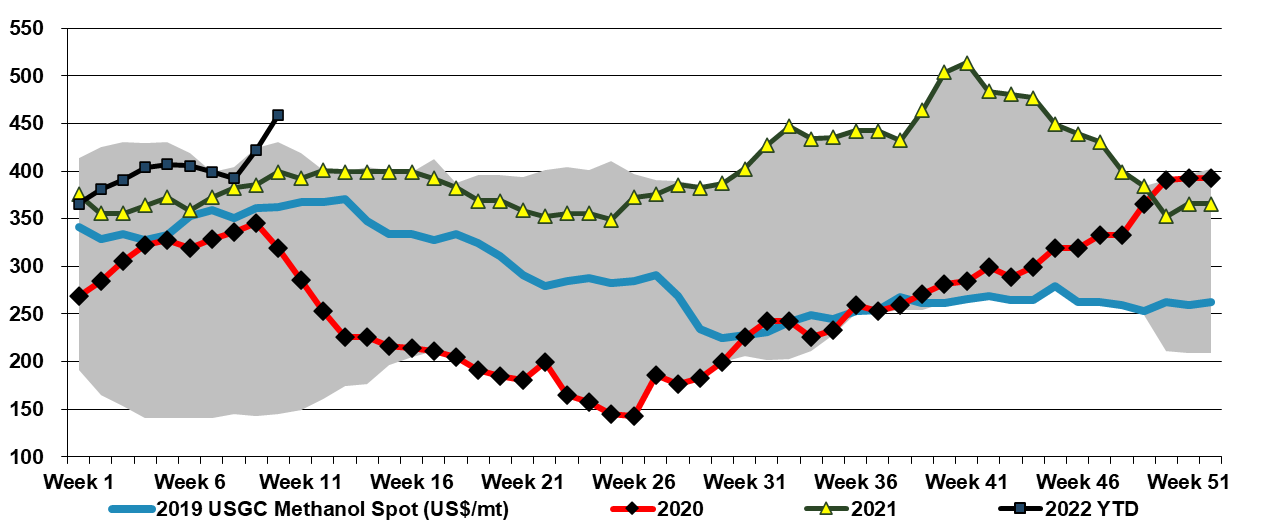
March And April Are Likely All About Price Increases
Mar 17, 2022 12:29:56 PM / by Cooley May posted in Chemicals, Polymers, Plastics, Methanol, Energy, natural gas, energy transition, US Methanol, materials, fuel, raw material
A couple of weeks ago we raised the idea that US methanol could be a significant beneficiary of the conflict in Central Europe, not just because it is very economically unattractive to make methanol in Europe, but because it might be possible for Europe to import methanol for its energy value - $40 per MMBTU natural gas can make all sort of alternates look attractive. The impetus behind the methanol spot price increase in the US may be in part rising local natural gas – or the fear of further increases – but export demand is likely the larger driving factor and this could continue or even increase further if potential European importers work out how to convert to use methanol as a fuel.